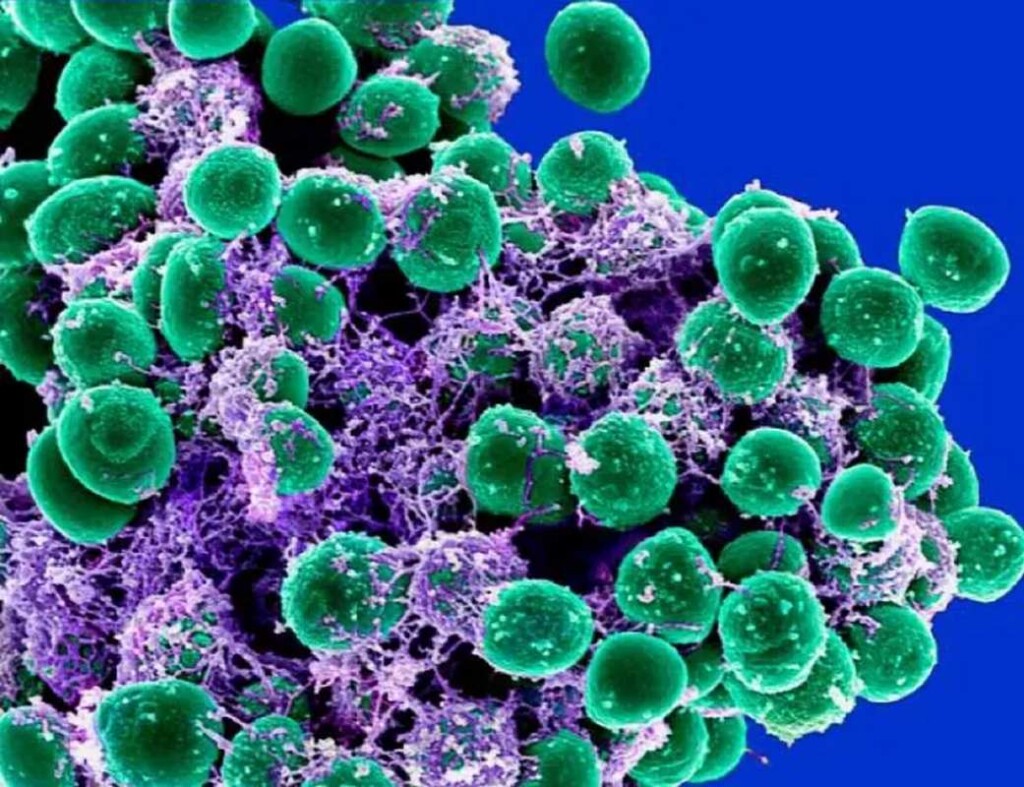
 A colorized scanning electron micrograph of Staphylococcus epidermidis (coloured inexperienced) – credit score NIAID: by way of Wikimedia Commons, CC BY 2.0 License
A colorized scanning electron micrograph of Staphylococcus epidermidis (coloured inexperienced) – credit score NIAID: by way of Wikimedia Commons, CC BY 2.0 License
Believe a global during which a vaccine is a cream you rub onto your pores and skin as an alternative of a needle a well being sector employee pushes into considered one of your muscle groups.
Even higher, it’s affordable, totally pain-free, and now not adopted by means of fever, swelling, redness, or a sore arm. No status in a protracted line to get it both.
That is the imaginative and prescient that researchers at Stanford hope to succeed in with a brand new tetanus vaccine derived from a bacterial species that’s discovered at the skins of almost all human beings; one who’s in large part innocuous to us, but nonetheless will cause a ferocious antibody reaction if it breaches the surface barrier or will get throughout the bloodstream.
A group of scientists led by means of the Standford Ph.D. in bioengineering Dr. Michael Fischbach hypothesized that Staphylococcus epidermidis, the innocuous and ubiquitous bacterium, might be used as a supply mechanism for the pathogen in a vaccine.
All over experiments, Fischbach discovered that once the S. epidermidis micro organism had been engineered to comprise a small genetic hint of the tetanus micro organism, the immune device centered it simply as ferociously as earlier than, whilst additionally leading to a separate immune reaction to the tetanus gene of the sort one would be expecting from a vaccine.
The group realized thru additional exam of S. epidermidis that it naturally produces a big protein referred to as Aap. This tree-shaped molecule is 5 instances greater than commonplace proteins, and so massive its ‘branches’ protrude from the cellular wall. Fischbach and his group imagine that this is why why the immune device’s reaction to this microbe is so tough: immune cells on our pores and skin and hair follicles can learn about it even with out coming in direct touch with it.
Mice, which don’t have any local colonization of S. epidermidis, had been discovered to have greater-than-vaccine degree immune responses to this computer virus after it was once swabbed without delay onto their fur.
Fischbach and his group made up our minds that this might be the foundation for a topical vaccine, one during which the micro organism is engineered to hold the genetic subject matter of humanity’s most threatening illnesses. Additional exams performed at the mice discovered that software of S. epidermidis engineered to hold tetanus generated sufficient antibodies to offer protection to mice from six instances the deadly dose of tetanus toxin—a in reality astonishing discovery.
MORE EXPERIMENTAL VACCINES: Hate Needles? Long term Vaccines May well be Delivered by means of a Delicate Puff of Air
“We expect this may increasingly paintings for viruses, micro organism, fungi, and one-celled parasites,” Fischbach instructed Stanford College press. “Maximum vaccines have substances that stimulate an inflammatory reaction and make you’re feeling just a little unwell. Those insects don’t do this. We predict that you simply wouldn’t enjoy any irritation in any respect.”
Maximum vaccines given to people are available in two bureaucracy, a reside vaccine or a lifeless vaccine. Reside vaccines comprise the true factor, and unwanted side effects of the sort one would be expecting from an an infection don’t seem to be unusual. In lifeless vaccines, the virus or bacterium can’t reflect. Antibody reaction to a lifeless vaccine is enhanced in trendy vaccines by means of the presence of an ‘adjuvant’—like aluminum salts.
PERSONALIZED CANCER VACCINES: Hope for Sufferers with Competitive Breast Most cancers: Vaccine Trial Leads to 88% Survival Charge After 3 Years
Aluminum is a poisonous heavy steel like cadmium or lead, and its identity when discovered with the virus reasons the immune device to reply a lot more severely. The brilliance of what Fischbach referred to as the “plug-and-play” vaccine cream evolved in his lab is that the adjuvant is a innocuous pores and skin micro organism that already exists at the pores and skin and hair of just about each human in the world.
Fischbach believes trials for the cream will start in people inside 2 to three years.
SHARE This Step forward On Topical Vaccine Utility With Your Buddies…
Stanford Scientists Change into Ubiquitous Pores and skin Bacterium right into a Topical Vaccine In opposition to Tetanus