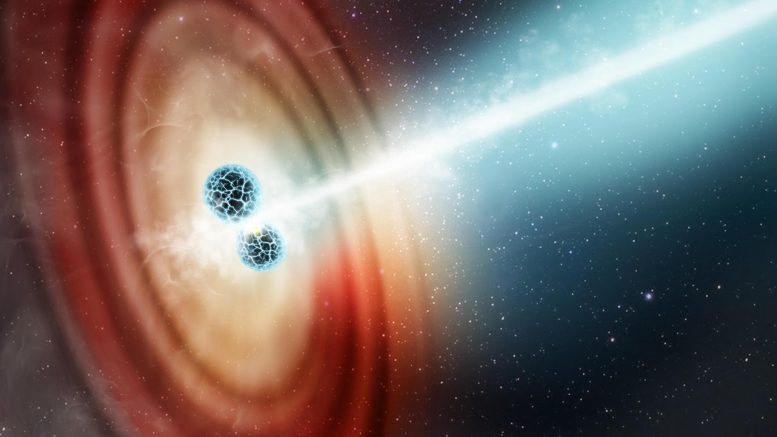
Artist’s impact of 2 neutron stars colliding, referred to as a “kilonova” match. Credit score: Elizabeth Wheatley (STScI)Astrophysicists suggest watching colliding neutron stars (kilonovae) as a brand new option to deal with inconsistencies in measuring the Universe’s growth charge, aiming to unravel the continued “Hubble Pressure.”In accordance to a few within the astrophysical group, there was one thing of a “Disaster in Cosmology” lately. Regardless that astronomers are all mindful that the Universe is in a state of growth, there was some inconsistency when measuring the speed of it (aka. the Hubble Consistent). This factor arises from the Cosmic Distance Ladder, the place astronomers use other easy methods to measure relative distances over longer scales. This contains making native distance estimates the use of parallax measurements, within reach variable stars, and supernovae (“same old candles”).In addition they behavior redshift measurements of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB), the relic radiation left over from the Large Bang, to decide cosmological distances. The discrepancy between those two strategies is referred to as the “Hubble Pressure,” and astronomers are desperate to unravel it.A Novel Option to Measuring the Hubble ConstantIn a up to date learn about, a world staff of astrophysicists from the Niels Bohr Institute advised a unique approach for measuring cosmic growth. They argue that through watching colliding neutron stars (kilonovae), astronomers can relieve the strain and procure constant measurements of the Hubble Consistent.The analysis was once led through astrophysicists from the Cosmic Break of day Heart (DAWN) and the Niels Bohr Institute on the College of Copenhagen. They had been joined through researchers from Tel Aviv College, the Cahill Heart for Astrophysics (California Institute of Era), the GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Analysis, the Astrophysical Large Bang Laboratory, Helmholtz Analysis Academy Hessen for FAIR, and the DARK analysis staff on the Niels Bohr Institute. The paper that describes their analysis not too long ago seemed within the magazine Astronomy & Astrophysics.
Artist’s impact of 2 neutron stars colliding, referred to as a “kilonova” match. Credit score: Elizabeth Wheatley (STScI)Astrophysicists suggest watching colliding neutron stars (kilonovae) as a brand new option to deal with inconsistencies in measuring the Universe’s growth charge, aiming to unravel the continued “Hubble Pressure.”In accordance to a few within the astrophysical group, there was one thing of a “Disaster in Cosmology” lately. Regardless that astronomers are all mindful that the Universe is in a state of growth, there was some inconsistency when measuring the speed of it (aka. the Hubble Consistent). This factor arises from the Cosmic Distance Ladder, the place astronomers use other easy methods to measure relative distances over longer scales. This contains making native distance estimates the use of parallax measurements, within reach variable stars, and supernovae (“same old candles”).In addition they behavior redshift measurements of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB), the relic radiation left over from the Large Bang, to decide cosmological distances. The discrepancy between those two strategies is referred to as the “Hubble Pressure,” and astronomers are desperate to unravel it.A Novel Option to Measuring the Hubble ConstantIn a up to date learn about, a world staff of astrophysicists from the Niels Bohr Institute advised a unique approach for measuring cosmic growth. They argue that through watching colliding neutron stars (kilonovae), astronomers can relieve the strain and procure constant measurements of the Hubble Consistent.The analysis was once led through astrophysicists from the Cosmic Break of day Heart (DAWN) and the Niels Bohr Institute on the College of Copenhagen. They had been joined through researchers from Tel Aviv College, the Cahill Heart for Astrophysics (California Institute of Era), the GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Analysis, the Astrophysical Large Bang Laboratory, Helmholtz Analysis Academy Hessen for FAIR, and the DARK analysis staff on the Niels Bohr Institute. The paper that describes their analysis not too long ago seemed within the magazine Astronomy & Astrophysics. Galaxies lie reasonably nonetheless in house, however the house itself is increasing. This reasons the galaxies to transport clear of every different at an ever-increasing charge. Precisely how briskly is a bit of of a thriller, although. Credit score: ESO/L. Calçada. Galaxies lie reasonably nonetheless in house, however the house itself is increasing. This reasons the galaxies to transport clear of every different at an ever-increasing charge. Precisely how briskly is a bit of of a thriller, although. Credit score: ESO/L. CalçadaHistorical Context of the Universe’s ExpansionThe growth of the cosmos is one thing astronomers have recognized about for over a century, due to Edwin Hubble. Via watching galaxies and measuring their mild curves for redshift, he demonstrated that the extra far-off a galaxy was once, the quicker it receded from the Milky Method. This showed what many suspected about Einstein’s Idea of Basic Relativity, which predicted that the cosmos was once both in a state of growth or retraction. Via measuring the velocities at which different galaxies had been shifting clear of our personal, scientists have tried to measure the Hubble Consistent.This growth charge is measured in “velocity according to distance,” and trendy estimates position it at simply over 20 km/s () according to million light-years. That implies a galaxy situated 100 million light-years away recedes from us at 2,000 km/s (1,242 mps), whilst every other galaxy 200 million light-years away recedes at 4,000 km/s (2,485 mps). Then again, the use of supernovae to measure distances and velocities of galaxies yields 22.7 ± 0.4 km/s, whilst inspecting the CMB yields 20.7 ± 0.2 km/s. That would possibly not sound like a lot, however the distinction additionally produces considerably other estimates for the age of the Universe -12.8 vs. 13.8 billion years, respectively.Rising Answers and New ResearchWhile uncertainties had been to be anticipated again within the early twentieth century, enhancements in measuring ways have come far, and the discrepancy between measurements has reduced. Consequently, astronomers and cosmologists at the moment are at some extent the place they are able to state with self assurance that the 2 values can’t each be proper. This has led many scientists to wonder whether systematic biasing might be influencing one of the crucial effects or if particular physics within the early Universe (a los angeles early Darkish Power) may well be concerned.Of their paper, the staff proposed a unique approach for measuring distances, thereby serving to to settle the continued dispute. The analysis was once led through Albert Sneppen, a Ph.D. pupil in astrophysics on the Cosmic Break of day Heart on the Niels Bohr Institute. As he defined not too long ago:“When two ultra-compact neutron stars — which in themselves are the remnants of supernovae — orbit every different and in the end merge, they move off in a brand new explosion; a so-called kilonova. We not too long ago demonstrated how this explosion is remarkedly symmetric, and it seems that this symmetry now not handiest is lovely, but in addition extremely helpful.”In a prior learn about (“Round symmetry within the kilonova AT2017gfo/GW170817“), Sneppen and lots of of his colleagues on this newest learn about reported at the discovery of a “absolute best explosion in house.” This contradicted earlier assumptions about kilonovae, indicating that the collision produced a wonderfully round explosion. As they reported on the time, this discovery may provide perception into basic physics and a brand new method of measuring the age of the Universe. In every other learn about launched in September (“At the Blackbody Spectrum of Kilonovae“), Sneppen demonstrated that regardless of their complexity, kilonovae will also be described through a unmarried temperature.
Galaxies lie reasonably nonetheless in house, however the house itself is increasing. This reasons the galaxies to transport clear of every different at an ever-increasing charge. Precisely how briskly is a bit of of a thriller, although. Credit score: ESO/L. Calçada. Galaxies lie reasonably nonetheless in house, however the house itself is increasing. This reasons the galaxies to transport clear of every different at an ever-increasing charge. Precisely how briskly is a bit of of a thriller, although. Credit score: ESO/L. CalçadaHistorical Context of the Universe’s ExpansionThe growth of the cosmos is one thing astronomers have recognized about for over a century, due to Edwin Hubble. Via watching galaxies and measuring their mild curves for redshift, he demonstrated that the extra far-off a galaxy was once, the quicker it receded from the Milky Method. This showed what many suspected about Einstein’s Idea of Basic Relativity, which predicted that the cosmos was once both in a state of growth or retraction. Via measuring the velocities at which different galaxies had been shifting clear of our personal, scientists have tried to measure the Hubble Consistent.This growth charge is measured in “velocity according to distance,” and trendy estimates position it at simply over 20 km/s () according to million light-years. That implies a galaxy situated 100 million light-years away recedes from us at 2,000 km/s (1,242 mps), whilst every other galaxy 200 million light-years away recedes at 4,000 km/s (2,485 mps). Then again, the use of supernovae to measure distances and velocities of galaxies yields 22.7 ± 0.4 km/s, whilst inspecting the CMB yields 20.7 ± 0.2 km/s. That would possibly not sound like a lot, however the distinction additionally produces considerably other estimates for the age of the Universe -12.8 vs. 13.8 billion years, respectively.Rising Answers and New ResearchWhile uncertainties had been to be anticipated again within the early twentieth century, enhancements in measuring ways have come far, and the discrepancy between measurements has reduced. Consequently, astronomers and cosmologists at the moment are at some extent the place they are able to state with self assurance that the 2 values can’t each be proper. This has led many scientists to wonder whether systematic biasing might be influencing one of the crucial effects or if particular physics within the early Universe (a los angeles early Darkish Power) may well be concerned.Of their paper, the staff proposed a unique approach for measuring distances, thereby serving to to settle the continued dispute. The analysis was once led through Albert Sneppen, a Ph.D. pupil in astrophysics on the Cosmic Break of day Heart on the Niels Bohr Institute. As he defined not too long ago:“When two ultra-compact neutron stars — which in themselves are the remnants of supernovae — orbit every different and in the end merge, they move off in a brand new explosion; a so-called kilonova. We not too long ago demonstrated how this explosion is remarkedly symmetric, and it seems that this symmetry now not handiest is lovely, but in addition extremely helpful.”In a prior learn about (“Round symmetry within the kilonova AT2017gfo/GW170817“), Sneppen and lots of of his colleagues on this newest learn about reported at the discovery of a “absolute best explosion in house.” This contradicted earlier assumptions about kilonovae, indicating that the collision produced a wonderfully round explosion. As they reported on the time, this discovery may provide perception into basic physics and a brand new method of measuring the age of the Universe. In every other learn about launched in September (“At the Blackbody Spectrum of Kilonovae“), Sneppen demonstrated that regardless of their complexity, kilonovae will also be described through a unmarried temperature. The left hemisphere presentations the increasing remnant of the supernova found out through Tycho Brahe in 1572, right here observeret in X-rays. Credit score: NASA/CXC/Rutgers/J.Warren & J.Hughes et al. At the proper is a map of the cosmic background radiation from one part of the sky, seen in microwaves. Credit score: NASA/WMAP Science TeamThis easy facet of kilonovae, mixed with their obvious symmetry, allowed Sneppen to infer precisely how a lot mild could be launched through an match. Evaluating this luminosity to how a lot mild reaches Earth, astronomers can measure the gap to the kilonova, thereby resulting in a unique and unbiased approach for calculating the gap to galaxies containing kilonovae. As Darach Watson, an affiliate professor on the Cosmic Break of day Heart and a co-author of the learn about, defined:“Supernovae, which till now had been used to measure the distances of galaxies, don’t all the time emit the same quantity of sunshine. Additionally, they first require us to calibrate the gap the use of every other form of stars, the so-called Cepheids, which in flip additionally will have to be calibrated. With kilonovae we will be able to circumvent those headaches that introduce uncertainties within the measurements.”To exhibit the brand new approach’s doable, the staff carried out it to a kilonova that was once seen through astronomers in 2017. The ensuing Hubble Consistent calculation is nearer to the price bought during the CMB approach, however whether or not this technique can unravel the Hubble Pressure is still observed. “We handiest have this one case learn about up to now, and wish many extra examples sooner than we will be able to identify a powerful consequence,” stated Sneppen. “However our approach a minimum of bypasses some recognized assets of uncertainty, and is an overly blank machine to review. It calls for no calibration, no correction issue.”For extra in this analysis, see Neutron Celebrity Collisions Light up the Growth of the Universe.Tailored from an editorial at first revealed on Universe As of late.
The left hemisphere presentations the increasing remnant of the supernova found out through Tycho Brahe in 1572, right here observeret in X-rays. Credit score: NASA/CXC/Rutgers/J.Warren & J.Hughes et al. At the proper is a map of the cosmic background radiation from one part of the sky, seen in microwaves. Credit score: NASA/WMAP Science TeamThis easy facet of kilonovae, mixed with their obvious symmetry, allowed Sneppen to infer precisely how a lot mild could be launched through an match. Evaluating this luminosity to how a lot mild reaches Earth, astronomers can measure the gap to the kilonova, thereby resulting in a unique and unbiased approach for calculating the gap to galaxies containing kilonovae. As Darach Watson, an affiliate professor on the Cosmic Break of day Heart and a co-author of the learn about, defined:“Supernovae, which till now had been used to measure the distances of galaxies, don’t all the time emit the same quantity of sunshine. Additionally, they first require us to calibrate the gap the use of every other form of stars, the so-called Cepheids, which in flip additionally will have to be calibrated. With kilonovae we will be able to circumvent those headaches that introduce uncertainties within the measurements.”To exhibit the brand new approach’s doable, the staff carried out it to a kilonova that was once seen through astronomers in 2017. The ensuing Hubble Consistent calculation is nearer to the price bought during the CMB approach, however whether or not this technique can unravel the Hubble Pressure is still observed. “We handiest have this one case learn about up to now, and wish many extra examples sooner than we will be able to identify a powerful consequence,” stated Sneppen. “However our approach a minimum of bypasses some recognized assets of uncertainty, and is an overly blank machine to review. It calls for no calibration, no correction issue.”For extra in this analysis, see Neutron Celebrity Collisions Light up the Growth of the Universe.Tailored from an editorial at first revealed on Universe As of late.
Stellar Answers: How Neutron Celebrity Collisions Might Remedy the “Disaster in Cosmology”