Scientists have found out a complete new technique to reduce the legs out from beneath drug-resistant bacterial infections.The brand new elegance of antibiotic was once known via researchers at Uppsala College in Sweden, and whilst it has best been examined on mice, the group hopes that additional building of the drug can “make a very powerful contribution to the continuing fight towards antibiotic resistance.”
The original drugs, like many different antibiotics these days in building, objectives the double membrane that surrounds gram-negative micro organism, like Escherichia coli, which will motive bowel and blood infections, and Klebsiella pneumoniae, which will motive lung, bladder, and blood infections.
Not like gram-positive micro organism, for which a large number of households of substances had been made, that bold 2d barrier surrounding gram-negative bacterial cells makes it tougher for antibiotics to have an impact.
The harsh outer membrane is embedded with lipopolysaccharides, which offer the mobile integrity, permit it to engage with different surfaces, and allow the go out of poisons and the access of vitamins.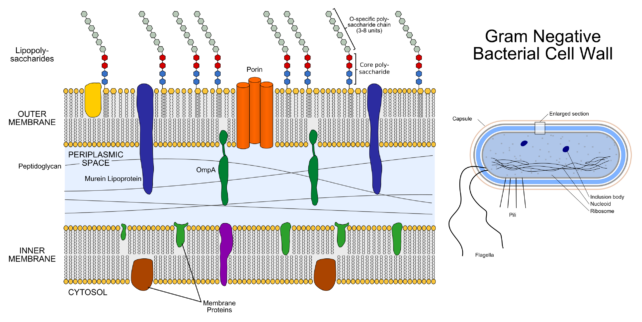 A diagram of a gram-negative bacterial mobile wall with lipopolysaccharides anchored within the outer membrane. (Jeff Dahl/Wikipedia/CC BY SA 4.0)For years now, scientists have attempted to clutter with the lipid membranes themselves, as they’re very important to the functioning of gram-negative micro organism. However researchers in Sweden are the primary to focus on an enzyme, referred to as LpxH, which is helping synthesize different crucial elements of the outer membrane referred to as lipopolysaccharides. Since more or less 70 p.c of gram-negative micro organism make the most of this enzyme, it will make an acceptable goal for a large number of infections.
A diagram of a gram-negative bacterial mobile wall with lipopolysaccharides anchored within the outer membrane. (Jeff Dahl/Wikipedia/CC BY SA 4.0)For years now, scientists have attempted to clutter with the lipid membranes themselves, as they’re very important to the functioning of gram-negative micro organism. However researchers in Sweden are the primary to focus on an enzyme, referred to as LpxH, which is helping synthesize different crucial elements of the outer membrane referred to as lipopolysaccharides. Since more or less 70 p.c of gram-negative micro organism make the most of this enzyme, it will make an acceptable goal for a large number of infections.
Mice injected with drug-resistant E. coli or Okay. pneumoniae had been dosed with an array of compounds an hour later designed to inhibit the micro organism’s LpxH. The consequences demonstrated it was once imaginable to regard bloodstream infections in simply 4 hours with only one dose.
“Throughout the process this an infection fashion, micro organism unfold to the bloodstream of the mice,” they provide an explanation for.
“The facility of those compounds to strongly scale back the selection of micro organism recovered from blood in just a single-dose remedy highlights their attainable to regard essentially the most life-threatening infections with gram-negative [multi drug resistant] pathogens.”
The researchers began with a compound referred to as JEDI-1444, which was once cobbled in combination from the result of a seek in the course of the literature for appropriate candidate inhibitors. Even though it confirmed unbelievable promise in fighting gram-negative enlargement, it wasn’t very soluable or strong in blood.
With a couple of changes, the group discovered luck in two permutations coded EBL-3599 and EBL-3647, that have been no longer dissolved higher in serum however confirmed “potent” antimicrobial task towards quite a lot of E. coli and Okay. pneumoniae isolates, “without reference to the resistance genotype.”
That is a crucial discovery, for the reason that each those micro organism are rising proof against the few to be had antibiotics that do paintings towards them. In 2019, dying from antibiotic resistant infections was once the 3rd main international reason behind dying. Via 2050, ten million deaths are anticipated in keeping with 12 months.
As micro organism adapt to our medication, new categories of drugs are desperately had to save lives. Nowadays, part of the antibiotics to be had in the marketplace are merely permutations of substances that had been known just about a century in the past.
In 2017, the Global Well being Group (WHO) launched an inventory of essentially the most unhealthy, drug-resistant pathogens and gram-negative micro organism which can be proof against top-of-the-line categories of broad-spectrum antibiotics are most sensible of the checklist. This comprises E. coli and Okay. pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which additionally reasons pneumonia, and Acinetobacter baumannii, which reasons blood, lung, and urine infections.
“Whilst the present effects are very promising,” researchers at Uppsala conclude, “there might be substantial further paintings required prior to compounds of this elegance might be able for medical trials.”The find out about was once revealed in PNAS.
Simply 1 Dose of New Antibiotic Magnificence Gets rid of Resistant Blood Infections in Mice