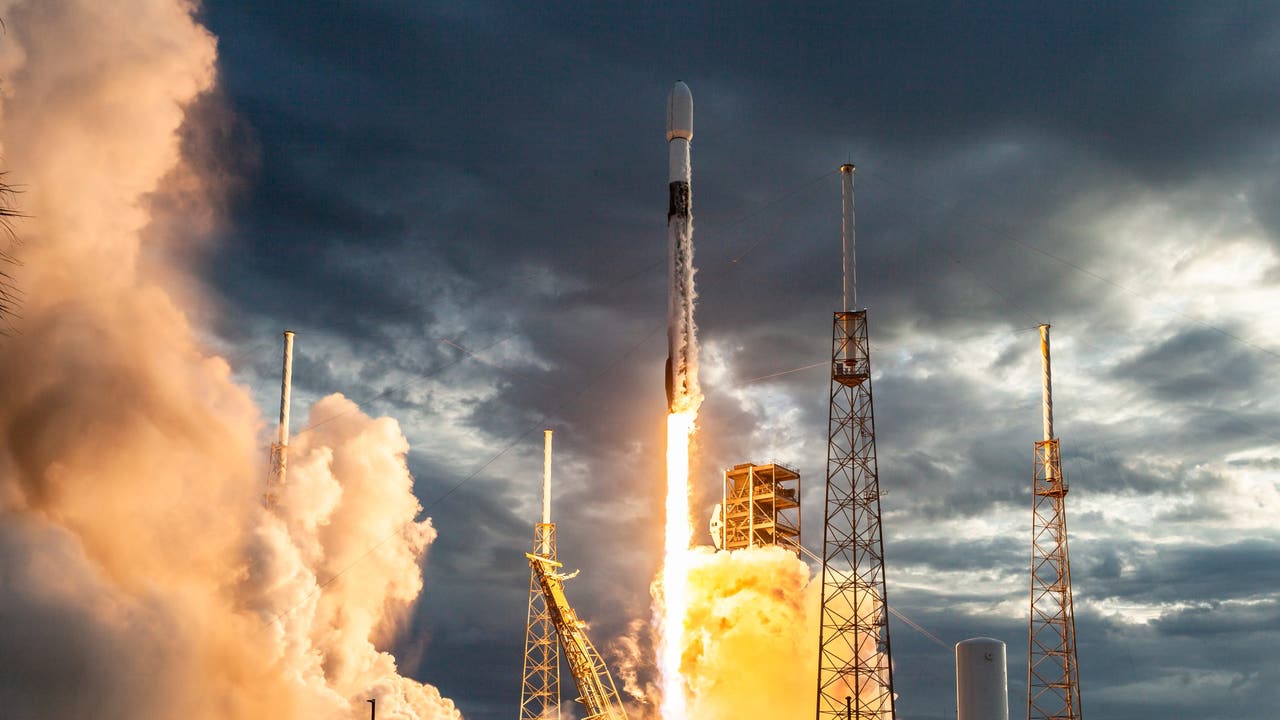
A big streak of crimson gentle left at the back of when a SpaceX rocket punched a hollow within the ionosphere above Arizona in July. (Symbol credit score: Jeremy Perez)De-orbiting SpaceX rockets are smashing brief holes within the higher surroundings, growing vivid blobs of sunshine within the sky. Now, scientists have warned that those “SpaceX auroras,” which appear to be sparkling crimson orbs of sunshine, might be inflicting unrecognized issues — despite the fact that they aren’t a danger to the surroundings or lifestyles on Earth. Researchers have identified for many years that launching rockets into area can punch holes within the higher ionosphere — the a part of the ambience between 50 and 400 miles (80 and 644 kilometers) above Earth’s floor the place fuel is ionized, or stripped of electrons. Those “ionospheric holes” can excite fuel molecules on this a part of the ambience and cause colourful streaks of crimson, aurora-like gentle. For instance, in July, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, which was once wearing Starlink satellites into orbit, ripped open a hollow above Arizona that made the sky bleed. And, in September, a U.S. Area Power rocket by accident punched an ionospheric hollow above California, which created a faint crimson glow.Now, astronomers on the McDonald Observatory in Texas have noticed equivalent however distinctive crimson lighting fixtures showing lengthy after SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rockets have left Earth’s surroundings. Those lighting fixtures, which can be smaller and extra round than the lengthy streaks created via launching rockets, are the results of ionospheric holes carved out via the rockets’ secondary boosters as they fall again to Earth after detaching from the rockets, Spaceweather.com reported.Astronomers noticed the primary of those SpaceX auroras above the observatory in February, and now are seeing “2 to five of them each and every month,” Stephen Hummel, an astronomer and outreach program coordinator at McDonald Observatory, advised Spaceweather.com. The crimson orbs are “very vivid” and “simply visual with the bare eye,” he added.Similar: SpaceX’s Starlink satellites are leaking radiation that is ‘photobombing’ our makes an attempt to review the cosmosAscending rockets and de-orbiting boosters each cause ionospheric holes via freeing gasoline into the ionosphere, which reasons ionized oxygen atoms to recombine, or flip again into common fuel molecules. This alteration excites the molecules and reasons them to unencumber crimson gentle, very similar to when the fuel is occupied with sun radiation throughout conventional auroral shows. This necessarily creates a hollow within the surrounding plasma, or ionized fuel. However the recombined molecules are are reionized, which closes up the holes inside of 10 to twenty mins.SpaceX’s de-orbiting boosters unencumber gasoline throughout quick burns to be able to manouver the falling particles to the touch down within the southern Atlantic Ocean as an alternative of crashing onto land. The ensuing holes generally shape above the south-central U.S. round 90 mins after release at an altitude of about 185 miles (300 km), in line with Spaceweather.com. Those holes are smaller and extra round than the holes torn open via launching rockets, so the ensuing lighting fixtures are extra round and don’t linger as lengthy. However they’re showing extra incessantly.Identical to the bigger gentle displays, the ionospheric holes pose no threat to lifestyles on Earth’s floor. Alternatively, “their have an effect on on astronomical science continues to be being evaluated,” Hummel mentioned. Because of this, it’s “a rising space of consideration” amongst researchers, he added.
A big streak of crimson gentle left at the back of when a SpaceX rocket punched a hollow within the ionosphere above Arizona in July. (Symbol credit score: Jeremy Perez)De-orbiting SpaceX rockets are smashing brief holes within the higher surroundings, growing vivid blobs of sunshine within the sky. Now, scientists have warned that those “SpaceX auroras,” which appear to be sparkling crimson orbs of sunshine, might be inflicting unrecognized issues — despite the fact that they aren’t a danger to the surroundings or lifestyles on Earth. Researchers have identified for many years that launching rockets into area can punch holes within the higher ionosphere — the a part of the ambience between 50 and 400 miles (80 and 644 kilometers) above Earth’s floor the place fuel is ionized, or stripped of electrons. Those “ionospheric holes” can excite fuel molecules on this a part of the ambience and cause colourful streaks of crimson, aurora-like gentle. For instance, in July, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, which was once wearing Starlink satellites into orbit, ripped open a hollow above Arizona that made the sky bleed. And, in September, a U.S. Area Power rocket by accident punched an ionospheric hollow above California, which created a faint crimson glow.Now, astronomers on the McDonald Observatory in Texas have noticed equivalent however distinctive crimson lighting fixtures showing lengthy after SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rockets have left Earth’s surroundings. Those lighting fixtures, which can be smaller and extra round than the lengthy streaks created via launching rockets, are the results of ionospheric holes carved out via the rockets’ secondary boosters as they fall again to Earth after detaching from the rockets, Spaceweather.com reported.Astronomers noticed the primary of those SpaceX auroras above the observatory in February, and now are seeing “2 to five of them each and every month,” Stephen Hummel, an astronomer and outreach program coordinator at McDonald Observatory, advised Spaceweather.com. The crimson orbs are “very vivid” and “simply visual with the bare eye,” he added.Similar: SpaceX’s Starlink satellites are leaking radiation that is ‘photobombing’ our makes an attempt to review the cosmosAscending rockets and de-orbiting boosters each cause ionospheric holes via freeing gasoline into the ionosphere, which reasons ionized oxygen atoms to recombine, or flip again into common fuel molecules. This alteration excites the molecules and reasons them to unencumber crimson gentle, very similar to when the fuel is occupied with sun radiation throughout conventional auroral shows. This necessarily creates a hollow within the surrounding plasma, or ionized fuel. However the recombined molecules are are reionized, which closes up the holes inside of 10 to twenty mins.SpaceX’s de-orbiting boosters unencumber gasoline throughout quick burns to be able to manouver the falling particles to the touch down within the southern Atlantic Ocean as an alternative of crashing onto land. The ensuing holes generally shape above the south-central U.S. round 90 mins after release at an altitude of about 185 miles (300 km), in line with Spaceweather.com. Those holes are smaller and extra round than the holes torn open via launching rockets, so the ensuing lighting fixtures are extra round and don’t linger as lengthy. However they’re showing extra incessantly.Identical to the bigger gentle displays, the ionospheric holes pose no threat to lifestyles on Earth’s floor. Alternatively, “their have an effect on on astronomical science continues to be being evaluated,” Hummel mentioned. Because of this, it’s “a rising space of consideration” amongst researchers, he added. SpaceX launches are turning into extra common, which will increase the danger of SpaceX auroras showing. (Symbol credit score: Getty Pictures)Adjustments to the ionosphere too can disrupt shortwave radio verbal exchange and intervene with GPS indicators, in line with Spaceweather.com.Learning those holes may additionally assist scientists be informed extra in regards to the ionosphere. “The ionospheric density is other night time to nighttime, so we will be informed one thing in regards to the potency of the [ionosphere’s] chemistry via staring at many occasions,” Jeffrey Baumgardner, a physicist at Boston College, advised Spaceweather.com.Similar: International’s greatest verbal exchange satellite tv for pc is a photobombing threat, astronomers warnThe crimson blobs don’t seem to be the one gentle displays created via SpaceX rockets. The corporate’s rocket boosters spin and unload their leftover gasoline in area ahead of they de-orbit, which creates a cloud of tiny ice crystals. Those crystals can every so often replicate daylight again towards Earth, and the illuminated gasoline creates vivid spirals within the night time sky, referred to as “SpaceX spirals.”There have already been two main SpaceX spirals this yr: The primary was once in January, which was once noticed forming above Mauna Kea in Hawaii, and the second one happened in April, which shone throughout a conventional auroral show in Alaska.The selection of SpaceX launches is all of a sudden expanding so the auroras and spirals are each more likely to develop into extra commonplace at some point.
SpaceX launches are turning into extra common, which will increase the danger of SpaceX auroras showing. (Symbol credit score: Getty Pictures)Adjustments to the ionosphere too can disrupt shortwave radio verbal exchange and intervene with GPS indicators, in line with Spaceweather.com.Learning those holes may additionally assist scientists be informed extra in regards to the ionosphere. “The ionospheric density is other night time to nighttime, so we will be informed one thing in regards to the potency of the [ionosphere’s] chemistry via staring at many occasions,” Jeffrey Baumgardner, a physicist at Boston College, advised Spaceweather.com.Similar: International’s greatest verbal exchange satellite tv for pc is a photobombing threat, astronomers warnThe crimson blobs don’t seem to be the one gentle displays created via SpaceX rockets. The corporate’s rocket boosters spin and unload their leftover gasoline in area ahead of they de-orbit, which creates a cloud of tiny ice crystals. Those crystals can every so often replicate daylight again towards Earth, and the illuminated gasoline creates vivid spirals within the night time sky, referred to as “SpaceX spirals.”There have already been two main SpaceX spirals this yr: The primary was once in January, which was once noticed forming above Mauna Kea in Hawaii, and the second one happened in April, which shone throughout a conventional auroral show in Alaska.The selection of SpaceX launches is all of a sudden expanding so the auroras and spirals are each more likely to develop into extra commonplace at some point.