A volcanic eruption in 2910 B.C. could also be the explanation Neolithic other folks on a small island within the Baltic Sea buried masses of stones adorned with plant and solar imagery, archaeologists counsel in a brand new find out about.”We now have identified for a very long time that the solar used to be the focus for the early agricultural cultures we all know of in Northern Europe,” Rune Iversen, an archaeologist on the College of Copenhagen, stated in a remark. Those stones “have been most definitely sacrificed to verify solar and expansion.”In a find out about printed Thursday (Jan. 16) within the magazine Antiquity, Iversen and co-workers detailed the invention of 614 stone plaques and plaque fragments at the Danish island of Bornholm, situated south of Sweden within the Baltic Sea. The items have been discovered scattered right through a palisade ditch. In line with the pottery taste and the radiocarbon dates from charcoal discovered within reach, the researchers concluded that the adorned stones have been intentionally positioned there round 2900 B.C.Nearly all of the stone plaques have been comprised of black shale — a dismal, flaky sedimentary rock discovered at the island — whilst others have been comprised of quartz and flint. Many of the plaques have been additionally adorned with incised designs, together with solar and plant motifs.Even though a handful of those “solar stones” had been discovered on Bornholm in the past, the huge selection of them present in one position spurred the researchers to hunt a possible reason why for the original deposit.Comparable: Ritually bent Bronze Age sword unearthed in Danish bathroom is ‘very uncommon to find’Symbol 1 of four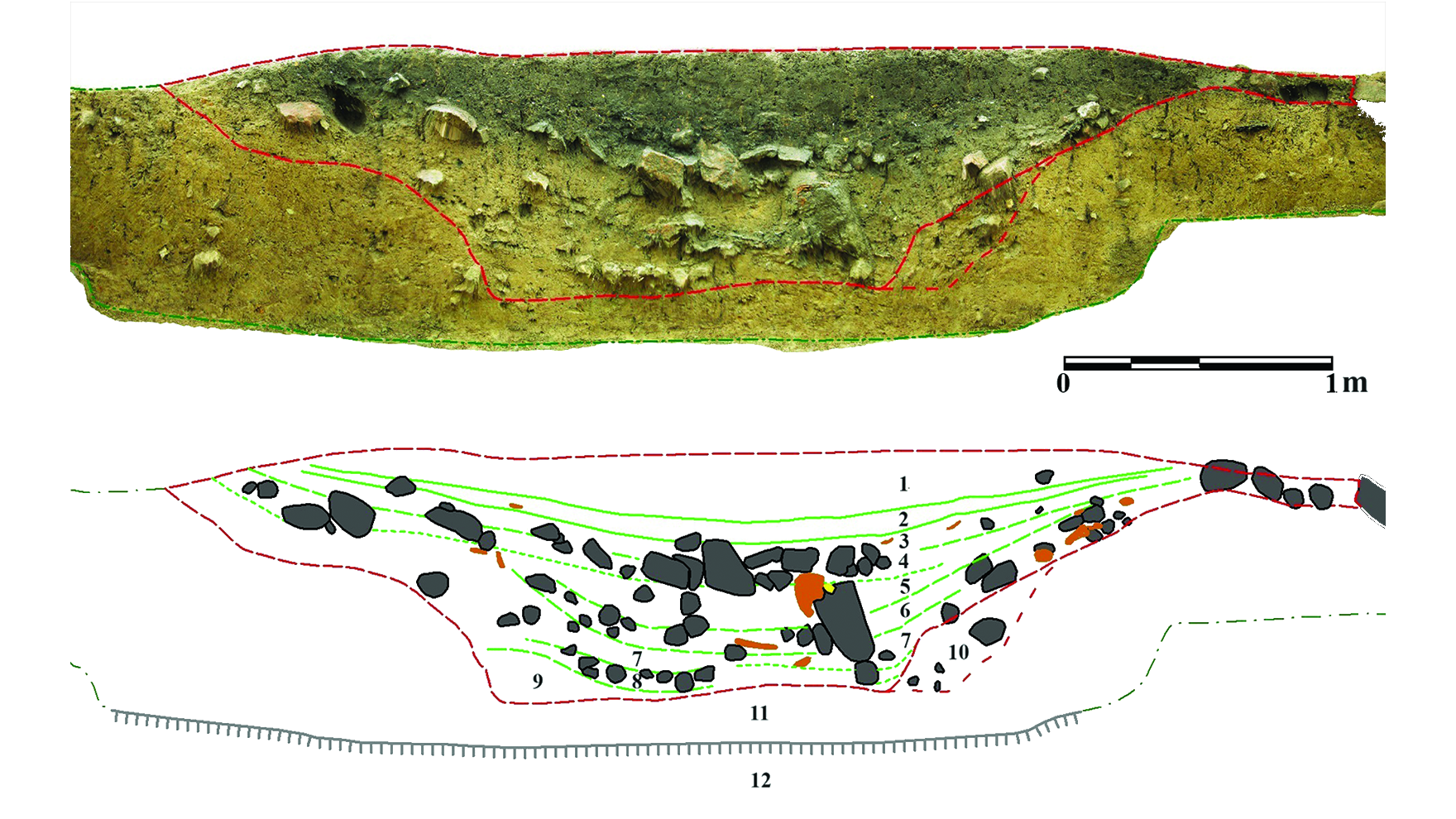 (Symbol credit score: Iversen et al. / Antiquity Publications Ltd.)An archaeological segment thru a ditch the place many of the engraved stones have been discovered within the Neolithic Bornholm website online.
(Symbol credit score: Iversen et al. / Antiquity Publications Ltd.)An archaeological segment thru a ditch the place many of the engraved stones have been discovered within the Neolithic Bornholm website online.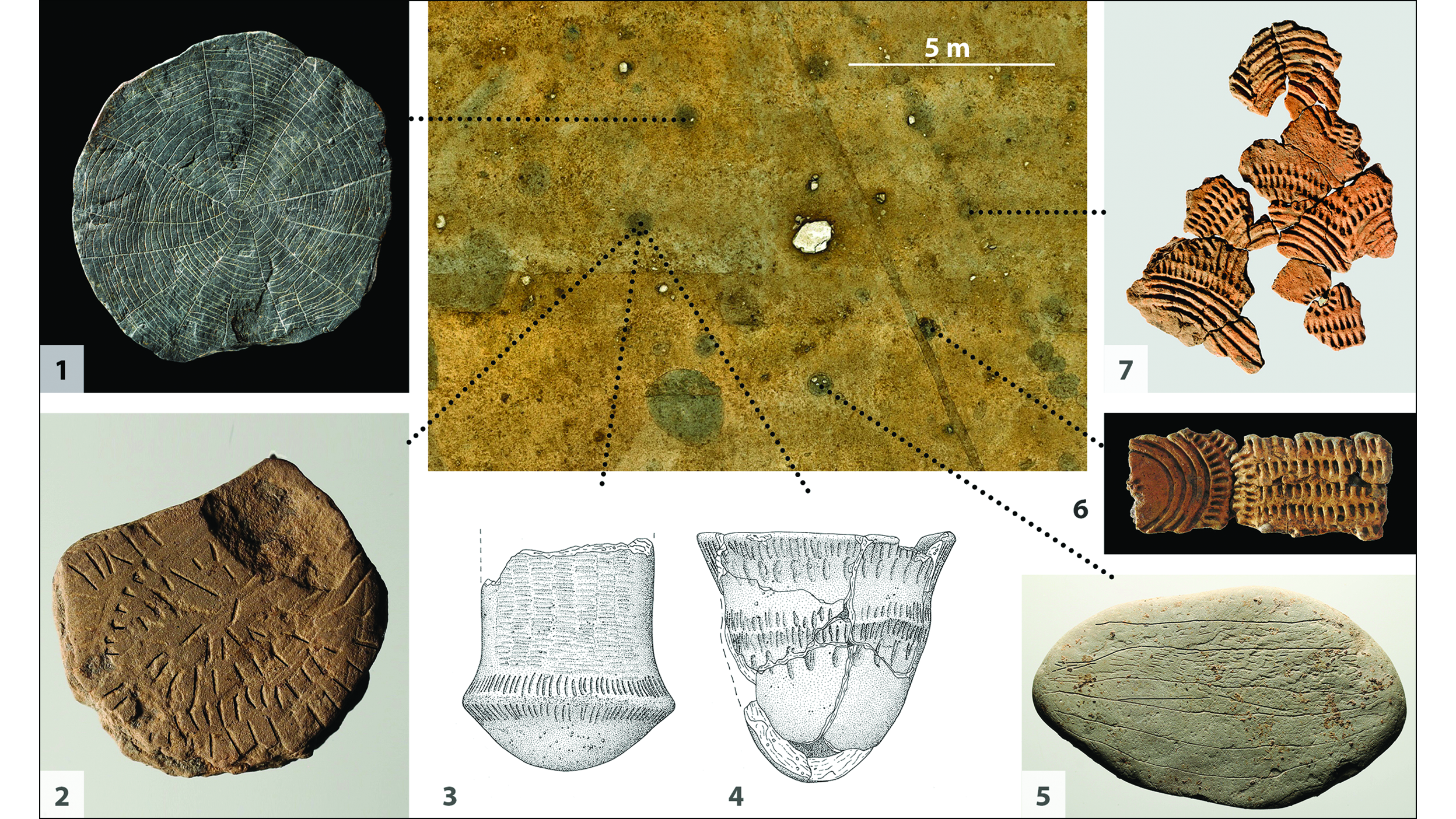 (Symbol credit score: Iversen et al. / Antiquity Publications Ltd.)Engraved stones, pottery and adorned daub from Neolithic Bornholm.
(Symbol credit score: Iversen et al. / Antiquity Publications Ltd.)Engraved stones, pottery and adorned daub from Neolithic Bornholm.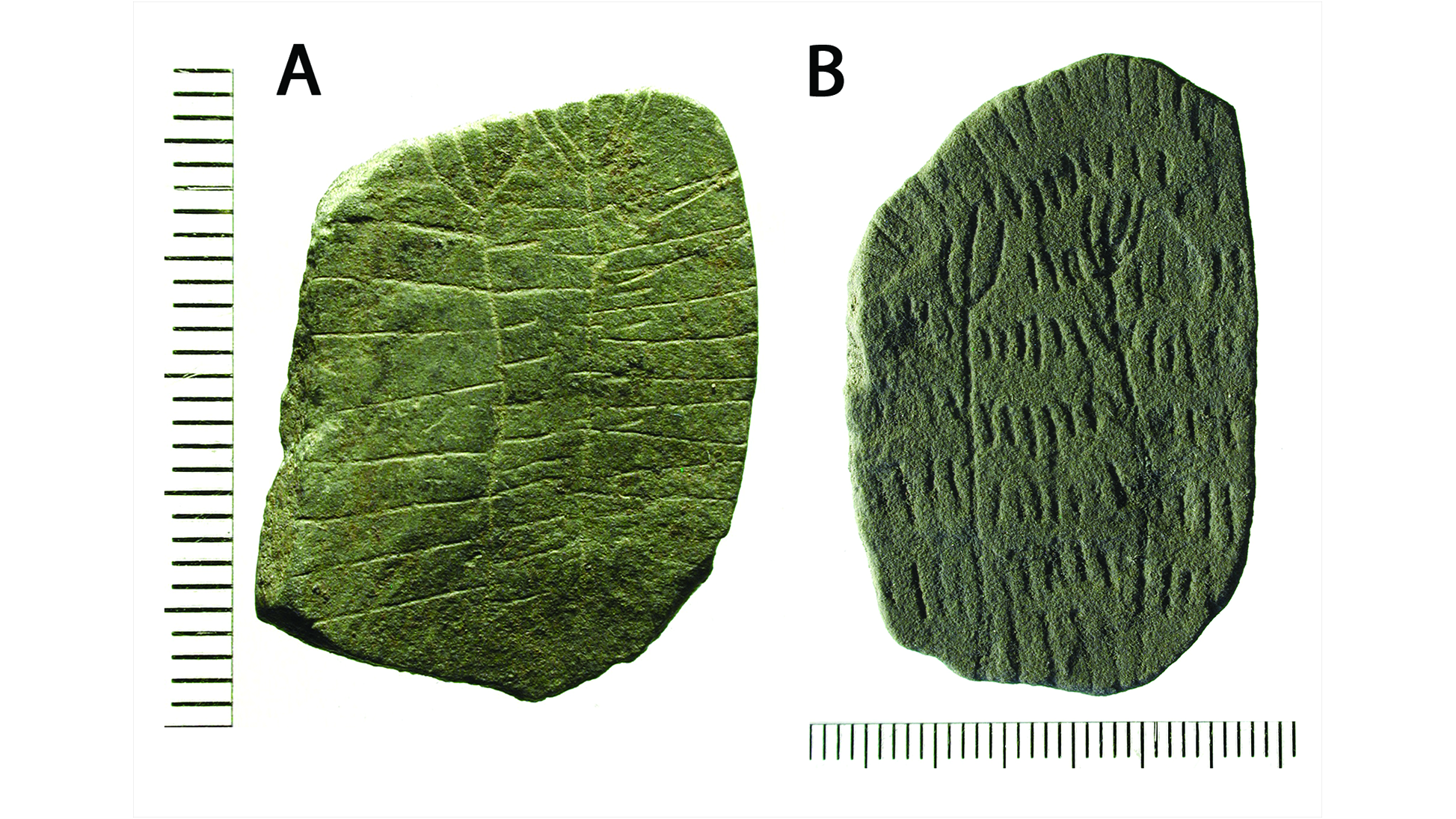 (Symbol credit score: Iversen et al. / Antiquity Publications Ltd.)Stone plaques with box and plant motifs discovered at a Neolithic website online on Bornholm.
(Symbol credit score: Iversen et al. / Antiquity Publications Ltd.)Stone plaques with box and plant motifs discovered at a Neolithic website online on Bornholm.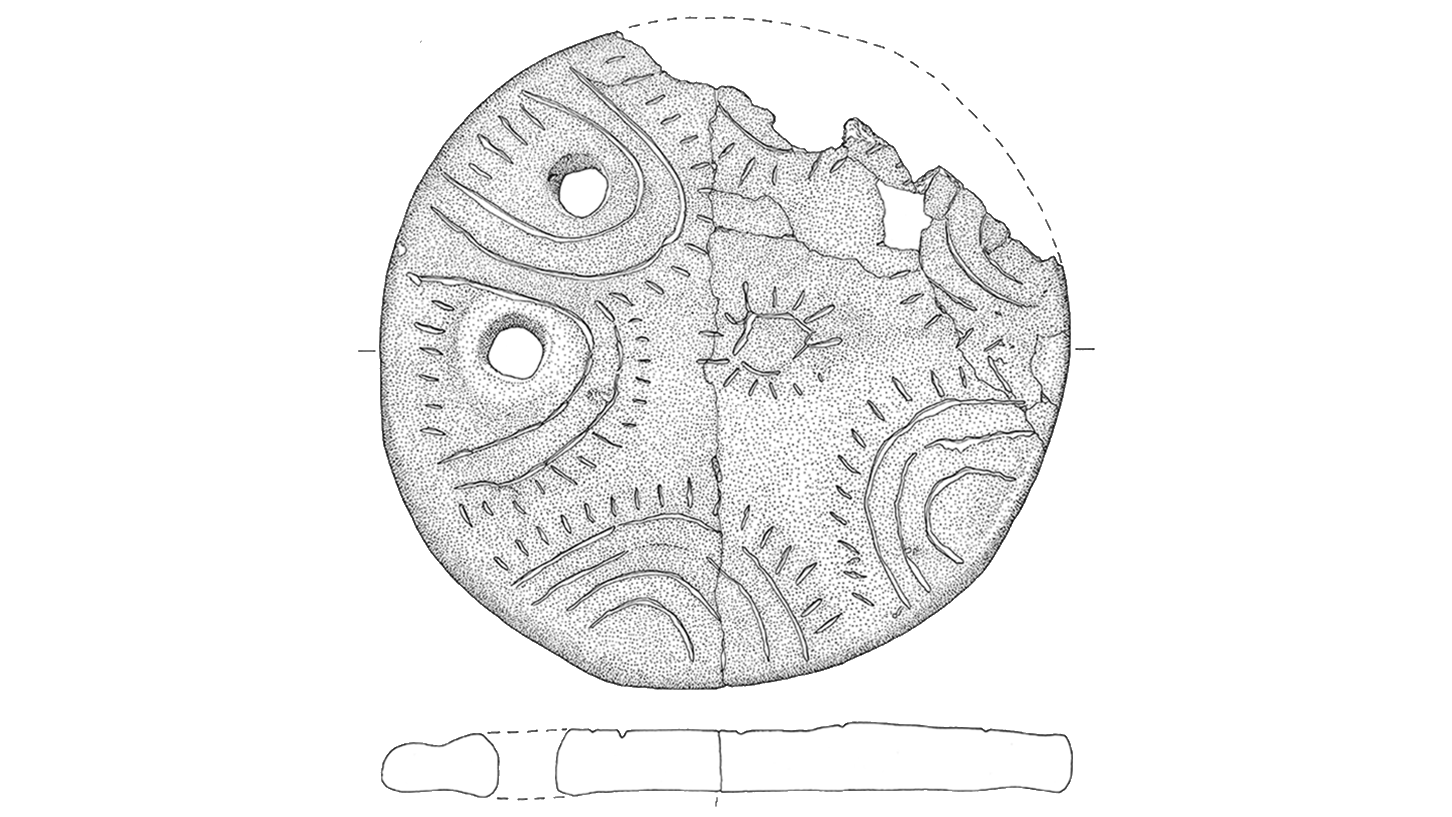 (Symbol credit score: Iversen et al. / Antiquity Publications Ltd.)Drawing of a clay disc with a solar motif from Neolithic Bornholm.Neolithic other folks seem to have buried the stones at a important juncture, because the researchers came upon that the realm used to be remodeled right into a extra forged, fortified website online simply after the stones have been deposited. Possibly a herbal crisis or climatic tournament that brought about vegetation to fail precipitated the stone “sacrifice,” the researchers prompt of their find out about.Get the arena’s most attractive discoveries delivered instantly on your inbox.In line with in depth proof of prehistoric local weather occasions, the researchers made a connection between the burial of the stones and a volcanic eruption in 2910 B.C. that just about no doubt negatively affected climate and harvests around the Northern Hemisphere.”Those depositions may have been made throughout a time of pressure with the aim of bringing again the solar and re-establishing agricultural manufacturing,” the researchers wrote of their find out about. “They might even have been made when the local weather disaster used to be over, as an act of birthday party for the go back of the solar.”After the stone deposit, a brand new more or less tradition started on Bornholm, the researchers defined within the find out about. Other people stopped development large tombs, started growing extra fortified settlements, and shaped new social networks with other folks in Scandinavia. However the significance of the solar would possibly not have lowered, as Neolithic societies throughout Europe relied at the solar for his or her harvest.”It’s reasonably merely an out of this world discovery, which demonstrates that depositions honouring the solar is an historic phenomenon, which we stumble upon once more in South Scandinavia throughout the local weather crisis brought about through a volcanic eruption within the 12 months 536 AD,” find out about co-author Lasse Vilien Sørensen, an archaeologist on the Nationwide Museum of Denmark, stated within the remark.
(Symbol credit score: Iversen et al. / Antiquity Publications Ltd.)Drawing of a clay disc with a solar motif from Neolithic Bornholm.Neolithic other folks seem to have buried the stones at a important juncture, because the researchers came upon that the realm used to be remodeled right into a extra forged, fortified website online simply after the stones have been deposited. Possibly a herbal crisis or climatic tournament that brought about vegetation to fail precipitated the stone “sacrifice,” the researchers prompt of their find out about.Get the arena’s most attractive discoveries delivered instantly on your inbox.In line with in depth proof of prehistoric local weather occasions, the researchers made a connection between the burial of the stones and a volcanic eruption in 2910 B.C. that just about no doubt negatively affected climate and harvests around the Northern Hemisphere.”Those depositions may have been made throughout a time of pressure with the aim of bringing again the solar and re-establishing agricultural manufacturing,” the researchers wrote of their find out about. “They might even have been made when the local weather disaster used to be over, as an act of birthday party for the go back of the solar.”After the stone deposit, a brand new more or less tradition started on Bornholm, the researchers defined within the find out about. Other people stopped development large tombs, started growing extra fortified settlements, and shaped new social networks with other folks in Scandinavia. However the significance of the solar would possibly not have lowered, as Neolithic societies throughout Europe relied at the solar for his or her harvest.”It’s reasonably merely an out of this world discovery, which demonstrates that depositions honouring the solar is an historic phenomenon, which we stumble upon once more in South Scandinavia throughout the local weather crisis brought about through a volcanic eruption within the 12 months 536 AD,” find out about co-author Lasse Vilien Sørensen, an archaeologist on the Nationwide Museum of Denmark, stated within the remark.
Stone Age other folks made solar stone ‘sacrifice’ to banish ‘darkened solar’ after a volcanic eruption, archaeologists say













