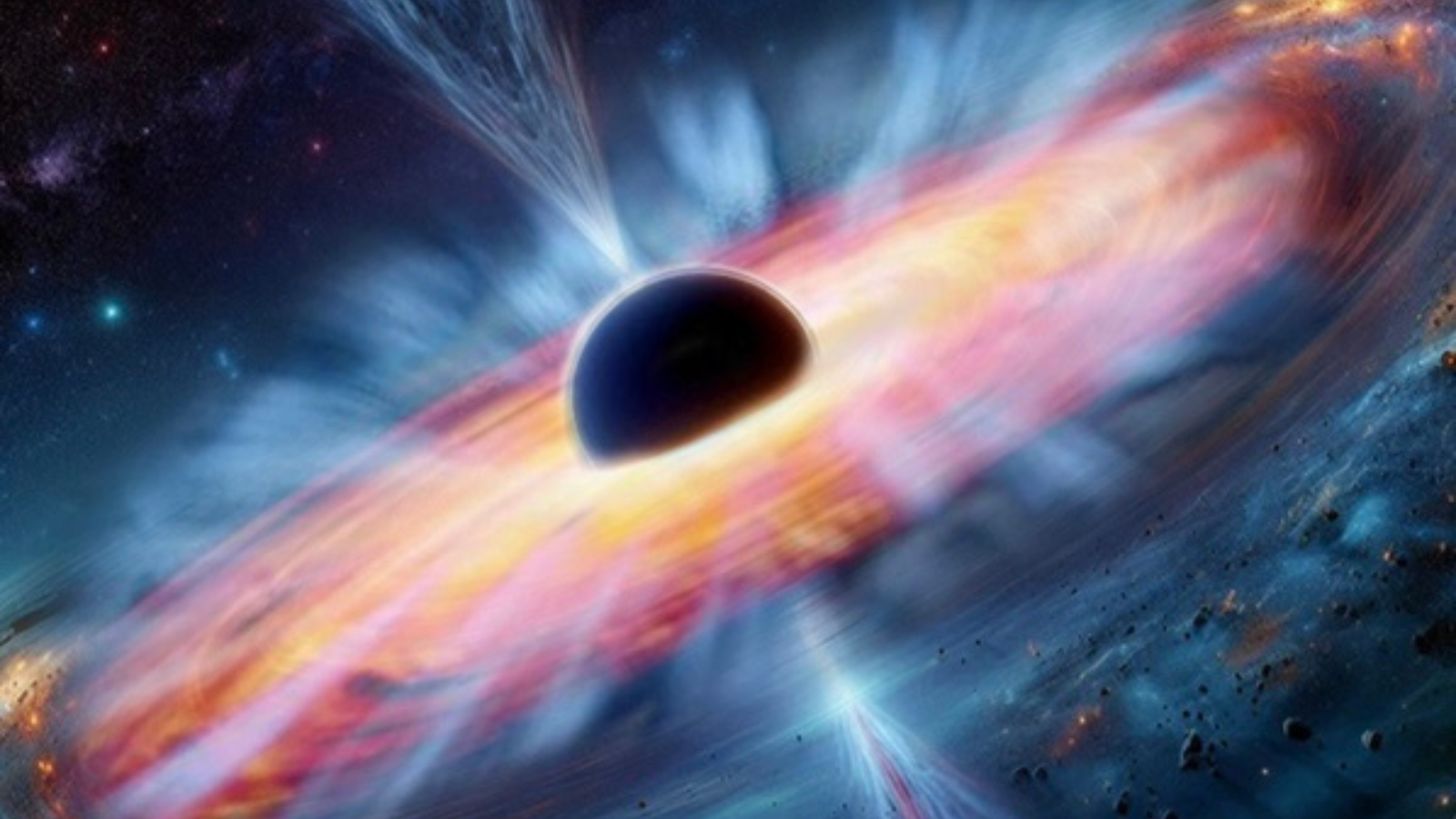
Binary pairings of small black holes may well be utilized by astronomers in a cosmic sport of “hide-and-seek” to seek a lot better, but extra elusive, supermassive black hollow binaries. The method may, subsequently, lend a hand clear up the thriller of the way supermassive black holes grew so rapid within the early universe.Detecting black holes is not any simple job regardless of their recognition as fearsome cosmic titans. All black holes are surrounded by way of a one-way light-trapping boundary known as an “tournament horizon” that guarantees they emit no gentle. Even the supermassive black holes on the hearts of galaxies with lots hundreds of thousands or billions of occasions that of the solar are best “visual” if they’re feasting on a limiteless quantity of surrounding topic or if they’re ripping aside an unlucky famous person. Alternatively, gentle, or “electromagnetic radiation” as it’s extra appropriately recognized, is just one form of radiation. Some other is “gravitational radiation,” which comes within the type of tiny ripples that set spacetime buzzing known as “gravitational waves,” which humanity is solely starting to come across. That implies moderately than searching for supermassive black hollow pairs on this sport of hide-and-seek, astronomers can concentrate for them as an alternative.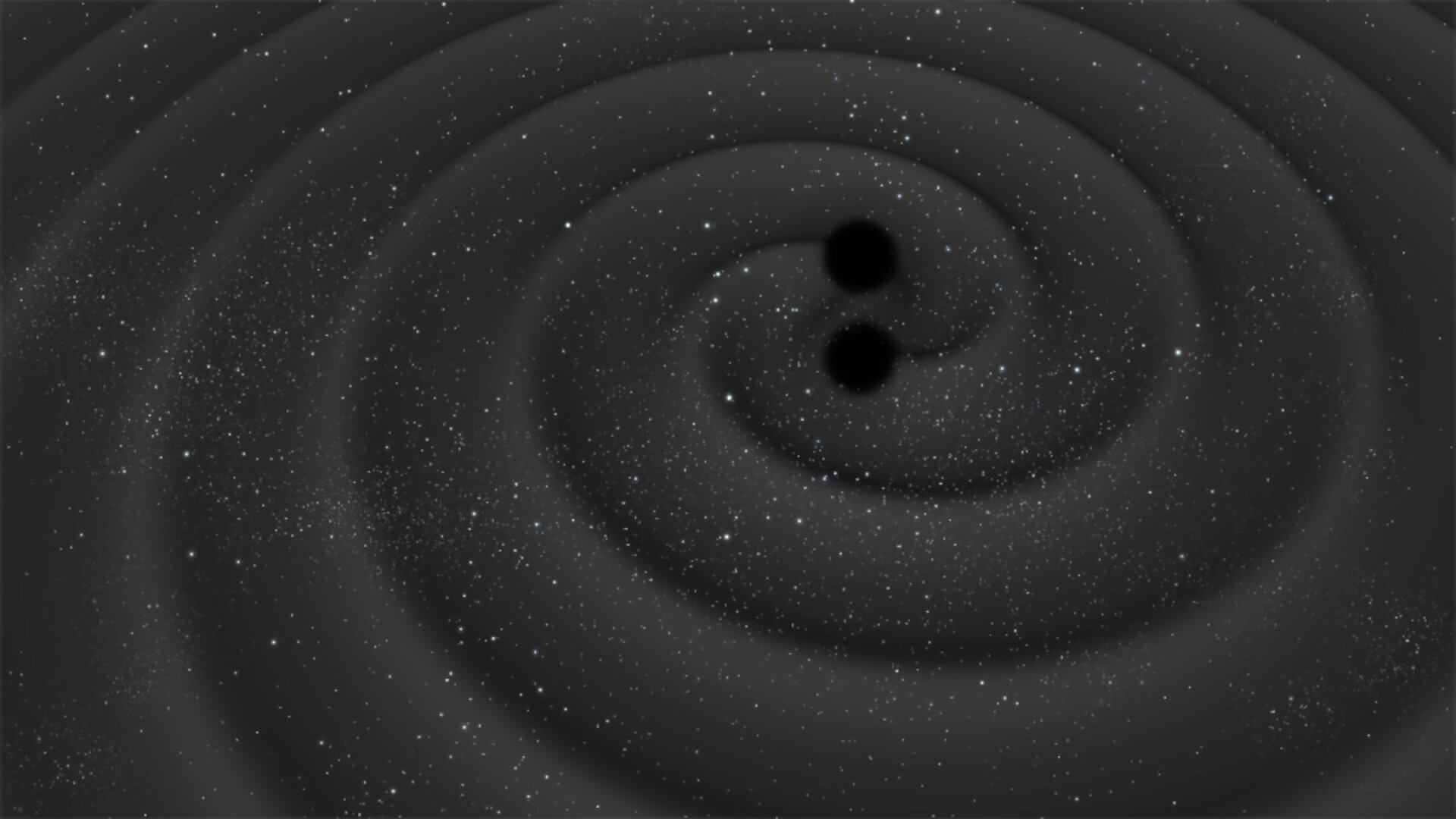 A demonstration of binary black holes ringing spacetime like a bell with gravitational waves. (Symbol credit score: ESA–C.Carreau)”Our concept principally works like paying attention to a radio channel. We advise to make use of the sign from pairs of small black holes very similar to how radio waves elevate the sign,” workforce chief Jakob Stegmann, a postdoctoral analysis fellow on the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics, mentioned in a observation. “The supermassive black holes are the song this is encoded within the frequency modulation (FM) of the detected sign.”Comparable: Cracking! Some binary black holes might roll round every different in egg-shaped orbitsSmall black hollow sing sopranoGravitational waves are a idea that used to be first urged by way of Albert Einstein typically relativity, his 1915 magnum opus idea of gravity.Common relativity means that gravity arises when an object with mass “warp” the very cloth of area and time, which Einstein had up to now united as a unmarried 4-dimensional entity (3 spatial dimensions, one size of time) known as “spacetime.”Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!The larger the mass, the higher the extremity of the curvature of area an object creates. That explains why planets have a larger gravitational affect than moons, why stars have a larger affect than planets, and why black holes have the most important affect of any unmarried object.
A demonstration of binary black holes ringing spacetime like a bell with gravitational waves. (Symbol credit score: ESA–C.Carreau)”Our concept principally works like paying attention to a radio channel. We advise to make use of the sign from pairs of small black holes very similar to how radio waves elevate the sign,” workforce chief Jakob Stegmann, a postdoctoral analysis fellow on the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics, mentioned in a observation. “The supermassive black holes are the song this is encoded within the frequency modulation (FM) of the detected sign.”Comparable: Cracking! Some binary black holes might roll round every different in egg-shaped orbitsSmall black hollow sing sopranoGravitational waves are a idea that used to be first urged by way of Albert Einstein typically relativity, his 1915 magnum opus idea of gravity.Common relativity means that gravity arises when an object with mass “warp” the very cloth of area and time, which Einstein had up to now united as a unmarried 4-dimensional entity (3 spatial dimensions, one size of time) known as “spacetime.”Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!The larger the mass, the higher the extremity of the curvature of area an object creates. That explains why planets have a larger gravitational affect than moons, why stars have a larger affect than planets, and why black holes have the most important affect of any unmarried object.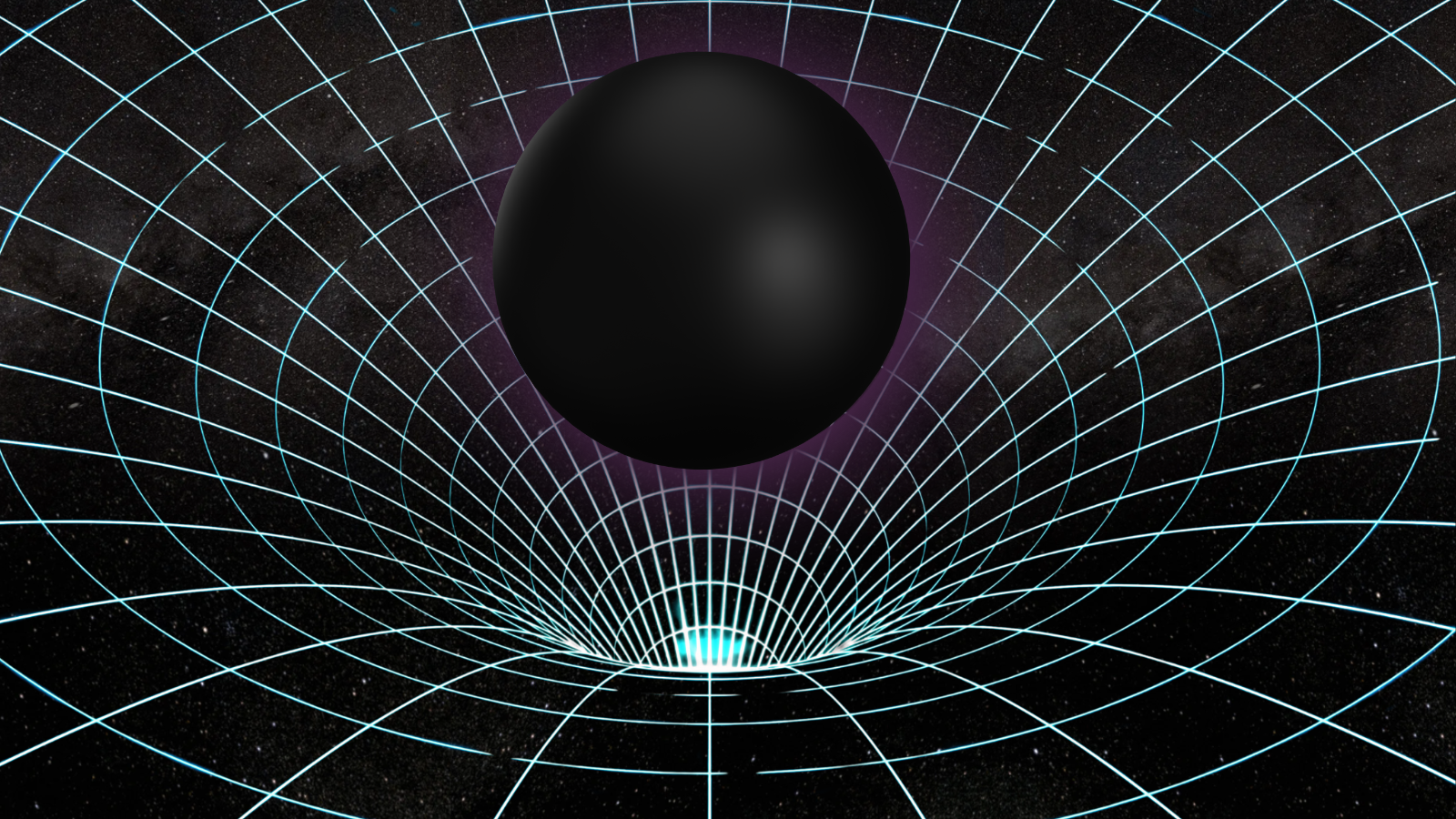 A demonstration displays a black hollow inflicting a “plunging” warp in spacetime. (Symbol credit score: Robert Lea (created with Canva))Einstein additionally predicted that once gadgets boost up in spacetime, they set its cloth “ringing” with ripples or gravitational waves. Those are utterly insignificant for gadgets with low lots, but if black holes orbit round every different (remembering that round movement is acceleration), they’ve sufficient mass to generate vital gravitational waves.As those black holes spiral round every different, they emit steady low-frequency gravitational waves. Those gravitational waves elevate away angular momentum (or spin), forcing the black holes in combination, a procedure known as “inspiralling.” This will increase the frequency of the gravitational waves, thus inflicting angular momentum to be over excited quicker and quicker.This is till the black holes in the end collide and merge, an tournament that sends out a better frequency “scream” of gravitational waves.
A demonstration displays a black hollow inflicting a “plunging” warp in spacetime. (Symbol credit score: Robert Lea (created with Canva))Einstein additionally predicted that once gadgets boost up in spacetime, they set its cloth “ringing” with ripples or gravitational waves. Those are utterly insignificant for gadgets with low lots, but if black holes orbit round every different (remembering that round movement is acceleration), they’ve sufficient mass to generate vital gravitational waves.As those black holes spiral round every different, they emit steady low-frequency gravitational waves. Those gravitational waves elevate away angular momentum (or spin), forcing the black holes in combination, a procedure known as “inspiralling.” This will increase the frequency of the gravitational waves, thus inflicting angular momentum to be over excited quicker and quicker.This is till the black holes in the end collide and merge, an tournament that sends out a better frequency “scream” of gravitational waves. 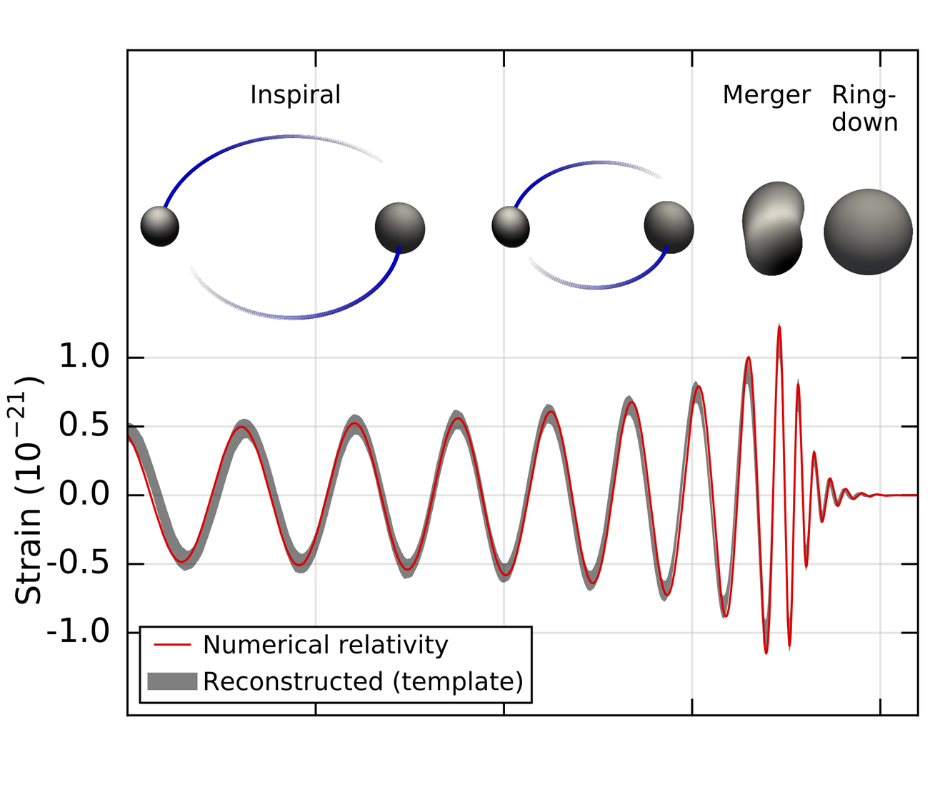 A diagram appearing the frequencies of gravitational waves emitted by way of binary black holes all the way through the merger procedure (Symbol credit score: LIGO)Even so, Einstein predicted that those spacetime ripples can be too faint to ever come across, particularly as they’d lose power as they propagated in the course of the cosmos and black hollow mergers happen hundreds of thousands and even billions of light-years away. Thankfully, we now know Einstein used to be flawed.Because the detection of the primary gravitational wave sign by way of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) in 2015, which originated from a binary black hollow merger 1.3 billion light-years away, many such black hollow collisions were detected.However those detections have something in not unusual. Once they concerned black holes, they have been all the time pairs within the stellar-mass black hollow vary, with lots between 3 and a couple of hundred occasions that of the solar. Supermassive black hollow mergers were elusive for terrestrial gravitational wave detectors like LIGO and its compatriots VIRGO in Italy and the Kamioka Gravitational Wave Detector (KAGRA) in Japan.
A diagram appearing the frequencies of gravitational waves emitted by way of binary black holes all the way through the merger procedure (Symbol credit score: LIGO)Even so, Einstein predicted that those spacetime ripples can be too faint to ever come across, particularly as they’d lose power as they propagated in the course of the cosmos and black hollow mergers happen hundreds of thousands and even billions of light-years away. Thankfully, we now know Einstein used to be flawed.Because the detection of the primary gravitational wave sign by way of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) in 2015, which originated from a binary black hollow merger 1.3 billion light-years away, many such black hollow collisions were detected.However those detections have something in not unusual. Once they concerned black holes, they have been all the time pairs within the stellar-mass black hollow vary, with lots between 3 and a couple of hundred occasions that of the solar. Supermassive black hollow mergers were elusive for terrestrial gravitational wave detectors like LIGO and its compatriots VIRGO in Italy and the Kamioka Gravitational Wave Detector (KAGRA) in Japan.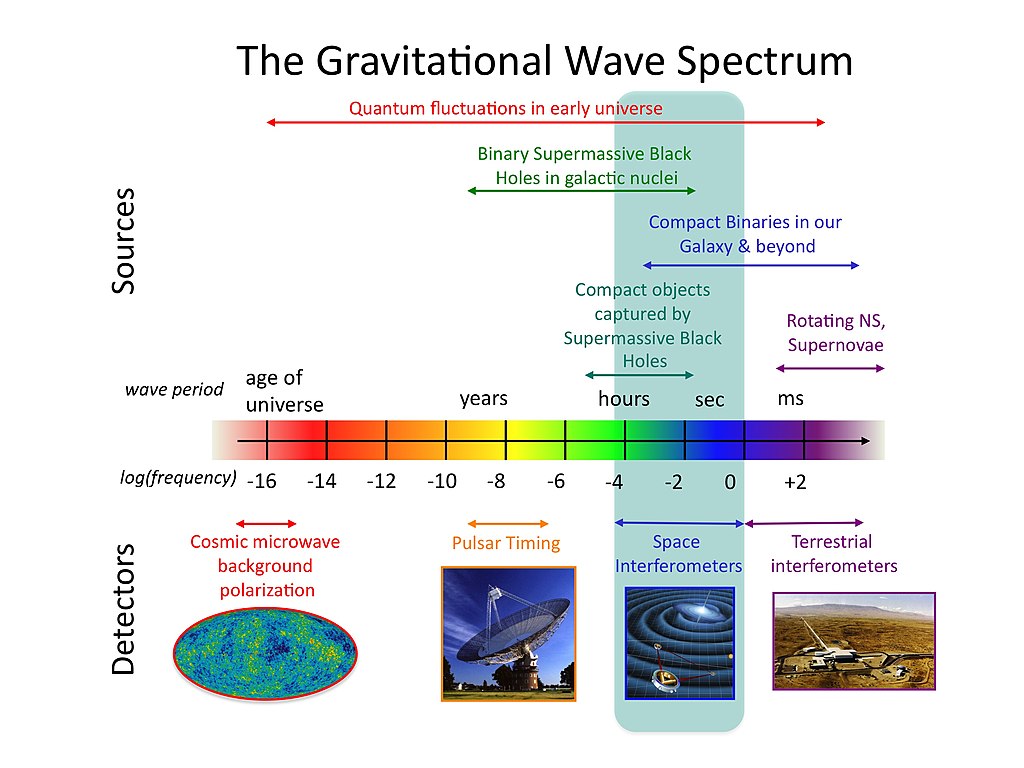 A diagram illustrating the graviational wave spectrum. (Symbol credit score: NASA Goddard House Flight Heart)Simply as our ears have developed to listen to sure frequencies of sound and no longer others, those tools can best come across a undeniable frequency vary of gravitational waves. The gravitational waves emitted by way of swirling pairs of supermassive black holes are too low-frequency for terrestrial gravitational wave detectors to “listen.”In different phrases, with their gravitational waves, stellar-mass binaries sing soprano, whilst supermassive pairings sing baritone. This workforce proposes detecting the delicate exchange in gravitational waves from stellar-mass black hollow binaries which might be brought about by way of interfering gravitational waves from supermassive binaries. Those small modulations may, subsequently, lend a hand divulge supermassive black hollow mergers which might be these days best detectable as a collective “background hum” the usage of huge collections of impulsively spinning neutron stars known as a “pulsar timing array.””The unconventional facet of this concept is to make use of prime frequencies which might be simple to come across to probe decrease frequencies that we don’t seem to be delicate to but,” Stegmann mentioned.The proposal may additionally lend a hand direct the design of long run gravitational wave detectors, equivalent to the approaching NASA and Eu House Company (ESA) space-based detector LISA (Laser Interferometer House Antenna).”As the trail for the LISA is now set, after adoption by way of ESA final January, the neighborhood wishes to guage the most efficient technique for the next era of gravitational wave detectors,” workforce member and College of Zurich black hollow theorist Lucio Mayer mentioned. “Specifically, which frequency vary they will have to goal – research like this deliver a powerful motivation to prioritize a deci-Hz [low-frequency] detector design.” The workforce’s analysis used to be revealed on Monday (August 5) within the magazine Nature.
A diagram illustrating the graviational wave spectrum. (Symbol credit score: NASA Goddard House Flight Heart)Simply as our ears have developed to listen to sure frequencies of sound and no longer others, those tools can best come across a undeniable frequency vary of gravitational waves. The gravitational waves emitted by way of swirling pairs of supermassive black holes are too low-frequency for terrestrial gravitational wave detectors to “listen.”In different phrases, with their gravitational waves, stellar-mass binaries sing soprano, whilst supermassive pairings sing baritone. This workforce proposes detecting the delicate exchange in gravitational waves from stellar-mass black hollow binaries which might be brought about by way of interfering gravitational waves from supermassive binaries. Those small modulations may, subsequently, lend a hand divulge supermassive black hollow mergers which might be these days best detectable as a collective “background hum” the usage of huge collections of impulsively spinning neutron stars known as a “pulsar timing array.””The unconventional facet of this concept is to make use of prime frequencies which might be simple to come across to probe decrease frequencies that we don’t seem to be delicate to but,” Stegmann mentioned.The proposal may additionally lend a hand direct the design of long run gravitational wave detectors, equivalent to the approaching NASA and Eu House Company (ESA) space-based detector LISA (Laser Interferometer House Antenna).”As the trail for the LISA is now set, after adoption by way of ESA final January, the neighborhood wishes to guage the most efficient technique for the next era of gravitational wave detectors,” workforce member and College of Zurich black hollow theorist Lucio Mayer mentioned. “Specifically, which frequency vary they will have to goal – research like this deliver a powerful motivation to prioritize a deci-Hz [low-frequency] detector design.” The workforce’s analysis used to be revealed on Monday (August 5) within the magazine Nature.
Small black holes may play ‘hide-and-seek’ with elusive supermassive black hollow pairs














