A ‘cage of cages’ is how scientists have described a brand new form of porous subject material, distinctive in its molecular construction, that may be used to lure carbon dioxide and every other, stronger greenhouse fuel.
Synthesized within the lab through researchers in the United Kingdom and China, the fabric is made in two steps, with reactions assembling triangular prism construction blocks into better, extra symmetrical tetrahedral cages – generating the primary molecular construction of its type, the crew claims.
The ensuing subject material, with its abundance of polar molecules, draws and holds greenhouse gasses corresponding to carbon dioxide (CO2) with sturdy affinity. It additionally confirmed very good balance in water, which might be important for its use in taking pictures carbon in business settings, from rainy or humid fuel streams.
“That is a thrilling discovery,” says Marc Little, a fabrics scientist at Heriot-Watt College in Edinburgh and senior creator of the learn about, “as a result of we want new porous fabrics to assist remedy society’s largest demanding situations, corresponding to taking pictures and storing greenhouse gasses.”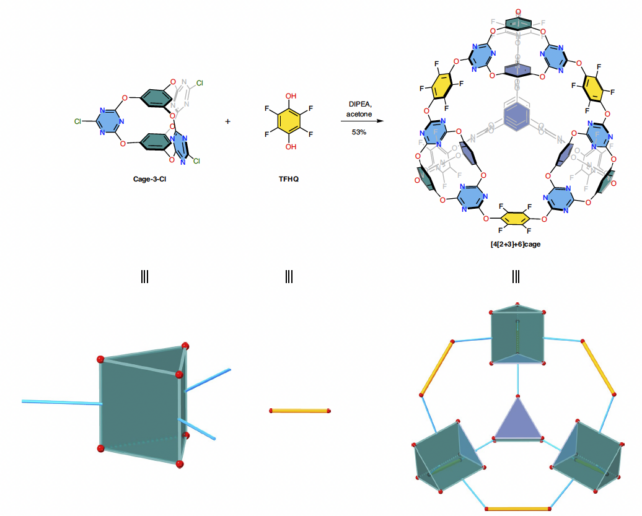 To make the porous subject material, precursor molecules with a triangular prism form compile into better, cage-like constructions. (Zhu et al., Nature Synthesis, 2024)Even supposing now not examined at scale, lab experiments confirmed the brand new cage-like subject material additionally had a prime uptake of sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), which in step with the Intergovernmental Panel on Local weather Trade, is probably the most potent greenhouse fuel.
To make the porous subject material, precursor molecules with a triangular prism form compile into better, cage-like constructions. (Zhu et al., Nature Synthesis, 2024)Even supposing now not examined at scale, lab experiments confirmed the brand new cage-like subject material additionally had a prime uptake of sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), which in step with the Intergovernmental Panel on Local weather Trade, is probably the most potent greenhouse fuel.
The place CO2 lingers within the surroundings for five–200 years, SF6 can dangle about for anyplace between 800 to a few,200 years. So even if SF6 ranges within the surroundings are a lot decrease, its extraordinarily lengthy lifetime provides SF6 a world warming attainable of round 23,500 instances that of CO2 when put next over 100 years.
Taking away massive quantities of SF6 and CO2 from the ambience, or preventing them from getting into it within the first position, is what we urgently wish to do to reign in local weather exchange.
Researchers estimate that we wish to extract round 20 billion lots of CO2 every 12 months to cancel out our carbon emissions which are handiest trending upwards.
Up to now, carbon elimination methods are taking away about 2 billion lots in keeping with 12 months, however that is most commonly timber and soils doing their factor. Simplest about 0.1 p.c of carbon elimination, round 2.3 million lots in keeping with 12 months, is because of new applied sciences corresponding to direct air seize, which makes use of porous fabrics to take in CO2 from the air.
Researchers are busy devising new fabrics to toughen direct air seize to make it extra environment friendly and not more energy-intensive, and this new subject material may well be an alternative choice. However to avert the worst affects of local weather exchange, we wish to cut back greenhouse fuel emissions quicker than those nascent applied sciences lately can.
However, we wish to throw the whole lot we will at this international downside. Making a subject material of such prime structural complexity wasn’t simple despite the fact that, even supposing the precursor molecules technically compile themselves.
This technique is named supramolecular self-assembly. It could possibly produce chemically interlocked constructions from more practical construction blocks, however it takes some fine-tuning as a result of “the most efficient response stipulations are regularly now not intuitively evident,” Little and associates give an explanation for of their revealed paper.
The extra complicated the overall molecule, the more difficult it turns into to synthesize and extra molecular ‘scrambling’ may happen in the ones reactions.
To get a care for on the ones in a different way invisible molecular interactions, the researchers used simulations to are expecting how their starter molecules would compile into this new form of porous subject material. They thought to be the geometry of attainable precursor molecules, and the chemical balance and pressure of the overall product.
With the exception of its attainable to take in greenhouse gasses, the researchers counsel their new subject material may be used to take away different poisonous fumes from the air, corresponding to risky natural compounds, which simply grow to be vapors or gasses from surfaces together with the interior of recent automobiles.
“We see this learn about as the most important step in opposition to unlocking such packages someday,” Little says.The learn about has been revealed in Nature Synthesis.
Scientists Uncover First-of-Its-Sort Molecule That Absorbs Greenhouse Gasses













