Vampire bats have a historical past of increasing their vary as climates exchange, researchers document in a brand new learn about, supporting considerations about additional northward growth because of human-induced international warming.The findings counsel warming climates in southern areas of the USA would possibly quickly trap vampire bats to transport in, some probably sporting illnesses like rabies that would unfold to flora and fauna, cattle or, in uncommon instances, other folks.That worry is in keeping with precedent, notes biologist and lead creator Paige Van de Vuurst from Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State College.”What we discovered was once that the distribution of vampire bats has moved northward throughout time because of previous weather exchange, which has corresponded with an building up in rabies instances in lots of Latin American nations,” Van de Vuurst says.There are 3 species of vampire bats dwelling within the wild lately, all of which inhabit handiest Mexico, Central and South The united states, and a couple of Caribbean islands.Fossil proof signifies vampire bats loved a much wider distribution in prehistoric occasions, together with extant species in addition to some now-extinct “massive” vampire bats.The brand new learn about makes a speciality of the typical vampire bat (Desmodus rotundus), which levels from northern Mexico thru all of Central The united states and maximum of South The united states. It flourishes in plenty of other habitats and elevations, from sea point as much as 3,600 meters within the Andes.Van de Vuurst and her colleagues document that because of weather exchange, portions of the USA may also start to be offering a viable house for commonplace vampire bats via the center of the century.Their analysis suggests the bats have traditionally unfold to new spaces in the hunt for stabler, extra temperate habitats, in line with higher seasonal temperature extremes of their current levels.Whilst the arriving of vampire bats on my own would not be motive for alarm, their attainable to transmit illnesses – particularly rabies – could be.That is principally a priority referring to farm animals and different cattle, which already chance contracting rabies from vampire bats of their present vary. Earlier analysis has discovered the bats not directly kill masses of cows in line with 12 months in some nations via infecting them with the fatal virus.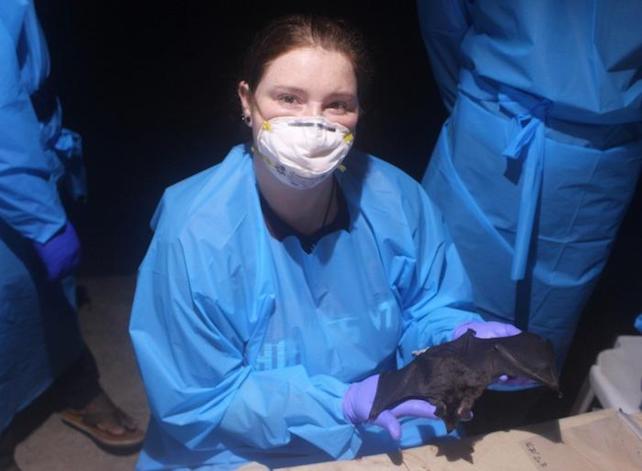 Paige Van de Vuurst poses with a vampire bat right through box analysis in Colombia. (Paige Van de Vuurst/Virginia Tech)Whilst vampire bats do not most often search blood from people, the chance is not 0, professionals say, particularly given the possibility of rabies to change an animal’s standard conduct.The fear facilities extra on the USA cattle business, since incoming vampire bats are a long way likelier to chunk animals like cows and horses than people.The brand new learn about is a part of a broader effort via researchers to spot precisely the place vampire bats are living lately, and to trace their motion inside of that vary and past.The usage of information of the bats’ levels from 1901 to 2019, the brand new learn about sought to elucidate how quite a lot of geographic and environmental elements affect the shift in vampire bat vary and rabies spillover.Ongoing paintings objectives to center of attention extra on Colombia’s bat variety, which ranks a number of the very best on this planet, reportedly 2d handiest to Indonesia.”Colombia is a mega-diverse nation, making it a really perfect herbal laboratory,” says illness ecologist Luis Escobar, assistant professor within the Division of Fish and Natural world Conservation at Virginia Tech’s School of Herbal Assets and Setting.With the assistance of ecological area of interest modeling, the researchers’ knowledge has already published how earlier adjustments in weather have corresponded with vary shifts amongst vampire bats.And due to a trove of regional rabies knowledge, the researchers additionally make clear the connection between weather exchange and distribution of rabies reservoirs through the years.Those findings assist hyperlink weather exchange with vary shift in vampire bats, they document, “in tandem with continental-level adjustments within the chance of RABV [rabies virus] spillover from flora and fauna to home animals.”The learn about additionally gives a unprecedented retrospective take a look at climate-driven vary shifts in a bat reservoir, along side the pathogen it transmits, “which till now has been extra repeatedly related to future-climate simulation-based fashions,” the researchers write.The learn about was once printed in Ecography.
Paige Van de Vuurst poses with a vampire bat right through box analysis in Colombia. (Paige Van de Vuurst/Virginia Tech)Whilst vampire bats do not most often search blood from people, the chance is not 0, professionals say, particularly given the possibility of rabies to change an animal’s standard conduct.The fear facilities extra on the USA cattle business, since incoming vampire bats are a long way likelier to chunk animals like cows and horses than people.The brand new learn about is a part of a broader effort via researchers to spot precisely the place vampire bats are living lately, and to trace their motion inside of that vary and past.The usage of information of the bats’ levels from 1901 to 2019, the brand new learn about sought to elucidate how quite a lot of geographic and environmental elements affect the shift in vampire bat vary and rabies spillover.Ongoing paintings objectives to center of attention extra on Colombia’s bat variety, which ranks a number of the very best on this planet, reportedly 2d handiest to Indonesia.”Colombia is a mega-diverse nation, making it a really perfect herbal laboratory,” says illness ecologist Luis Escobar, assistant professor within the Division of Fish and Natural world Conservation at Virginia Tech’s School of Herbal Assets and Setting.With the assistance of ecological area of interest modeling, the researchers’ knowledge has already published how earlier adjustments in weather have corresponded with vary shifts amongst vampire bats.And due to a trove of regional rabies knowledge, the researchers additionally make clear the connection between weather exchange and distribution of rabies reservoirs through the years.Those findings assist hyperlink weather exchange with vary shift in vampire bats, they document, “in tandem with continental-level adjustments within the chance of RABV [rabies virus] spillover from flora and fauna to home animals.”The learn about additionally gives a unprecedented retrospective take a look at climate-driven vary shifts in a bat reservoir, along side the pathogen it transmits, “which till now has been extra repeatedly related to future-climate simulation-based fashions,” the researchers write.The learn about was once printed in Ecography.
Scientists Warn Vampire Bats Would possibly Quickly Unfold Into The Southern US