A not unusual, well-liked fungus that is most probably hiding to your lawn soil proper this second is able to reworking into an impressive predator when it will get too hungry.Scientists have identified concerning the searching skills of Arthrobotrys oligospora since a minimum of the Eighties, however they are nonetheless within the means of understanding precisely how this in a different way non violent fungus transforms right into a malicious program’s worst nightmare.Now, a analysis workforce from Taiwan and the USA led through molecular biologist Hung-Che Lin from Academia Sinica in Taipei, has unraveled one of the most methods the fungus makes use of to entice and devour its prey.In most cases, A. oligospora survives on natural topic that is already useless. But if nitrogen provides develop into scarce, it does what it should to live to tell the tale.This fungi is only one of a number of that may entice and kill prey when important. “Other trapping gadgets, together with adhesive nets, columns, knobs, non-constricting and constricting rings, are shaped relying at the fungal species,” the authors write.Predator mode is simplest totally activated when the fungus senses roundworms are within reach. frameborder=”0″ permit=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” allowfullscreen>In the past, Lin was once on a workforce that recognized the precise gene pathway that provides A. oligospora its talent to ‘scent’ malicious program pheromones. This new analysis tracks the molecular frenzy that follows.They discovered that after the fungus detects its prey, DNA replication and ribosome manufacturing will increase, which on this case, is just a little just like the microbial similar of researching and collecting apparatus in preparation for the search.Within the subsequent degree, researchers noticed an build up within the process of genes fascinated with development and running malicious program traps. “Amongst at all times issues sampled, we noticed the best differential expression (each up- and down-regulation) at 10 hours submit publicity, which corresponds to a length of intense entice formation and adhesion between fungal and nematode cells,” they write.They recognized a brand new elegance of proteins at the entice’s floor they have got referred to as entice enriched proteins (TEP), which have been discovered to be crucial for entice adhesion to nematodes.In fungi the place this protein was once deactivated, simplest 10 % of nematodes positioned at the fungi have been stuck after 10 mins – a greatly decrease hit price than the 100% price for intact traps measured all over the experiment.Any other identified protein concerned on this degree syntaxin, is fascinated with transporting ‘malicious program adhesive’ – one of those herbal ‘glue’ that oozes from the entice, making it too sticky for the prey to wiggle loose. When this protein was once deleted from the fungi, 70 % of nematodes have been in a position to flee the mutant traps, in comparison with nearly no misses for wild-type fungi.As soon as the fungus traps its prey, it penetrates the malicious program’s frame and digests it the use of filaments referred to as hyphae. As a substitute of consuming through chewing and swallowing like we do, this hyphae community fills the malicious program from the interior to wreck down and soak up vitamins for shipping to anywhere they are wanted.Right through this degree, the researchers noticed a spike in process of the genes that encode for protease enzymes. Proteases are the most important for digestion – in people, they’re produced within the abdomen, pancreas, and small gut. The flurry of protease-related gene process in A. oligospora’s a hit traps suggests the fungus is the use of those enzymes to lend a hand digest their prey. To know the position of protease in digesting nematodes, the researchers gave some fungi a protease-inhibiting cocktail. Twelve hours after nematode publicity, it was once evident the proteases have been certainly enjoying an important position, specifically in how temporarily and successfully the malicious program was once digested, which was once some distance much less for the ones given the cocktail.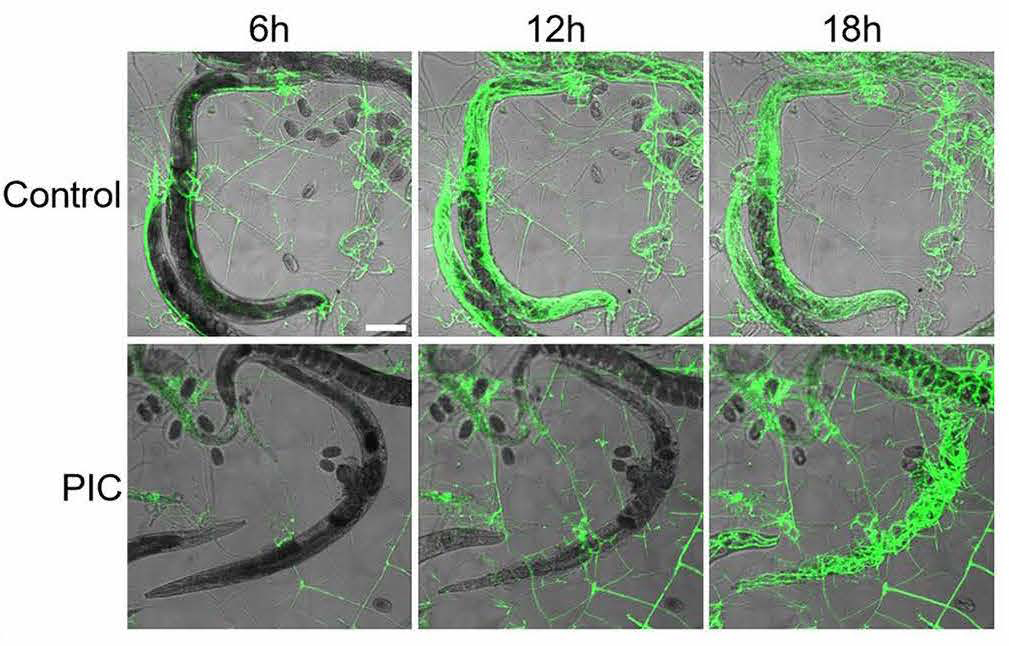 The fungi have been in a position to colonise their prey a lot sooner when proteases weren’t inhibited. (Hung-Che Lin et al., PLOS Biology, 2023)Any other experiment examined the affect of deleting the genes for positive proteases – mutant fungi have been nonetheless in a position to entice and digest their prey, however there have been minor defects in the best way the hyphae colonized the malicious program’s carcass.”Our complete transcriptomics and practical analyses spotlight the position of higher DNA replication, translation, and secretion in entice building and efficacy,” the authors provide an explanation for.”Those effects furthered our figuring out of the important thing processes required for fungal carnivory.”The analysis is revealed in PLOS Biology.
The fungi have been in a position to colonise their prey a lot sooner when proteases weren’t inhibited. (Hung-Che Lin et al., PLOS Biology, 2023)Any other experiment examined the affect of deleting the genes for positive proteases – mutant fungi have been nonetheless in a position to entice and digest their prey, however there have been minor defects in the best way the hyphae colonized the malicious program’s carcass.”Our complete transcriptomics and practical analyses spotlight the position of higher DNA replication, translation, and secretion in entice building and efficacy,” the authors provide an explanation for.”Those effects furthered our figuring out of the important thing processes required for fungal carnivory.”The analysis is revealed in PLOS Biology.
Scientists Uncover Genes That Flip a Non violent Fungus Right into a Carnivorous Killer