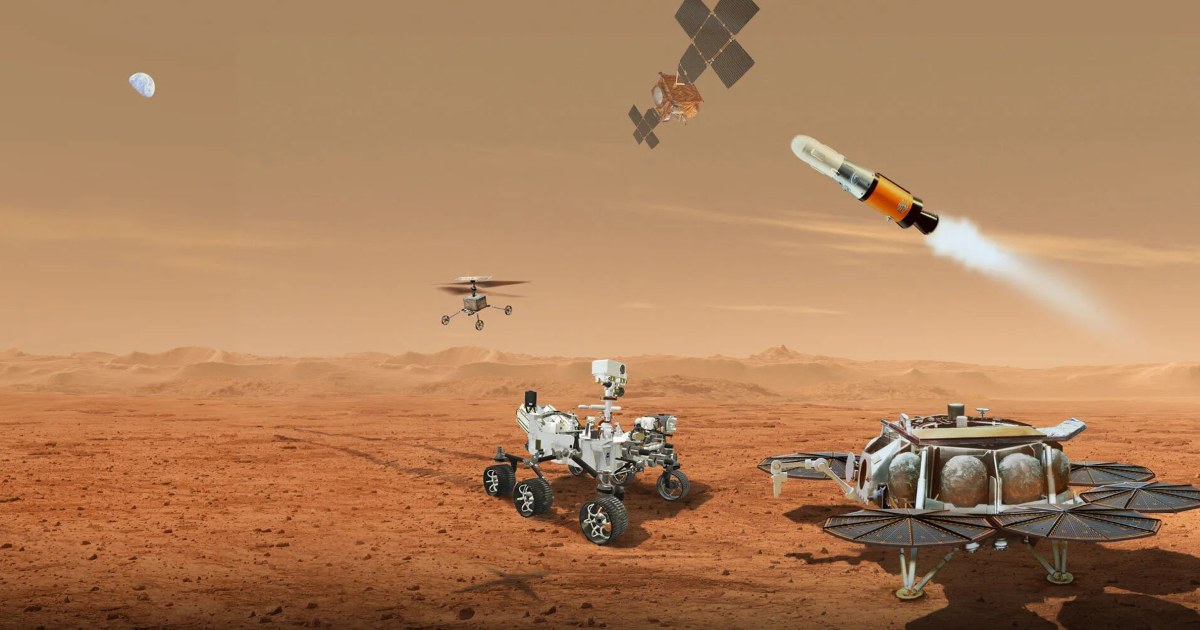
As a substitute of chilled glasses and fizz bubbles to ring within the New Yr, how about gassy geysers and frosty avalanches? That’s precisely what you’ll be able to be expecting because the Martian New Yr starts at the Crimson Planet with the onset of spring throughout its Northern Hemisphere.The time period “strolling in a wintry weather wonderland” on Mars is composed extra like sprinting around the floor, having to dodge the crash of cliffsides and explosions of carbon dioxide. Not like our northern hemisphere on Earth, at the Crimson Planet, the brand new yr begins off with the start of the spring season. The Martian New Yr started on Nov. 12, 2024, and spans for 687 Earth days, with the temperature beginning to upward push and moderately the shift in season from wintry weather to spring.”Springtime on Earth has numerous trickling as water ice regularly melts. However on Mars, the whole thing occurs with a bang,” Serina Diniega, who research planetary surfaces at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, mentioned in a observation. “You get numerous cracks and explosions as a substitute of melting, and I believe it will get in reality noisy.”
New Yr, New Mars: Crimson Planet Will get Energetic as Spring Starts (Mars File) – YouTube

Watch On
The ambience on Mars could be very distinctive in comparison to on Earth. As an example, when the ice melts the liquid does no longer shape puddles and pool at the floor; as a substitute, sublimation takes position which switches the cast ice at once right into a gasoline. The abrupt shift can also be moderately violent, as each dry ice (composed of carbon dioxide) and common ice (made from water) grow to be a lot weaker and start to wreck.Since we aren’t in a position to witness this first-hand on Mars, scientists depend on NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) to be their eyes to trace those adjustments. The Crimson Planet has been house to MRO because it introduced in 2005, and it’s provided with other gear that offer photographs and observations from the outside.”Probability observations we get are reminders of simply how other Mars is from Earth, particularly in springtime, when those floor adjustments are maximum noticeable,” Diniega mentioned. “We are fortunate we now have had a spacecraft like MRO watching Mars for so long as it has. Looking at for nearly two decades has allow us to catch dramatic moments like avalanches.”Check out probably the most other phenomena scientists have noticed or have been in a position to recreate from knowledge throughout the Martian springtime, because of tools like MRO’s Top-Solution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) digital camera.Breaking house information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!Frost avalanches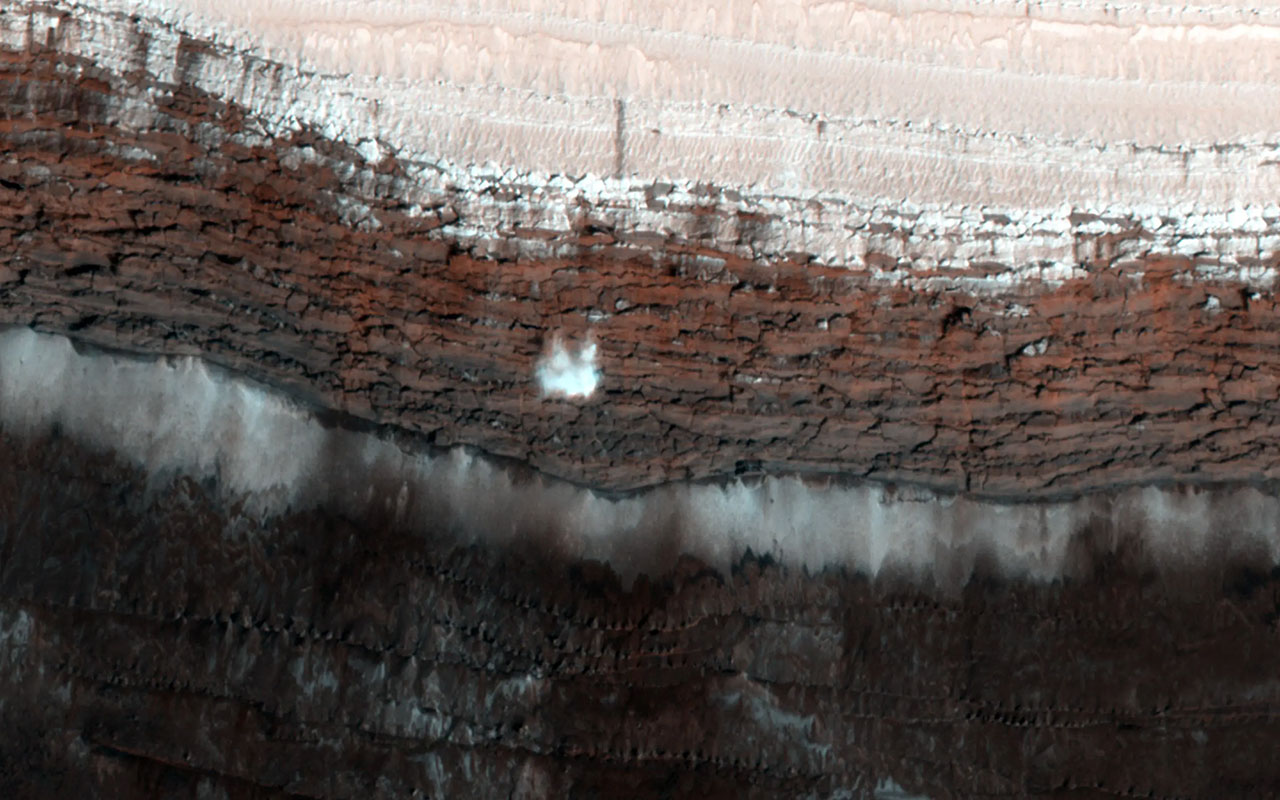 Martian spring comes to numerous cracking ice, which resulted in this 66-foot-wide (20-meter-wide) chew of carbon dioxide frost captured in freefall via the HiRISE digital camera aboard NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter in 2015. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona)Because the temperature begins its seasonal climb, chunks of frost composed of carbon dioxide start to wreck aside and crash to the outside. This procedure used to be captured on digital camera via HiRISE in 2015, when a 66-foot-wide (20-meter-wide) block broke off and used to be photographed mid-air crashing to the bottom.Fuel geysers
Martian spring comes to numerous cracking ice, which resulted in this 66-foot-wide (20-meter-wide) chew of carbon dioxide frost captured in freefall via the HiRISE digital camera aboard NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter in 2015. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona)Because the temperature begins its seasonal climb, chunks of frost composed of carbon dioxide start to wreck aside and crash to the outside. This procedure used to be captured on digital camera via HiRISE in 2015, when a 66-foot-wide (20-meter-wide) block broke off and used to be photographed mid-air crashing to the bottom.Fuel geysers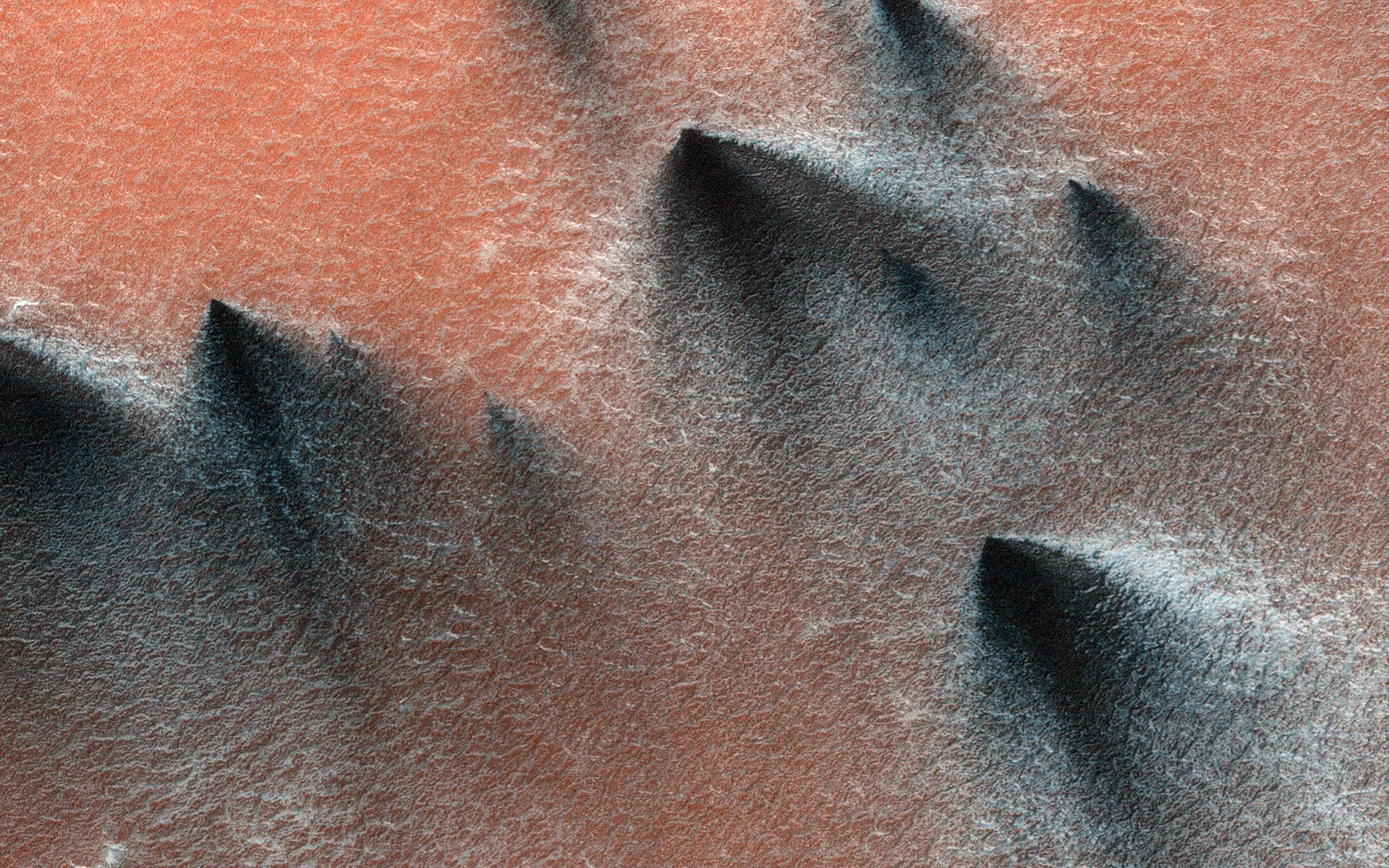 As gentle shines via carbon dioxide ice on Mars, it heats up its backside layers, which, slightly than melting right into a liquid, become gasoline. The accumulation gasoline sooner or later ends up in explosive geysers that toss darkish lovers of particles directly to the outside. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona)Consider geysers in Yellowstone firing up water into the sky, simplest on Mars, they include darkish particles from below the outside carried up via bursts of gasoline. Because the solar turns the ice into gasoline underground, the increase will get so robust that it sooner or later fires up darkish subject matter into the air, leaving in the back of darkish lovers at the Martian floor.Floor “Dust” Spiders
As gentle shines via carbon dioxide ice on Mars, it heats up its backside layers, which, slightly than melting right into a liquid, become gasoline. The accumulation gasoline sooner or later ends up in explosive geysers that toss darkish lovers of particles directly to the outside. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona)Consider geysers in Yellowstone firing up water into the sky, simplest on Mars, they include darkish particles from below the outside carried up via bursts of gasoline. Because the solar turns the ice into gasoline underground, the increase will get so robust that it sooner or later fires up darkish subject matter into the air, leaving in the back of darkish lovers at the Martian floor.Floor “Dust” Spiders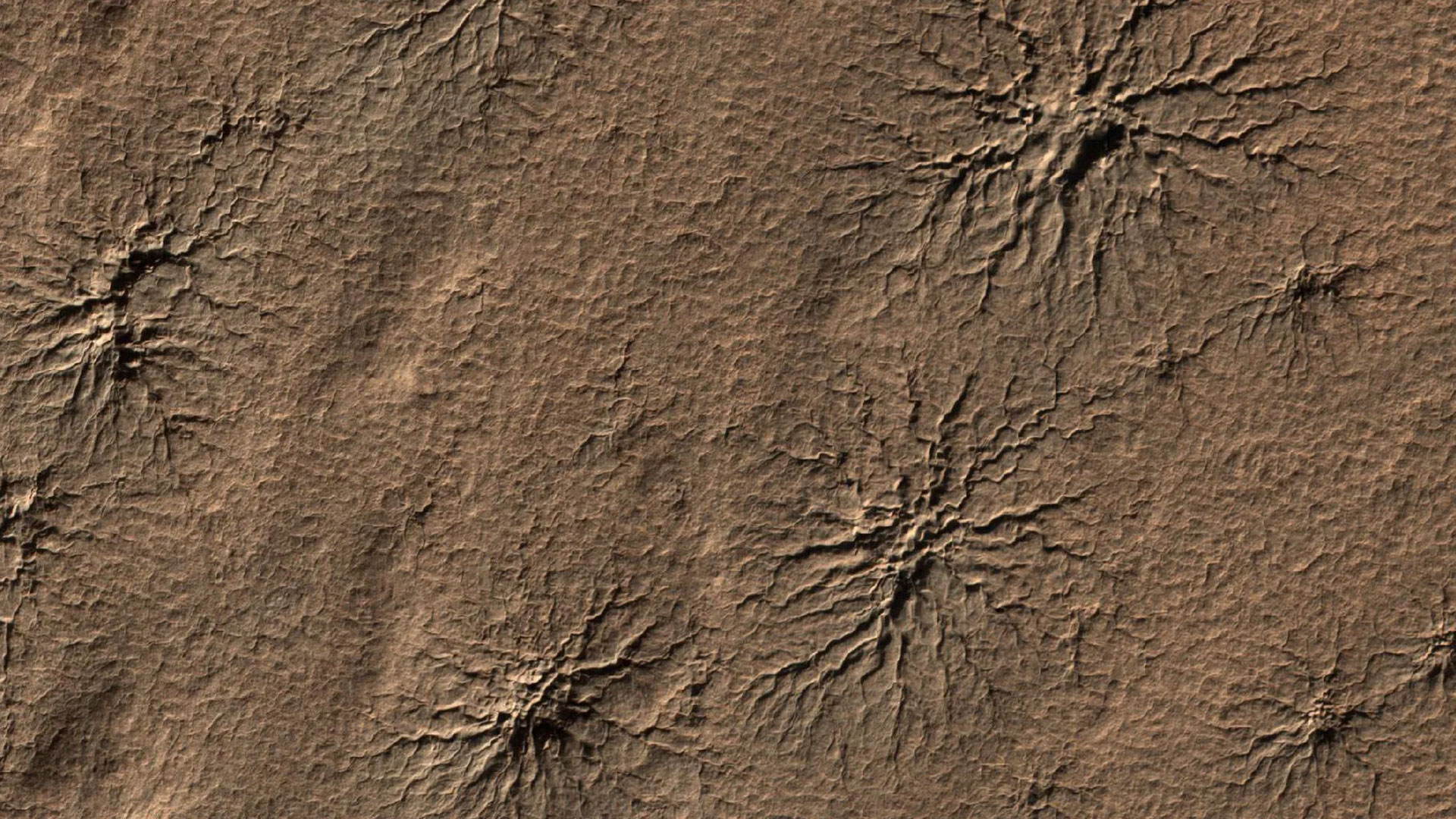 Every so often, after carbon dioxide geysers have erupted from ice-covered spaces on Mars, they depart scour marks at the floor. When the ice is all long past via summer time, those lengthy scour marks seem like the legs of big spiders. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona)It will not be as horrifying because it sounds, however it undoubtedly may glance that means from house! The use of a modeling at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), researchers have been in a position to recreate what it will seem like at the floor after sublimation takes position with the ice close to probably the most northern geysers – which resembles giant spider legs!Wild Winds
Every so often, after carbon dioxide geysers have erupted from ice-covered spaces on Mars, they depart scour marks at the floor. When the ice is all long past via summer time, those lengthy scour marks seem like the legs of big spiders. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona)It will not be as horrifying because it sounds, however it undoubtedly may glance that means from house! The use of a modeling at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), researchers have been in a position to recreate what it will seem like at the floor after sublimation takes position with the ice close to probably the most northern geysers – which resembles giant spider legs!Wild Winds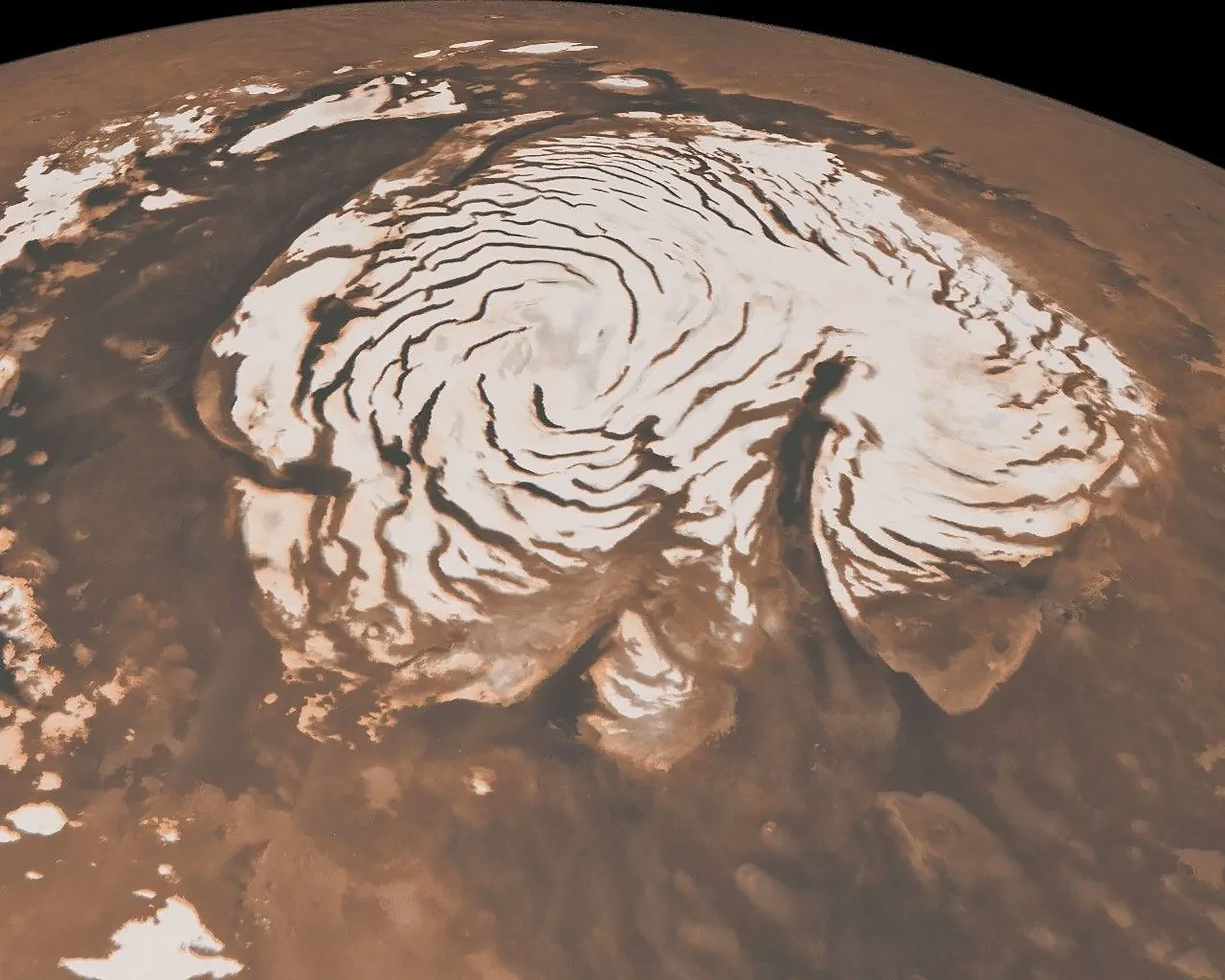 As temperatures upward push, robust winds kick up that carve deep troughs into the ice cap of Mars’ north pole. A few of these troughs are so long as California, and provides the Martian north pole its trademark swirls. This symbol used to be captured via NASA’s now-inactive Mars International Surveyor. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS)Do you know at Mars’ north pole, there may be an ice cap within the springtime that is as giant because the state of Texas? As heat, sturdy winds whirl around the area, deep troughs are carved out because the ice thaws. Because of this, a swirling trend takes form around the ice cap from above, observed right here via NASA’s retired Mars International Surveyor.Drifting Dunes
As temperatures upward push, robust winds kick up that carve deep troughs into the ice cap of Mars’ north pole. A few of these troughs are so long as California, and provides the Martian north pole its trademark swirls. This symbol used to be captured via NASA’s now-inactive Mars International Surveyor. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS)Do you know at Mars’ north pole, there may be an ice cap within the springtime that is as giant because the state of Texas? As heat, sturdy winds whirl around the area, deep troughs are carved out because the ice thaws. Because of this, a swirling trend takes form around the ice cap from above, observed right here via NASA’s retired Mars International Surveyor.Drifting Dunes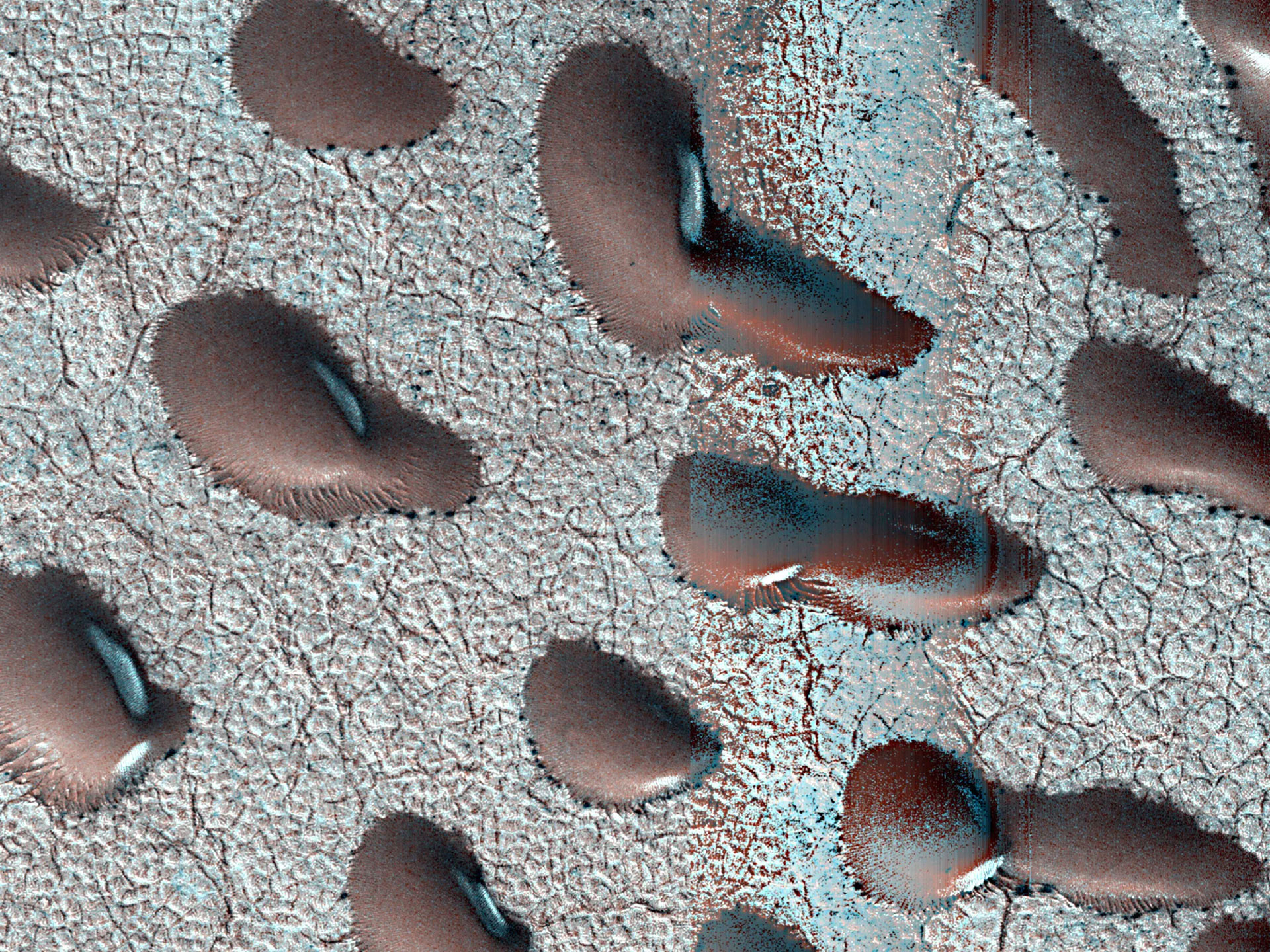 Surrounded via frost, those Martian dunes in Mars’ northern hemisphere have been captured from above via NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter the use of its HiRISE digital camera on Sept. 8, 2022. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona)Some other implausible sight to peer throughout the springtime on Mars is the reshaping of its sand dunes via the similar heat and wild winds that have an effect on the north pole. The Martian dunes are created and migrate as the quantity of sand grows on one facet simply because it’s got rid of from the opposite via the wind.Within the wintertime, carbon dioxide frost bureaucracy over the tops of the sand dunes, freezes, and holds them in position till the spring thaw permits them to transfer once more.
Surrounded via frost, those Martian dunes in Mars’ northern hemisphere have been captured from above via NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter the use of its HiRISE digital camera on Sept. 8, 2022. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona)Some other implausible sight to peer throughout the springtime on Mars is the reshaping of its sand dunes via the similar heat and wild winds that have an effect on the north pole. The Martian dunes are created and migrate as the quantity of sand grows on one facet simply because it’s got rid of from the opposite via the wind.Within the wintertime, carbon dioxide frost bureaucracy over the tops of the sand dunes, freezes, and holds them in position till the spring thaw permits them to transfer once more.