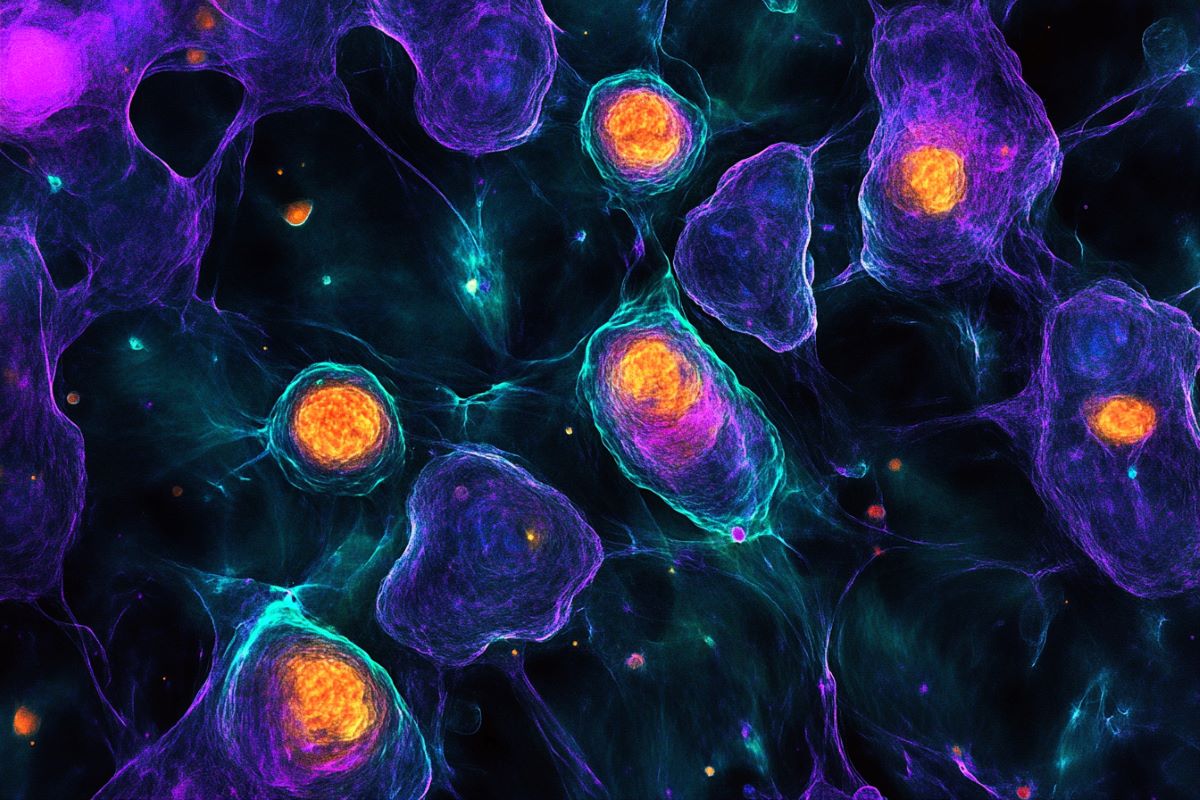
Abstract: A brand new learn about unearths a robust affiliation between youngster hashish use and a considerably larger possibility of growing psychotic problems. This possibility seems to be age-dependent, with teenagers being specifically at risk of the results of hashish on their growing brains. Whilst additional analysis is wanted, those findings carry considerations about early hashish use and spotlight the significance of prevention methods.Key Information:Teenagers the usage of hashish are 11 instances much more likely to increase psychotic problems.The affiliation is more potent in early life than younger maturity.Maximum teenagers identified with psychotic problems have a historical past of hashish use.Supply: Institute for Medical Evaluative SciencesA new learn about printed within the magazine Mental Medication estimates that teenagers the usage of hashish are at 11 instances upper possibility of growing a psychotic dysfunction in comparison to teenagers no longer the usage of hashish. This discovering means that the affiliation between hashish and psychotic problems could also be more potent than indicated by way of earlier analysis, which has relied in large part on older information when hashish was once much less potent than nowadays. For context, the typical THC efficiency of hashish in Canada has larger from more or less 1% in 1980 to twenty% in 2018.  Of the teenagers who had been hospitalized or visited an ED for a psychotic dysfunction, more or less 5 in 6 had up to now reported hashish use. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsResearchers from the College of Toronto, the Centre for Dependancy and Psychological Well being (CAMH), and ICES, connected contemporary population-based survey information from over 11,000 early life in Ontario, Canada, to well being provider use information together with hospitalizations, emergency division (ED) visits, and outpatient visits. The learn about is the primary to turn an age-dependent affiliation between self-reported hashish use and next psychotic dysfunction analysis, which provides to a rising frame of analysis at the psychological well being dangers related to hashish. “We discovered an excessively robust affiliation between hashish use and possibility of psychotic dysfunction in early life. Strangely, we didn’t to find proof of affiliation in younger maturity,” says lead creator André McDonald, who carried out the learn about at ICES as a part of his PhD on the College of Toronto. McDonald is now a postdoctoral fellow on the Peter Boris Centre for Addictions Analysis and the Michael G. DeGroote Centre for Medicinal Hashish Analysis at McMaster College.“Those findings are in line with the neurodevelopmental idea that teenagers are particularly at risk of the results of hashish.” Of the teenagers who had been hospitalized or visited an ED for a psychotic dysfunction, more or less 5 in 6 had up to now reported hashish use. McDonald issues out that, “the majority of teenagers who use hashish is not going to increase a psychotic dysfunction, however in line with those information, maximum teenagers who’re identified with a psychotic dysfunction most probably have a historical past of hashish use.” The researchers may just no longer totally rule out opposite causation, in that teenagers with psychotic signs could have been self-medicating with hashish ahead of receiving a scientific analysis. In addition they may just no longer account for doubtlessly necessary elements reminiscent of genetics and historical past of trauma.Those boundaries make it unimaginable to mention definitively that youngster hashish use reasons psychotic problems. The authors additionally observe that their estimates are handiest approximate, suggesting that additional research with higher samples are required. Nonetheless, the findings upload to worries about early hashish use, specifically within the wake of legalization. “As commercialized hashish merchandise have grow to be extra extensively to be had, and feature a better THC content material, the advance of prevention methods concentrated on teenagers is extra necessary than ever,” says senior creator Susan Bondy, an associate scientist at ICES and affiliate professor on the College of Toronto’s Dalla Lana Faculty of Public Well being. McDonald provides, “Canadian early life are a few of the heaviest customers of hashish on this planet. If we observe the precautionary concept, the hot button is that extra must be accomplished to stop early hashish use.” About this psychosis and CUD analysis newsAuthor: Misty Pratt
Of the teenagers who had been hospitalized or visited an ED for a psychotic dysfunction, more or less 5 in 6 had up to now reported hashish use. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsResearchers from the College of Toronto, the Centre for Dependancy and Psychological Well being (CAMH), and ICES, connected contemporary population-based survey information from over 11,000 early life in Ontario, Canada, to well being provider use information together with hospitalizations, emergency division (ED) visits, and outpatient visits. The learn about is the primary to turn an age-dependent affiliation between self-reported hashish use and next psychotic dysfunction analysis, which provides to a rising frame of analysis at the psychological well being dangers related to hashish. “We discovered an excessively robust affiliation between hashish use and possibility of psychotic dysfunction in early life. Strangely, we didn’t to find proof of affiliation in younger maturity,” says lead creator André McDonald, who carried out the learn about at ICES as a part of his PhD on the College of Toronto. McDonald is now a postdoctoral fellow on the Peter Boris Centre for Addictions Analysis and the Michael G. DeGroote Centre for Medicinal Hashish Analysis at McMaster College.“Those findings are in line with the neurodevelopmental idea that teenagers are particularly at risk of the results of hashish.” Of the teenagers who had been hospitalized or visited an ED for a psychotic dysfunction, more or less 5 in 6 had up to now reported hashish use. McDonald issues out that, “the majority of teenagers who use hashish is not going to increase a psychotic dysfunction, however in line with those information, maximum teenagers who’re identified with a psychotic dysfunction most probably have a historical past of hashish use.” The researchers may just no longer totally rule out opposite causation, in that teenagers with psychotic signs could have been self-medicating with hashish ahead of receiving a scientific analysis. In addition they may just no longer account for doubtlessly necessary elements reminiscent of genetics and historical past of trauma.Those boundaries make it unimaginable to mention definitively that youngster hashish use reasons psychotic problems. The authors additionally observe that their estimates are handiest approximate, suggesting that additional research with higher samples are required. Nonetheless, the findings upload to worries about early hashish use, specifically within the wake of legalization. “As commercialized hashish merchandise have grow to be extra extensively to be had, and feature a better THC content material, the advance of prevention methods concentrated on teenagers is extra necessary than ever,” says senior creator Susan Bondy, an associate scientist at ICES and affiliate professor on the College of Toronto’s Dalla Lana Faculty of Public Well being. McDonald provides, “Canadian early life are a few of the heaviest customers of hashish on this planet. If we observe the precautionary concept, the hot button is that extra must be accomplished to stop early hashish use.” About this psychosis and CUD analysis newsAuthor: Misty Pratt
Supply: Institute for Medical Evaluative Sciences
Touch: Misty Pratt – Institute for Medical Evaluative Sciences
Symbol: The picture is credited to Neuroscience NewsOriginal Analysis: Open get entry to.
“Age-dependent affiliation of hashish use with possibility of psychotic dysfunction” by way of André McDonald et al. Mental MedicineAbstractAge-dependent affiliation of hashish use with possibility of psychotic disorderBackgroundEpidemiologic analysis means that early life hashish use is related to psychotic problems. Then again, present proof is founded closely on Twentieth-century information when hashish was once considerably much less potent than nowadays.MethodsWe connected population-based survey information from 2009 to 2012 with information of well being services and products coated underneath common healthcare in Ontario, Canada, as much as 2018. The cohort integrated respondents elderly 12–24 years at baseline without a prior psychotic dysfunction (N = 11 363). The main result was once days to first hospitalization, ED consult with, or outpatient consult with associated with a psychotic dysfunction in line with validated diagnostic codes. Because of non-proportional hazards, we estimated age-specific danger ratios all over early life (12–19 years) and younger maturity (20–33 years). Sensitivity analyses explored selection fashion stipulations together with limiting the result to hospitalizations and ED visits to extend specificity.ResultsCompared to no hashish use, hashish use was once considerably related to psychotic problems all over early life (aHR = 11.2; 95% CI 4.6–27.3), however no longer all over younger maturity (aHR = 1.3; 95% CI 0.6–2.6). Once we limited the result to hospitalizations and ED visits handiest, the power of affiliation larger markedly all over early life (aHR = 26.7; 95% CI 7.7–92.8) however didn’t exchange meaningfully all over younger maturity (aHR = 1.8; 95% CI 0.6–5.4).ConclusionsThis learn about supplies new proof of a robust however age-dependent affiliation between hashish use and possibility of psychotic dysfunction, in line with the neurodevelopmental idea that early life is a inclined time to make use of hashish. The power of affiliation all over early life was once significantly more than in earlier research, perhaps reflecting the new upward thrust in hashish efficiency.
Sturdy Hyperlink Between Youngster Hashish Use and Psychosis Possibility – Neuroscience Information








![Google releases new Pixel 4a replace, some loose battery replacements introduced [U] Google releases new Pixel 4a replace, some loose battery replacements introduced [U]](https://9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2021/02/Google-Pixel-4a-1.jpg?quality=82&strip=all&w=1600)


