A rock that smashed violently into our planet some 66 million years in the past modified the process existence on Earth.The chain response of adjustments around the globe marked the top of days for the giants that roamed. Non-avian dinosaurs disappeared into the fossil file – however their death opened the way in which for different types of existence to upward push and thrive.
No longer lengthy after the have an effect on, the earliest ancestors of these days’s birds emerged. And now, scientists have discovered strains of the disaster in birds’ genomes – dramatic adjustments wrought through the mass extinction match that allowed birds to diversify, turning into the wildly a hit and sundry elegance of animals that fills our international these days.
“Through learning the DNA of residing birds, we will attempt to locate patterns of genetic sequences that modified simply after probably the most essential occasions in Earth’s historical past,” says ornithologist Jake Berv of the College of Michigan.
“The signature of the ones occasions turns out to have imprinted into the genomes of the survivors in some way that we will locate tens of hundreds of thousands of years later.”
The have an effect on of an enormous asteroid slamming into what’s now the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico used to be devastating. Now referred to as the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction, it burnt up an estimated 76 p.c of all animal existence on Earth.
That colossal loss left a vacuum that used to be stuffed slightly temporarily through the existence that survived, evolving and diversifying to ascertain a spot throughout the recreated international. Avian dinosaurs modified dramatically, turning into the ten,000 or so species of birds that we see round us these days.
Now, when an animal adjustments via evolution, there may also be shifts within the composition of DNA in its genome.
The elemental construction blocks of DNA – nucleotides – are composed of 4 other bases, categorized A, C, G, and T. The ratios of those nucleotide bases throughout the genome can shift, leading to adjustments to the improvement of the critter. frameborder=”0″ permit=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>Earlier research of the evolution of birds had assumed a hard and fast DNA composition that used to be no longer ready to modify. The use of newly advanced device, the researchers have been ready to chill out this assumption, working beneath a paradigm that did permit for nucleotide-base ratio shifts.
Berv and his colleagues used this device to investigate the diversities within the genome between the entire main teams of birds. This allowed them to spot shifts within the genome composition because the Cretaceous-Permian extinction.
They centered their efforts at the 5 million-year length right away following the asteroid have an effect on, and located that the extinction match produced a number of important shifts within the avian genome inside 3 to five million years.
Those adjustments in particular needed to do with the dimensions of the grownup chook, their metabolism, and the way they advanced as hatchlings.
As an example, birds ended up being considerably smaller than avian dinosaurs as adults. And there used to be a shift against smaller, weaker young children, born with out feathers and requiring a length of intense parental care. There are some birds these days that do not want this care, like ducklings and chickens, a trait referred to as precociality, and there is proof for it in avian dinosaurs.
“We discovered that grownup frame measurement and patterns of pre-hatching construction are two essential options of chook biology we will hyperlink to the genetic adjustments we are detecting,” Berv says.
“So far as we all know, adjustments in DNA composition have no longer been prior to now related to the end-Cretaceous mass extinction in the sort of transparent approach.”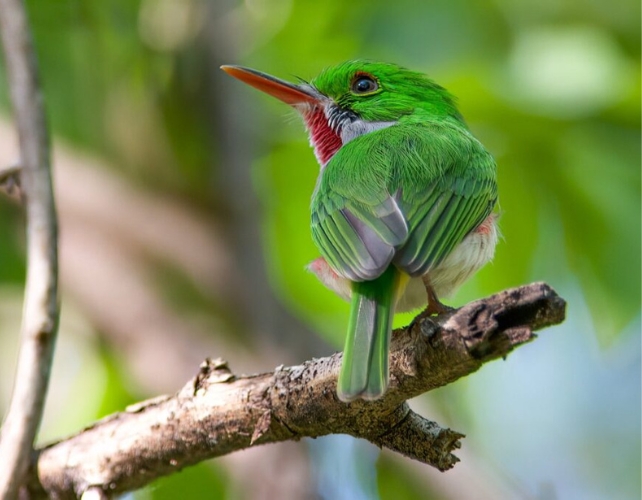 The Huge-billed tody, (Todus subulatus), is a member of Coraciimorphae, one chook team recognized as having shut ties to the end-Cretaceous mass extinction. (Daniel Box/College of Cambridge)In the past, compositional adjustments in DNA have no longer been intently tested within the context of a mass extinction. And but we all know that mass extinctions may have a dramatic impact at the international, converting complete ecosystems and their relationships, in addition to the relationships between the organisms inside them.
The Huge-billed tody, (Todus subulatus), is a member of Coraciimorphae, one chook team recognized as having shut ties to the end-Cretaceous mass extinction. (Daniel Box/College of Cambridge)In the past, compositional adjustments in DNA have no longer been intently tested within the context of a mass extinction. And but we all know that mass extinctions may have a dramatic impact at the international, converting complete ecosystems and their relationships, in addition to the relationships between the organisms inside them.
This learn about signifies that there are depths to the adjustments we’ve got but to plumb.
“Our learn about emphasizes that those extinction occasions can in reality affect organismal biology much more profoundly – through changing essential facets of the way genomes evolve,” says paleontologist Daniel Box of the College of Cambridge in the United Kingdom.
“This paintings furthers our figuring out of the dramatic organic affects of mass extinction occasions and highlights that the mass extinction that burnt up the large dinosaurs used to be probably the most biologically impactful occasions in all of the historical past of our planet.”The analysis has been revealed in Science Advances.
Strains of Dinosaur Disaster Present in Genes of These days’s Birds












:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1231124954-fac4ab8390b34b8690301febddb0a92b.jpg)
