Abstract: find out about finds that ultrafine debris from site visitors emissions considerably regulate gene expression in human olfactory mucosa cells.This primary-of-its-kind find out about mixed analyses of diesel gas emissions and their results on a human-derived cellular fashion. It discovered that each renewable and fossil diesel emissions disrupt a lot of mobile purposes, however renewable diesel, particularly with cleaner engine generation, reasons fewer hostile results.Those findings make clear the possible pathway for environmental pollution to have an effect on the mind throughout the olfactory gadget.Key Information:The find out about confirmed that publicity to ultrafine debris from site visitors emissions alters gene expression associated with irritation, xenobiotic metabolism, and olfactory signaling.Renewable diesel mixed with cleaner engine generation led to fewer cellular serve as alterations in comparison to fossil diesel.The analysis supplies proof that ultrafine debris might mediate hostile mind results by means of the olfactory pathway, underscoring the desire for tracking and regulating those emissions.Supply: College of Jap FinlandExposure to ultrafine debris from site visitors alters the expression of many genes in human olfactory mucosa cells, a brand new find out about presentations. The find out about, led by way of the College of Jap Finland, is the primary to mix an research of emissions from other diesel fuels and exhaust after-treatment programs with an exam in their results in a human-derived cellular fashion of the olfactory mucosa.  The human olfactory mucosa is a tissue immediately uncovered to the surroundings and in direct touch with the mind. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsThe findings had been printed in Science of the Overall Atmosphere.Particle emissions from street site visitors had been regulated within the EU for many years, however emissions of ultrafine debris with a diameter lower than 100 nanometres in dimension aren’t monitored or limited but.The human olfactory mucosa is a tissue immediately uncovered to the surroundings and in direct touch with the mind.“The olfactory gadget has been discovered to mediate the consequences of environmental pollution at the mind, thus contributing to the pathogenesis of mind illnesses. Alternatively, the precise signalling pathways wherein the consequences are mediated stay unknown,” says first creator, Doctoral Researcher Laura Mussalo of the Kanninen Lab on the College of Jap Finland.The find out about explored molecular-level adjustments going on in human olfactory mucosa cells when uncovered to other emissions derived from site visitors. The researchers tested the consequences of emissions on gene expression, i.e., what sort of alterations emissions motive, and how much mechanisms they turn on.The researchers additionally tested whether or not fossil and renewable diesel fuels motive other results, and the way trendy after-treatment units, equivalent to particulate filters, have an effect on emissions.The olfactory mucosa cells used within the find out about had been received from voluntary donors, accrued in collaboration with Kuopio College Medical institution. The multidisciplinary find out about mixed medical drugs, gene analysis, molecular biology, environmental toxicology and aerosol physics.Results on inflammatory reaction and xenobiotic metabolismThe particle samples used within the publicity research had been accrued by way of VTT Technical Analysis Centre of Finland, and so they had been analysed and characterized by way of VTT and Tampere College.The samples had been accrued from exhausts of a heavy-duty-engine automobile run on paraffinic renewable diesel and on common fossil diesel. The 3rd pattern was once a mix of the similar renewable diesel and cleaner engine generation complying with the Euro 6d-temp same old.All emissions contained ultrafine debris. As well as, emissions from each renewable and fossil diesel contained an important quantity of polycyclic fragrant hydrocarbons (PAHs) and reactive nitrogen compounds. Alternatively, renewable diesel mixed with cleaner engine generation produced little or no emissions.Publicity to ultrafine debris altered human olfactory mucosa cellular serve as, and other fuels and engines led to other hostile results. Moreover, molecular-level research published disturbance in numerous programs that keep an eye on cellular serve as. Publicity to emissions from each renewable and fossil diesel considerably altered the expression of genes related to inflammatory reaction, xenobiotic metabolism, olfactory signalling and olfactory mucosa integrity. Alternatively, renewable diesel led to much less hostile results than fossil diesel.Emissions from renewable diesel run on cleaner engine generation led to simplest negligible alterations in cellular serve as, demonstrating the potency of engine after-treatment units.The findings again previous research suggesting that PAHs might disturb the inflammatory reaction and xenobiotic metabolism in human olfactory mucosa cells, and that ultrafine debris might mediate hostile results to the mind by means of the olfactory pathway.The find out about gives vital perception into the hostile results of ultrafine debris in a human-derived cellular fashion of the olfactory mucosa, offering a foundation for conceivable measures to mitigate and save you toxicological hazards.Investment: The find out about constitutes a part of TUBE mission, which is funded by way of the Horizon 2020 programme of the Ecu Union. The find out about has additionally gained investment from the Kuopio House Respiration Basis, the Finnish Mind Basis, Yrjö Jahnsson Basis, and Päivikki and Sakari Sohlberg Basis.About this olfaction and neuroscience analysis newsAuthor: Maj Vuorre
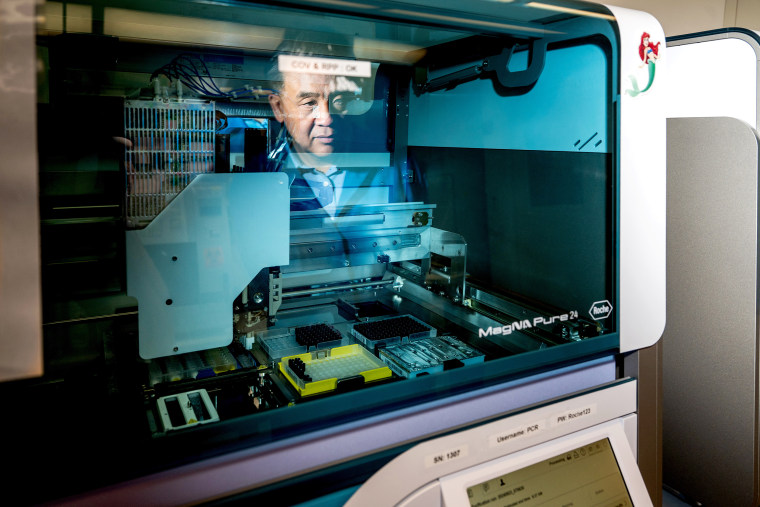
The human olfactory mucosa is a tissue immediately uncovered to the surroundings and in direct touch with the mind. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsThe findings had been printed in Science of the Overall Atmosphere.Particle emissions from street site visitors had been regulated within the EU for many years, however emissions of ultrafine debris with a diameter lower than 100 nanometres in dimension aren’t monitored or limited but.The human olfactory mucosa is a tissue immediately uncovered to the surroundings and in direct touch with the mind.“The olfactory gadget has been discovered to mediate the consequences of environmental pollution at the mind, thus contributing to the pathogenesis of mind illnesses. Alternatively, the precise signalling pathways wherein the consequences are mediated stay unknown,” says first creator, Doctoral Researcher Laura Mussalo of the Kanninen Lab on the College of Jap Finland.The find out about explored molecular-level adjustments going on in human olfactory mucosa cells when uncovered to other emissions derived from site visitors. The researchers tested the consequences of emissions on gene expression, i.e., what sort of alterations emissions motive, and how much mechanisms they turn on.The researchers additionally tested whether or not fossil and renewable diesel fuels motive other results, and the way trendy after-treatment units, equivalent to particulate filters, have an effect on emissions.The olfactory mucosa cells used within the find out about had been received from voluntary donors, accrued in collaboration with Kuopio College Medical institution. The multidisciplinary find out about mixed medical drugs, gene analysis, molecular biology, environmental toxicology and aerosol physics.Results on inflammatory reaction and xenobiotic metabolismThe particle samples used within the publicity research had been accrued by way of VTT Technical Analysis Centre of Finland, and so they had been analysed and characterized by way of VTT and Tampere College.The samples had been accrued from exhausts of a heavy-duty-engine automobile run on paraffinic renewable diesel and on common fossil diesel. The 3rd pattern was once a mix of the similar renewable diesel and cleaner engine generation complying with the Euro 6d-temp same old.All emissions contained ultrafine debris. As well as, emissions from each renewable and fossil diesel contained an important quantity of polycyclic fragrant hydrocarbons (PAHs) and reactive nitrogen compounds. Alternatively, renewable diesel mixed with cleaner engine generation produced little or no emissions.Publicity to ultrafine debris altered human olfactory mucosa cellular serve as, and other fuels and engines led to other hostile results. Moreover, molecular-level research published disturbance in numerous programs that keep an eye on cellular serve as. Publicity to emissions from each renewable and fossil diesel considerably altered the expression of genes related to inflammatory reaction, xenobiotic metabolism, olfactory signalling and olfactory mucosa integrity. Alternatively, renewable diesel led to much less hostile results than fossil diesel.Emissions from renewable diesel run on cleaner engine generation led to simplest negligible alterations in cellular serve as, demonstrating the potency of engine after-treatment units.The findings again previous research suggesting that PAHs might disturb the inflammatory reaction and xenobiotic metabolism in human olfactory mucosa cells, and that ultrafine debris might mediate hostile results to the mind by means of the olfactory pathway.The find out about gives vital perception into the hostile results of ultrafine debris in a human-derived cellular fashion of the olfactory mucosa, offering a foundation for conceivable measures to mitigate and save you toxicological hazards.Investment: The find out about constitutes a part of TUBE mission, which is funded by way of the Horizon 2020 programme of the Ecu Union. The find out about has additionally gained investment from the Kuopio House Respiration Basis, the Finnish Mind Basis, Yrjö Jahnsson Basis, and Päivikki and Sakari Sohlberg Basis.About this olfaction and neuroscience analysis newsAuthor: Maj Vuorre
Supply: College of Jap Finland
Touch: Maj Vuorre – College of Jap Finland
Symbol: The picture is credited to Neuroscience NewsOriginal Analysis: Open get right of entry to.
“Emissions from trendy engines induce distinct results in human olfactory mucosa cells, relying on gas and aftertreatment” by way of Laura Mussalo et al. Science of The Overall EnvironmentAbstractEmissions from trendy engines induce distinct results in human olfactory mucosa cells, relying on gas and aftertreatmentUltrafine debris (UFP) with a diameter of ≤0.1 μm, are members to ambient air air pollution and derived principally from site visitors emissions, but their well being results stay poorly characterised.The olfactory mucosa (OM) is positioned on the rooftop of the nasal hollow space and immediately uncovered to each the surroundings and the mind. Mounting proof means that pollutant debris have an effect on the mind throughout the olfactory tract, alternatively, the precise mobile mechanisms of the way the OM responds to air pollution stay poorly recognized.Right here we display that the responses of number one human OM cells are altered upon publicity to UFPs and that other fuels and engines elicit other hostile results.We used UFPs accrued from exhausts of a heavy-duty-engine run with renewable diesel (A0) and fossil diesel (A20), and from a contemporary diesel automobile run with renewable diesel (Euro6) and in comparison their well being results at the OM cells by way of assessing mobile processes at the purposeful and transcriptomic ranges.Quantification published all samples as UFPs with nearly all of debris being ≤0.1 μm by way of an aerodynamic diameter. Publicity to A0 and A20 precipitated really extensive alterations in processes related to inflammatory reaction, xenobiotic metabolism, olfactory signaling, and epithelial integrity. Euro6 led to simplest negligible adjustments, demonstrating the efficacy of aftertreatment units.Moreover, when in comparison to A20, A0 elicited much less pronounced results on OM cells, suggesting renewable diesel induces much less hostile results in OM cells.Prior research and those effects recommend that PAHs might disturb the inflammatory procedure and xenobiotic metabolism within the OM and that UFPs would possibly mediate destructive results at the mind throughout the olfactory course.This find out about supplies vital data at the hostile results of UFPs in a human-based in vitro fashion, due to this fact offering new perception to shape the foundation for mitigation and preventive movements in opposition to the conceivable toxicological impairments led to by way of UFP publicity.
Site visitors Ultrafine Debris Have an effect on Human Olfactory Cells – Neuroscience Information










![Apple simply launched new AirPods Professional 2 and AirPods 4 firmware for all customers [U] – 9to5Mac Apple simply launched new AirPods Professional 2 and AirPods 4 firmware for all customers [U] – 9to5Mac](https://9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2024/09/airpods-4.jpg?quality=82&strip=all&w=1600)

