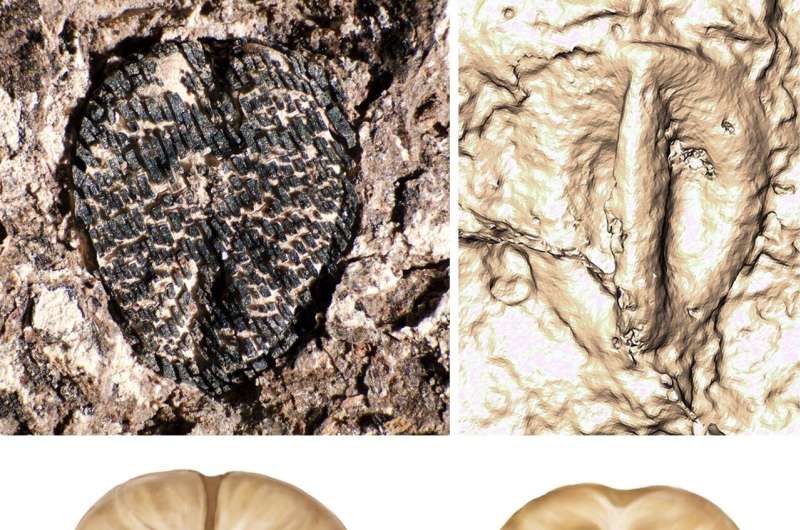
Lithouva – the earliest fossil grape from the Western Hemisphere, ~60 million years outdated from Colombia. Best determine presentations fossil accompanied with CT scan reconstruction. Backside presentations artist reconstruction. Credit score: Fabiany Herrera, artwork by means of Pollyanna von Knorring.
When you’ve ever snacked on raisins or loved a tumbler of wine, you might, partially, have the extinction of the dinosaurs to thank for it. In a discovery described within the magazine Nature Vegetation, researchers discovered fossil grape seeds that vary from 60 to 19 million years outdated in Colombia, Panama, and Perú. This kind of species represents the earliest recognized instance of crops from the grape circle of relatives within the Western Hemisphere. Those fossil seeds assist display how the grape circle of relatives unfold within the years following the loss of life of the dinosaurs.
“Those are the oldest grapes ever discovered on this a part of the sector, and they are a couple of million years more youthful than the oldest ones ever discovered at the different aspect of the planet,” says Fabiany Herrera, an assistant curator of paleobotany on the Box Museum in Chicago’s Negaunee Integrative Analysis Heart and the lead writer of the paper. “This discovery is necessary as it presentations that when the extinction of the dinosaurs, grapes truly began to unfold internationally.”
It is uncommon for comfortable tissues like culmination to be preserved as fossils, so scientists’ figuring out of historical culmination continuously comes from the seeds, which can be much more likely to fossilize. The earliest recognized grape seed fossils had been present in India and are 66 million years outdated. It is not a twist of fate that grapes seemed within the fossil file 66 million years in the past—that is round when an enormous asteroid hit the Earth, triggering a large extinction that altered the process lifestyles in the world.
“We at all times consider the animals, the dinosaurs, as a result of they had been the most important issues to be affected, however the extinction match had an enormous affect on crops too,” says Herrera. “The woodland reset itself, in some way that modified the composition of the crops.”
Herrera and his colleagues hypothesize that the disappearance of the dinosaurs may have helped modify the forests. “Huge animals, corresponding to dinosaurs, are recognized to change their surrounding ecosystems. We expect that if there have been massive dinosaurs roaming during the woodland, they had been most likely pulling down bushes, successfully keeping up forests extra open than they’re as of late,” says Mónica Carvalho, a co-author of the paper and assistant curator on the College of Michigan’s Museum of Paleontology.
However with out massive dinosaurs to prune them, some tropical forests, together with the ones in South The usa, was extra crowded, with layers of bushes forming an understory and a cover.
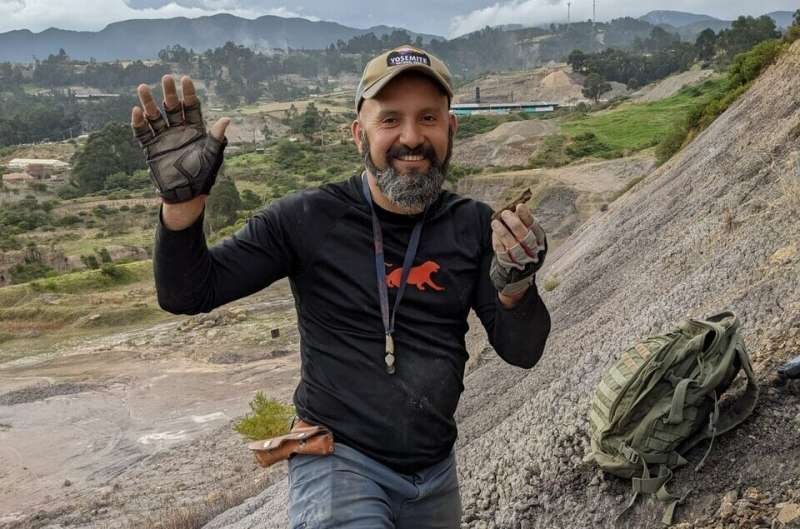

Lead writer Fabiany Herrera protecting a fossil of the oldest grape ever discovered within the Western Hemisphere. Credit score: Fabiany Herrera
Those new, dense forests equipped a possibility. “Within the fossil file, we begin to see extra crops that use vines to climb up bushes, like grapes, round this time,” says Herrera. The diversification of birds and mammals within the years following the mass extinction can have additionally aided grapes by means of spreading their seeds.
In 2013, Herrera’s Ph.D. consultant and senior writer of the brand new paper, Steven Manchester, printed a paper describing the oldest recognized grape seed fossil, from India. Whilst no fossil grapes had ever been present in South The usa, Herrera suspected that they could be there too.
“Grapes have an intensive fossil file that begins about 50 million years in the past, so I sought after to find one in South The usa, however it was once like searching for a needle in a haystack,” says Herrera. “I have been searching for the oldest grape within the Western Hemisphere since I used to be an undergrad scholar.”
However in 2022, Herrera and his co-author Mónica Carvalho had been engaging in fieldwork within the Colombian Andes when a fossil stuck Carvalho’s eye. “She checked out me and stated, ‘Fabiany, a grape!’ After which I checked out it, I used to be like, ‘Oh my God.’ It was once so thrilling,” recollects Herrera. The fossil was once in a 60-million-year-old rock, making it no longer handiest the primary South American grape fossil, however a number of the global’s oldest grape fossils as smartly.
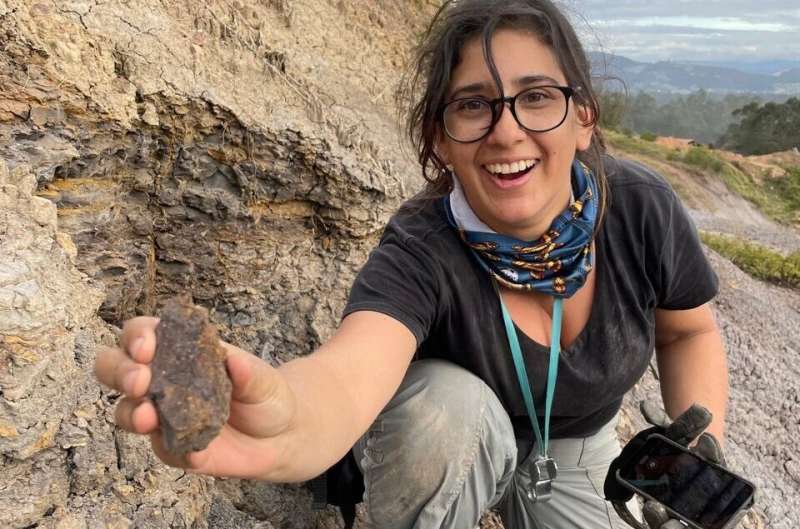

Mónica Carvalho, a co-author of the paper, protecting the fossil of the oldest grape seed discovered within the Western Hemisphere. Credit score: Fabiany Herrera
The fossil seed itself is tiny, however Herrera and Carvalho had been in a position to spot it in response to its explicit form, dimension, and different morphological options. Again within the lab, they carried out CT scans appearing its inner construction that showed its identification.
The workforce named the fossil Lithouva susmanii, “Susman’s stone grape,” in honor of Arthur T. Susman, a supporter of South American paleobotany on the Box Museum. “This new species may be necessary as it helps a South American foundation of the crowd during which the typical grape vine Vitis advanced,” says co-author Gregory Stull of the Nationwide Museum of Herbal Historical past.
The workforce carried out additional fieldwork in South and Central The usa, and within the Nature Vegetation paper, Herrera and his co-authors in the long run described 9 new species of fossil grapes from Colombia, Panama, and Perú, spanning from 60 to 19 million years outdated. Those fossilized seeds no longer handiest inform the tale of grapes’ unfold around the Western Hemisphere, but additionally of the numerous extinctions and dispersals the grape circle of relatives has gone through.
The fossils are handiest far-off family members of the grapes local to the Western Hemisphere and a couple of, like the 2 species of Leea are handiest discovered within the Jap Hemisphere as of late. Their puts inside the grape circle of relatives tree point out that their evolutionary adventure has been a tumultuous one.
“The fossil file tells us that grapes are an excessively resilient order. They are a bunch that has suffered numerous extinction within the Central and South American area, however additionally they controlled to evolve and live on in different portions of the sector,” says Herrera.
Given the mass extinction our planet is lately going through, Herrera says that research like this one are precious as a result of they expose patterns about how biodiversity crises play out. “However the thing more I love about those fossils is that those little tiny, humble seeds can let us know such a lot in regards to the evolution of the woodland,” says Herrera.
This learn about was once authored by means of Fabiany Herrera (Box Museum), Mónica Carvalho (College of Michigan), Gregory Stull (Nationwide Museum of Herbal Historical past, Smithsonian Establishment), Carlos Jarramillo (Smithsonian Tropical Analysis Institute), and Steven Manchester (Florida Museum of Herbal Historical past, College of Florida).
Additional information:
Cenozoic seeds of Vitaceae expose a deep historical past of extinction and dispersal within the Neotropics, Nature Vegetation (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41477-024-01717-9
Quotation:
Sixty-million-year-old grape seeds expose how the loss of life of the dinosaurs can have cleared the path for grapes to unfold (2024, July 1)
retrieved 1 July 2024
from
This file is matter to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal learn about or analysis, no
section could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions handiest.