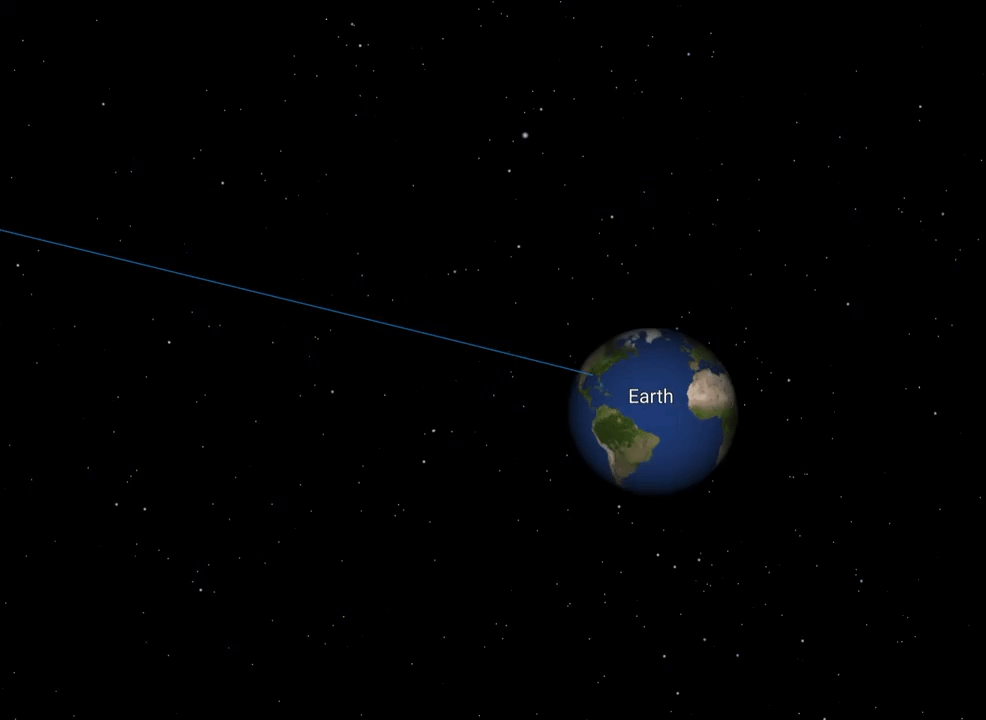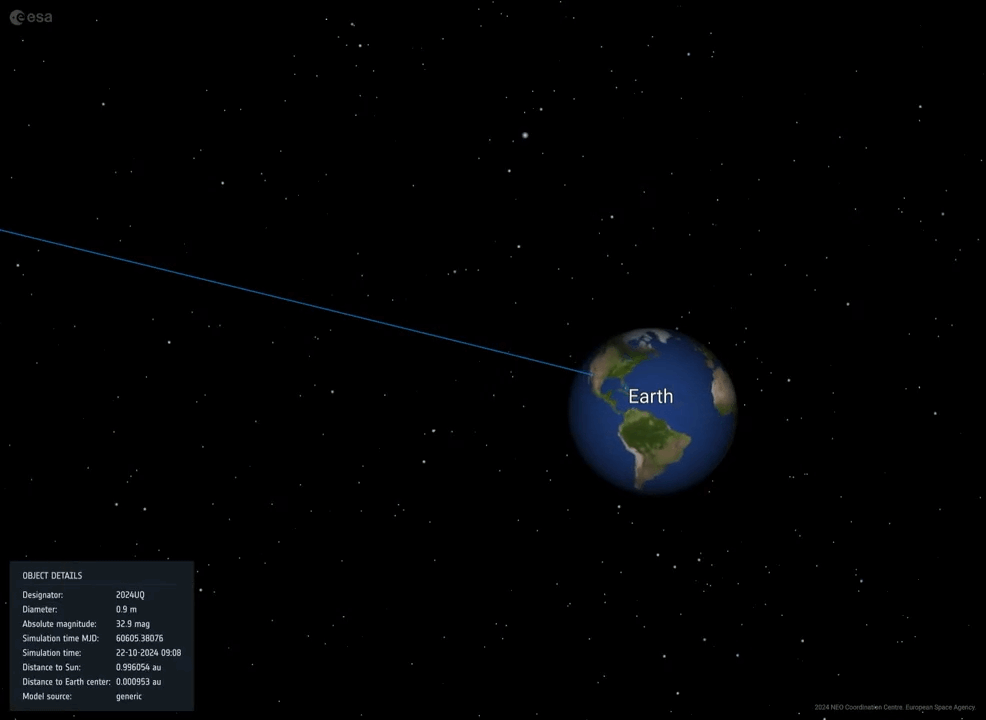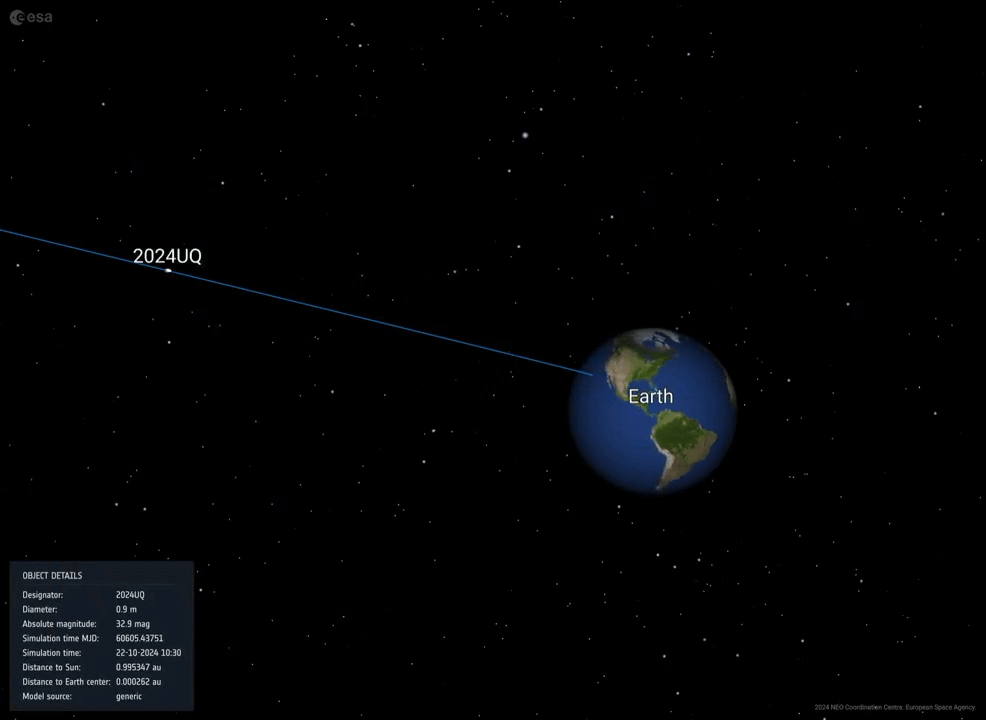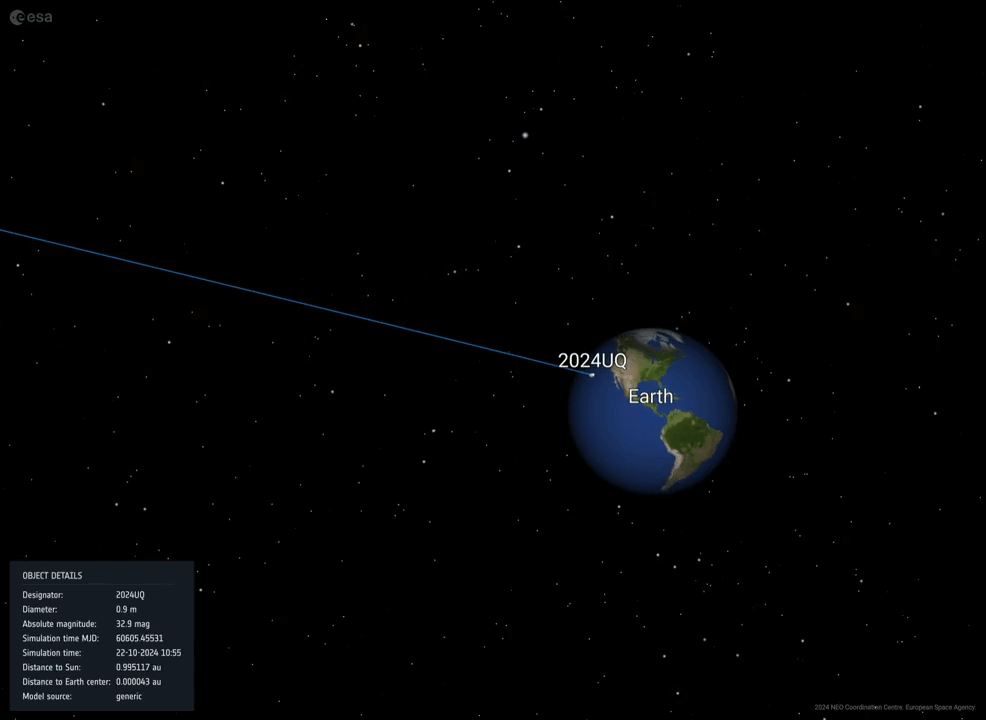
(The Hill) — An asteroid the dimensions of a soccer stadium threaded the needle between Earth and the moon Saturday morning — the second one of 2 astronomical close to misses in 3 days.
Close to omit, on this case, is a relative time period: Saturday’s asteroid, 2024 MK, got here inside 180,000 miles of Earth. On Thursday, in the meantime, asteroid 2011 UL21 flew inside 4 million miles.
However the Saturday passage of 2024 MK — which scientists found out handiest two weeks in the past — coincides with a sobering reminder of threats from area.
Sunday is Asteroid Day, the anniversary of the 1908 explosion of a rock from area above a Russian the city — one of these threat that, astronomers warn, is all the time lurking because the Earth hurtles via area.
Right here’s what you wish to have to learn about asteroids, the danger from area and Saturday’s fly-by close to omit.
What’s an asteroid?
Asteroids are rocks in area that orbit the solar, slightly just like the planets with which they sometimes pass paths.
Additionally like planets, asteroids shaped greater than 4.6 billion years in the past out of the condensing cloud of mud and fuel that shaped the sun machine — making them in impact time pills of the far away time sooner than the formation of Earth or the solar.
Scientists have recognized about 1.3 million of them, most commonly orbiting within the huge area between Mars and Jupiter. Each personally and within the combination, they have a tendency to be small — all of the weight of the entire asteroids within the sun machine is thought to be less than that of the moon.
Over the lengthy sweep of historical past, asteroid affects additionally will have been an important to lifestyles on Earth.
In any other piece of asteroid information closing week, scientists on Wednesday introduced the result of a 2023 venture to the asteroid Bennu that had returned with samples, suggesting the likelihood that it used to be stuffed with the substances for water.
Those findings recommended an upside to asteroid affects. “Asteroids akin to this may increasingly have performed a key position in handing over water and the development blocks of lifestyles to Earth,” coauthor Nick Timms of Curtin College stated.
What occurs if one hits the Earth now?
An asteroid doesn’t need to be specifically huge to do injury. In 2013, for example, an asteroid about 62 ft throughout that broke aside just about 20 miles above Siberia launched 30 instances as a lot power because the atomic bomb that hit Hiroshima.
Whilst many of the affect power used to be absorbed by means of the ambience, the detonation brought about a surprise wave that blew out home windows and injured greater than one thousand other folks.
Asteroid Day on Sunday commemorates an excellent larger affect, the 1908 Tunguska match, which additionally came about above Siberia.
In that match, the Russian newspaper Sibir (Siberia) reported that peasants taking a look upward noticed a “surprisingly vibrant (inconceivable to take a look at) bluish-white heavenly frame, which for 10 mins moved downwards.”
The frame seemed to be a “pipe” cylinder, which started to “smudge” because it hit the denser surroundings above the woodland and broke aside into billowing black smoke,” the object stated.
“A noisy knocking (now not thunder) used to be heard as though huge stones had been falling, or artillery used to be fired. All structures shook. On the similar time the cloud started emitting flames of unsure shapes. All villagers had been troubled with panic and took to the streets, ladies cried, considering it used to be the tip of the arena.”
If 2024 MK, with a diameter of 500 to 800 ft, had been to hit slightly than go by means of Earth on Saturday, it wouldn’t be the tip of the arena — a minimum of, now not somewhat. Such an affect would “have the similar affect power within the masses of megaton drawing near a gigaton,” Peter Brown of Canada’s Western College instructed the Canadian Broadcasting Carrier.
That’s a huge possible affect — for context, the explosion can be 10-20 instances larger than that from maximum hydrogen bombs which were examined, which are within the 50-megaton vary.
“It’s one of these factor that if it hit the east coast of the U.S., you could possibly have catastrophic results over many of the japanese seaboard. Nevertheless it’s now not large enough to have an effect on the entire global,” Brown stated.
The affect of a hypothetical collision with 2011 UL21, the asteroid that flew by means of Thursday, can be way more disastrous. Whilst it used to be very easily a ways out in area and had no likelihood of hitting the Earth, it used to be additionally very huge: the approximate measurement of Mount Everest.
At 1.5 miles in diameter, that asteroid used to be a couple of quarter the dimensions of the asteroid that struck the earth 65 million years in the past, wiping out all dinosaurs that walked, in addition to the vast majority of lifestyles on earth.
How top is the danger of a collision?
Analysis suggests it’s very, very low. NASA has estimated {that a} civilization-ending match (just like the collision of an asteroid the dimensions of Thursday’s with the Earth) must handiest occur each and every few million years.
And such an affect from an asteroid 880 yards in diameter or larger can be nearly inconceivable for a long time, in step with findings printed closing yr in The Astronomical Magazine.
“It’s excellent information,” learn about chief Oscar Fuentes-Muñoz of the College of Colorado Boulder instructed the MIT Era Assessment. “So far as we all know, there’s no affect within the subsequent 1,000 years.”
NASA’s catalog of enormous and perilous gadgets like 2011 UL21 is now 95 % entire, the Era Assessment reported.
However because the 1908 and 2013 explosions recommended, a fairly small asteroid can nonetheless “motive a large number of injury,” Áine O’Brien of the College of Glasgow cautioned the Era Assessment.
The map of asteroids the dimensions of the only passing between the Earth and Moon on Saturday — which might wreck a town if it struck the planet — remains to be simply 40 % entire, the mag reported, in step with Giant Assume.
How do scientists hit upon and observe asteroids?
They accomplish that by means of regularly scanning the sky, in search of fairly small, fast-moving gadgets. The Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Final Alert Machine that detected 2024 MK is without doubt one of the many surveys in search of dangers.
Those surveys be offering early warnings that would lend a hand save you asteroid affects, Alan Fitzsimmons of Queen’s College Northern Eire instructed the CBC.
“It’s the one herbal crisis that we will forestall. You’ll’t forestall a tsunami, you’ll be able to’t forestall an earthquake, you’ll be able to’t forestall a volcano,” he stated. “You’ll if truth be told forestall or save you an asteroid affect, a minimum of in concept.”
NASA controlled to knock an asteroid off its direction in 2022, when its Double Asteroid Redirection Take a look at (DART) slammed a satellite tv for pc the approximate weight of a small automobile into Dimorphos, a rock about the similar measurement as 2024 MK — changing its orbit somewhat.
The DART venture, which required NASA to execute an actual collision 7 million miles away, confirmed “that NASA is making an attempt to be able for regardless of the universe throws at us,” company Administrator Invoice Nelson stated all through a briefing on the time.
However there’s an previous pronouncing in science that whilst in concept there’s no distinction between concept and apply, in apply there’s. Pulling off a feat just like the DART venture to forestall an asteroid from hitting Earth “is surely conceivable, however can be a troublesome and costly activity,” astronomer Alistair Gunn of the College of Manchester wrote for the British Broadcasting Company.
“The important thing can be in deflecting the asteroid clear of its collision direction with Earth slightly than shattering it into similarly unhealthy particles,” Gunn added.
He additionally famous pulling that off would take a lead time of a minimum of 5 years — which is why early caution is “vitally vital.”
That want for early caution is one explanation why the passage of 2024 MK is so disquieting: Scientists found out it simply this month.
Previous this week, NASA introduced plans to deflect an asteroid nonetheless had “top degree gaps,” USA Lately reported.
“We’re the use of the functions that we need to truly attempt to optimistically retire that danger, to grasp what’s available in the market, and know if anything else poses a risk,” Kelly Speedy, NASA’s appearing planetary protection officer, instructed the opening.
Had been American citizens be capable of see Saturday’s asteroid?
Sure — in the event that they had been in the precise area and are each very ready and fortunate.
American citizens within the U.S. Southwest — or Hawaii — who had been from mild air pollution and keen to upward thrust within the predawn hours will have a shot at seeing 2024 MK as a hastily shifting dot, which can come closest to the Earth at about 9:46 Japanese time.
That’s 90 mins sooner than first light in Hawaii and about an hour after first light at the West Coast — regardless that the asteroid can be dimly visual sooner than it makes the passage.
For everybody out of doors the ones spaces, the Digital Telescope Undertaking is livestreamed the passage.
Even those that are in the precise area would possibly to find viewing the passage difficult, Fitzsimmons of Queen’s College instructed CBC. Skywatchers will want a telescope, and be ready to identify a faint, fast-moving object. “You’ve were given to grasp precisely the place to seem,” he stated. “It’s motoring.”