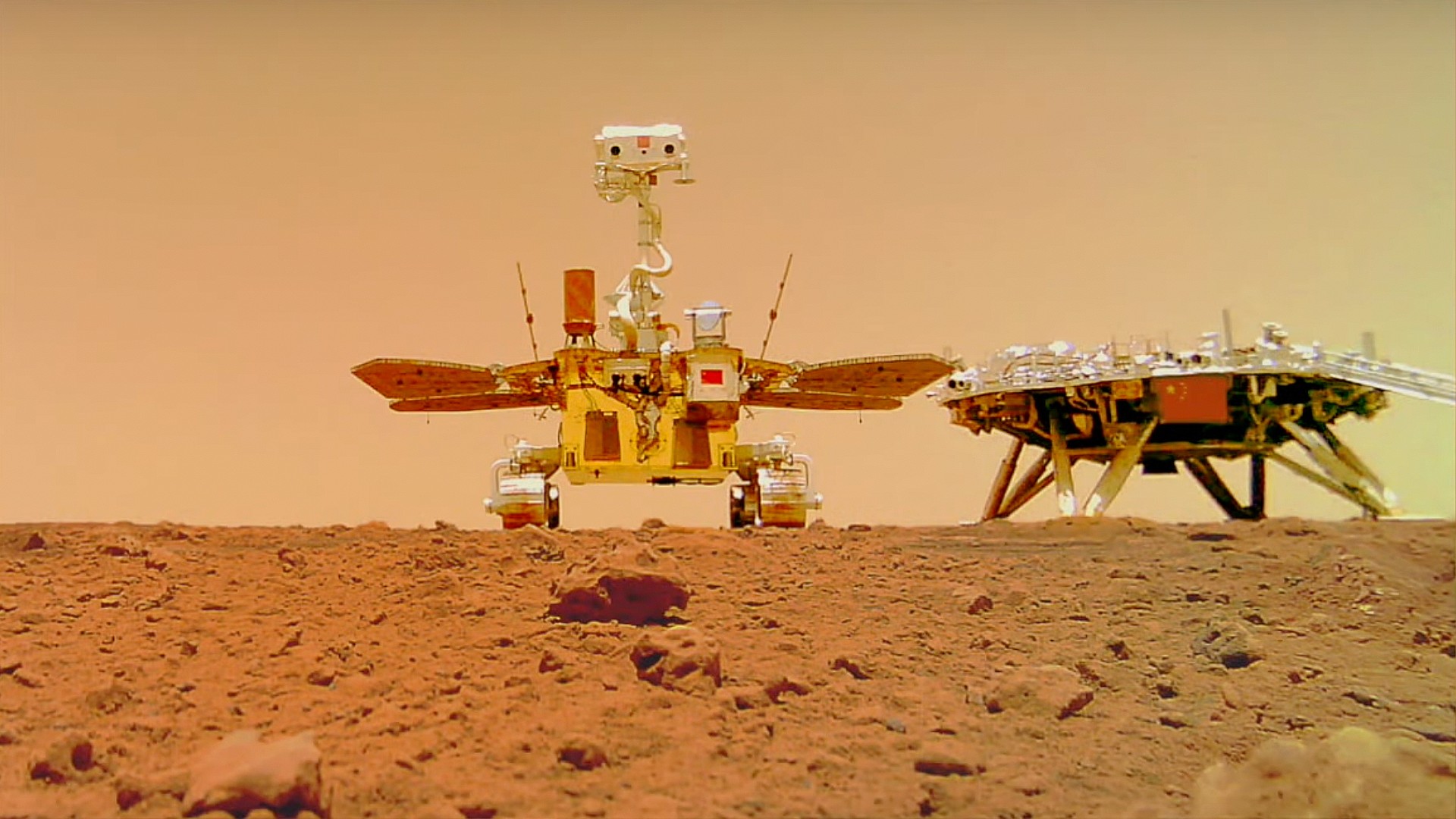
A find out about suggests Mars had a chilly, subarctic local weather very similar to Newfoundland, according to soil analyses from Gale Crater. This discovering supplies new insights into the preservation of amorphous fabrics and Mars’ doable to toughen lifestyles. (Artist’s thought.) Credit score: SciTechDaily.comA new find out about reveals vital clues lurking within the Purple Planet’s soil.Fresh analysis evaluating soils from Earth and Mars suggests Mars’ ancient local weather was once chilly and subarctic, very similar to Newfoundland. The find out about enthusiastic about amorphous fabrics in Gale Crater’s soil, probably preserved via near-freezing stipulations, providing new insights into Mars’ environmental stipulations and its doable for lifestyles.Exploring Mars’ Previous Local weather Thru Earth’s SoilsThe query of whether or not Mars ever supported lifestyles has captivated the creativeness of scientists and the general public for many years. Central to the invention is gaining perception into the previous local weather of Earth’s neighbor: was once the planet heat and rainy, with seas and rivers just like the ones discovered on our personal planet? Or was once it frigid and icy, and due to this fact probably much less susceptible to supporting lifestyles as we realize it?A brand new find out about reveals proof to toughen the latter via figuring out similarities between soils discovered on Mars and the ones of Canada’s Newfoundland, a chilly subarctic local weather.
A find out about suggests Mars had a chilly, subarctic local weather very similar to Newfoundland, according to soil analyses from Gale Crater. This discovering supplies new insights into the preservation of amorphous fabrics and Mars’ doable to toughen lifestyles. (Artist’s thought.) Credit score: SciTechDaily.comA new find out about reveals vital clues lurking within the Purple Planet’s soil.Fresh analysis evaluating soils from Earth and Mars suggests Mars’ ancient local weather was once chilly and subarctic, very similar to Newfoundland. The find out about enthusiastic about amorphous fabrics in Gale Crater’s soil, probably preserved via near-freezing stipulations, providing new insights into Mars’ environmental stipulations and its doable for lifestyles.Exploring Mars’ Previous Local weather Thru Earth’s SoilsThe query of whether or not Mars ever supported lifestyles has captivated the creativeness of scientists and the general public for many years. Central to the invention is gaining perception into the previous local weather of Earth’s neighbor: was once the planet heat and rainy, with seas and rivers just like the ones discovered on our personal planet? Or was once it frigid and icy, and due to this fact probably much less susceptible to supporting lifestyles as we realize it?A brand new find out about reveals proof to toughen the latter via figuring out similarities between soils discovered on Mars and the ones of Canada’s Newfoundland, a chilly subarctic local weather.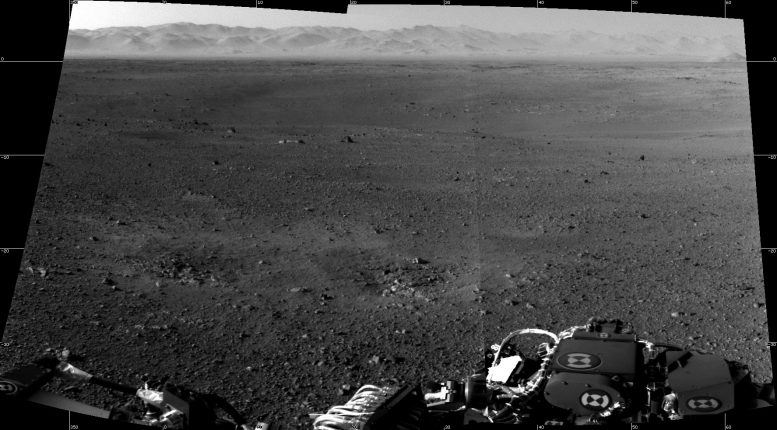 The rim and flooring of Gale Crater as observed from NASA’s Interest Rover. Credit score: NASA/JPL-CaltechInsights From Gale Crater’s Soil AnalysisThe find out about, revealed within the magazine Communications Earth and Surroundings on July seventh, regarded for soils on Earth with similar fabrics to Mars’ Gale Crater. Scientists steadily use soil to depict environmental historical past, because the minerals provide can inform the tale of panorama evolution via time. Figuring out extra about how those fabrics shaped may assist resolution long-standing questions on ancient stipulations at the purple planet. The soils and rocks of Gale Crater supply a report of Mars’ local weather between 3 and four billion years in the past, all through a time of somewhat ample water on this planet – and the similar period of time that noticed lifestyles first seem on Earth.“Gale Crater is a paleo lakebed—there was once clearly water provide. However what had been the environmental stipulations when the water was once there?” says Anthony Feldman, a soil scientist and geomorphologist now at DRI. “We’re by no means going to seek out an immediate analog to the Martian floor, as a result of stipulations are so other between Mars and Earth. However we will be able to have a look at traits beneath terrestrial stipulations and use the ones to take a look at to extrapolate to Martian questions.”
The rim and flooring of Gale Crater as observed from NASA’s Interest Rover. Credit score: NASA/JPL-CaltechInsights From Gale Crater’s Soil AnalysisThe find out about, revealed within the magazine Communications Earth and Surroundings on July seventh, regarded for soils on Earth with similar fabrics to Mars’ Gale Crater. Scientists steadily use soil to depict environmental historical past, because the minerals provide can inform the tale of panorama evolution via time. Figuring out extra about how those fabrics shaped may assist resolution long-standing questions on ancient stipulations at the purple planet. The soils and rocks of Gale Crater supply a report of Mars’ local weather between 3 and four billion years in the past, all through a time of somewhat ample water on this planet – and the similar period of time that noticed lifestyles first seem on Earth.“Gale Crater is a paleo lakebed—there was once clearly water provide. However what had been the environmental stipulations when the water was once there?” says Anthony Feldman, a soil scientist and geomorphologist now at DRI. “We’re by no means going to seek out an immediate analog to the Martian floor, as a result of stipulations are so other between Mars and Earth. However we will be able to have a look at traits beneath terrestrial stipulations and use the ones to take a look at to extrapolate to Martian questions.”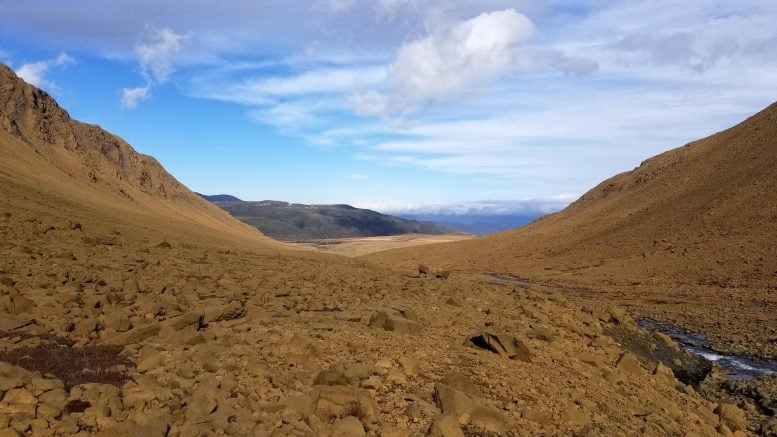 The find out about website within the Tablelands of Newfoundland. Credit score: Anthony Feldman/DRIChallenges in Inspecting Martian MaterialsNASA’s Interest Rover has been investigating Gale Crater since 2011, and has discovered a plethora of soil fabrics referred to as “X-ray amorphous subject material.” Those parts of the soil lack the everyday repeating atomic construction that defines minerals, and due to this fact can’t be simply characterised the use of conventional ways like X-ray diffraction. When X-rays are shot at crystalline fabrics like a diamond, as an example, the X-rays scatter at function angles according to the mineral’s interior construction. Alternatively, X-ray amorphous subject material does now not produce those function “fingerprints.” This X-ray diffraction approach was once utilized by the Interest Rover to display that X-ray amorphous subject material comprised between 15 and 73% of the soil and rock samples examined in Gale Crater.“You’ll be able to call to mind X-ray amorphous fabrics like Jello,” Feldman says. “It’s this soup of various components and chemical substances that simply slide previous every different.”The Interest Rover additionally carried out chemical analyses at the soil and rock samples, discovering that the amorphous subject material was once wealthy in iron and silica however poor in aluminum. Past the restricted chemical data, scientists don’t but perceive what the amorphous subject material is, or what its presence implies about Mars’ ancient surroundings. Uncovering extra details about how those enigmatic fabrics shape and persist on Earth may assist resolution continual questions concerning the purple planet.Box Research Mimicking Martian ConditionsFeldman and his colleagues visited 3 places searching for equivalent X-ray amorphous subject material: the Tablelands of Gros Morne Nationwide Park in Newfoundland, Northern California’s Klamath Mountains, and western Nevada. Those 3 websites had serpentine soils that the researchers anticipated to be chemically very similar to the X-ray amorphous subject material at Gale Crater: wealthy in iron and silicon however missing in aluminum. The 3 places additionally supplied a spread of rainfall, snow fall, and temperature that might assist supply perception into the kind of environmental stipulations that produce amorphous subject material and inspire its preservation.At every website, the analysis group tested the soils the use of X-ray diffraction research and transmission electron microscopy, which allowed them to peer the soil fabrics at a extra detailed stage. The subarctic stipulations of Newfoundland produced fabrics chemically very similar to the ones present in Gale Crater that still lacked in crystalline construction. The soils produced in hotter climates like California and Nevada didn’t.“This displays that you want the water there to be able to shape those fabrics,” Feldman says. “However it must be chilly, near-freezing imply annual temperature stipulations to be able to keep the amorphous subject material within the soils.”Amorphous subject material is steadily regarded as to be somewhat risky, that means that at an atomic stage, the atoms haven’t but arranged into their ultimate, extra crystalline paperwork. “There’s one thing occurring within the kinetics — or the velocity of response — this is slowing it down in order that those fabrics may also be preserved over geologic time scales,” Feldman says. “What we’re suggesting is that very chilly, as regards to freezing stipulations, is one explicit kinetic proscribing issue that permits for those fabrics to shape and be preserved.”“This find out about improves our figuring out of the local weather of Mars,” Feldman says. “The consequences recommend that the abundance of this subject material in Gale Crater is in step with subarctic stipulations, very similar to what we’d see in, as an example, Iceland.”Reference: “Fe-rich X-ray amorphous subject material data previous local weather and endurance of water on Mars” via Anthony D. Feldman, Elisabeth M. Hausrath, Elizabeth B. Rampe, Valerie Tu, Tanya S. Peretyazhko, Christopher DeFelice and Thomas Sharp, 7 July 2024, Communications Earth & Surroundings.
The find out about website within the Tablelands of Newfoundland. Credit score: Anthony Feldman/DRIChallenges in Inspecting Martian MaterialsNASA’s Interest Rover has been investigating Gale Crater since 2011, and has discovered a plethora of soil fabrics referred to as “X-ray amorphous subject material.” Those parts of the soil lack the everyday repeating atomic construction that defines minerals, and due to this fact can’t be simply characterised the use of conventional ways like X-ray diffraction. When X-rays are shot at crystalline fabrics like a diamond, as an example, the X-rays scatter at function angles according to the mineral’s interior construction. Alternatively, X-ray amorphous subject material does now not produce those function “fingerprints.” This X-ray diffraction approach was once utilized by the Interest Rover to display that X-ray amorphous subject material comprised between 15 and 73% of the soil and rock samples examined in Gale Crater.“You’ll be able to call to mind X-ray amorphous fabrics like Jello,” Feldman says. “It’s this soup of various components and chemical substances that simply slide previous every different.”The Interest Rover additionally carried out chemical analyses at the soil and rock samples, discovering that the amorphous subject material was once wealthy in iron and silica however poor in aluminum. Past the restricted chemical data, scientists don’t but perceive what the amorphous subject material is, or what its presence implies about Mars’ ancient surroundings. Uncovering extra details about how those enigmatic fabrics shape and persist on Earth may assist resolution continual questions concerning the purple planet.Box Research Mimicking Martian ConditionsFeldman and his colleagues visited 3 places searching for equivalent X-ray amorphous subject material: the Tablelands of Gros Morne Nationwide Park in Newfoundland, Northern California’s Klamath Mountains, and western Nevada. Those 3 websites had serpentine soils that the researchers anticipated to be chemically very similar to the X-ray amorphous subject material at Gale Crater: wealthy in iron and silicon however missing in aluminum. The 3 places additionally supplied a spread of rainfall, snow fall, and temperature that might assist supply perception into the kind of environmental stipulations that produce amorphous subject material and inspire its preservation.At every website, the analysis group tested the soils the use of X-ray diffraction research and transmission electron microscopy, which allowed them to peer the soil fabrics at a extra detailed stage. The subarctic stipulations of Newfoundland produced fabrics chemically very similar to the ones present in Gale Crater that still lacked in crystalline construction. The soils produced in hotter climates like California and Nevada didn’t.“This displays that you want the water there to be able to shape those fabrics,” Feldman says. “However it must be chilly, near-freezing imply annual temperature stipulations to be able to keep the amorphous subject material within the soils.”Amorphous subject material is steadily regarded as to be somewhat risky, that means that at an atomic stage, the atoms haven’t but arranged into their ultimate, extra crystalline paperwork. “There’s one thing occurring within the kinetics — or the velocity of response — this is slowing it down in order that those fabrics may also be preserved over geologic time scales,” Feldman says. “What we’re suggesting is that very chilly, as regards to freezing stipulations, is one explicit kinetic proscribing issue that permits for those fabrics to shape and be preserved.”“This find out about improves our figuring out of the local weather of Mars,” Feldman says. “The consequences recommend that the abundance of this subject material in Gale Crater is in step with subarctic stipulations, very similar to what we’d see in, as an example, Iceland.”Reference: “Fe-rich X-ray amorphous subject material data previous local weather and endurance of water on Mars” via Anthony D. Feldman, Elisabeth M. Hausrath, Elizabeth B. Rampe, Valerie Tu, Tanya S. Peretyazhko, Christopher DeFelice and Thomas Sharp, 7 July 2024, Communications Earth & Surroundings.
DOI: 10.1038/s43247-024-01495-4
Subarctic Secrets and techniques: Mars’ Chilly and Icy Previous Published in New Analysis