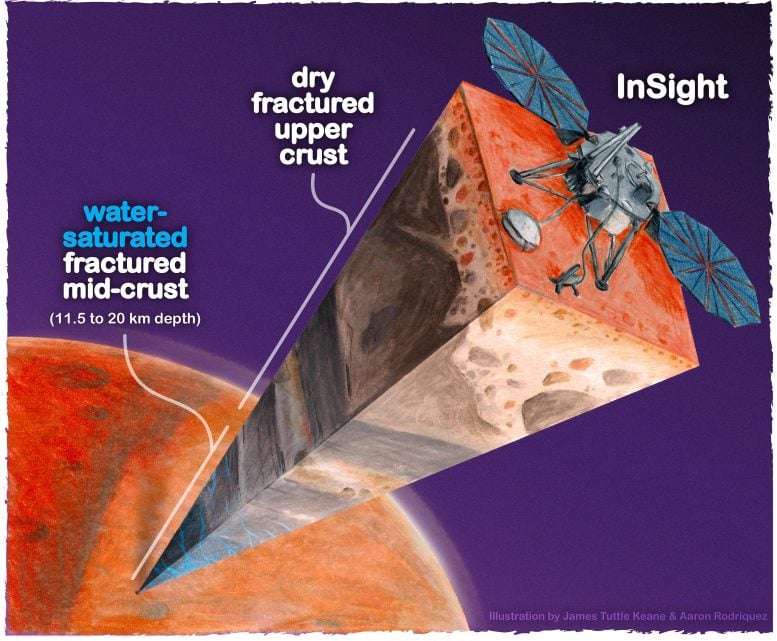
 A cutout of the Martian internal underneath NASA’s Perception lander. The highest 5 kilometers of the crust seem to be dry, however a brand new learn about supplies proof for a zone of fractured rock 11.5-20 km underneath the skin that is filled with liquid water — greater than the quantity proposed to have crammed hypothesized historical Martian oceans. Credit score: James Tuttle Keane and Aaron Rodriquez, courtesy of Scripps Institute of Oceanography
A cutout of the Martian internal underneath NASA’s Perception lander. The highest 5 kilometers of the crust seem to be dry, however a brand new learn about supplies proof for a zone of fractured rock 11.5-20 km underneath the skin that is filled with liquid water — greater than the quantity proposed to have crammed hypothesized historical Martian oceans. Credit score: James Tuttle Keane and Aaron Rodriquez, courtesy of Scripps Institute of Oceanography
Geophysicists the use of seismic knowledge from NASA’s Perception lander have came upon a vital underground water reservoir on Mars, probably sufficient to have as soon as crammed historical oceans.
This reservoir, trapped throughout the mid-crust of Mars, means that the pink planet’s water didn’t totally get away into area however was once absorbed into its crust, changing earlier theories about Martian aridity and most likely offering a habitat that would reinforce existence.
The usage of seismic task to probe the internal of Mars, geophysicists have discovered proof for a big underground reservoir of liquid water — sufficient to fill oceans on the earth’s floor.
The knowledge from NASA’s Perception lander allowed the scientists to estimate that the volume of groundwater may quilt all of the planet to a intensity of between 1 and a couple of kilometers, or a couple of mile.
Whilst that’s excellent information for the ones monitoring the destiny of water on the earth after its oceans disappeared greater than 3 billion years in the past, the reservoir received’t be of a lot use to any individual seeking to faucet into it to offer a long term Mars colony. It’s positioned in tiny cracks and pores in rock in the course of the Martian crust, between 11.5 and 20 kilometers underneath the skin. Even on Earth, drilling a hollow a kilometer deep is a problem.
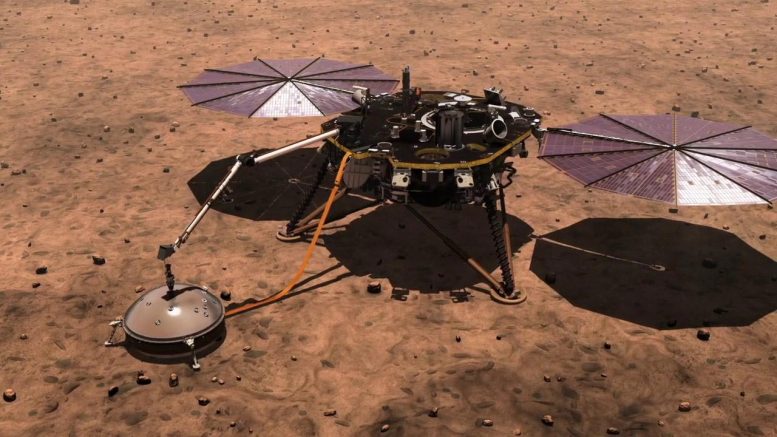 This representation displays NASA’s Mars InSight lander at the Martian floor. Credit score: NASA
This representation displays NASA’s Mars InSight lander at the Martian floor. Credit score: NASA
Implications for Martian Colonization and Astrobiology
The discovering does pinpoint some other promising position to search for existence on Mars, alternatively, if the reservoir may also be accessed. For the instant, it is helping resolution questions in regards to the geological historical past of the planet.
“Working out the Martian water cycle is important for working out the evolution of the local weather, floor and internal,” stated Vashan Wright, a former UC Berkeley postdoctoral fellow who’s now an assistant professor at UC San Diego’s Scripps Establishment of Oceanography. “An invaluable start line is to spot the place water is and what sort of is there.”
Wright, along colleagues Michael Manga of UC Berkeley and Matthias Morzfeld of Scripps Oceanography, detailed their research in a paper that can seem this week within the magazine Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
Tactics and Theories: Unveiling Martian Geology
The scientists hired a mathematical type of rock physics, similar to fashions used on Earth to map underground aquifers and oil fields, to conclude that the seismic knowledge from Perception are best possible defined through a deep layer of fractured igneous rock saturated with liquid water. Igneous rocks are cooled sizzling magma, just like the granite of the Sierra Nevada.
“Setting up that there’s a giant reservoir of liquid water supplies some window into what the local weather was once like or might be like,” stated Manga, a UC Berkeley professor of earth and planetary science. “And water is vital for existence as we are aware of it. I don’t see why [the underground reservoir] isn’t a liveable surroundings. It’s surely true on Earth — deep, deep mines host existence, the ground of the sea hosts existence. We haven’t discovered any proof for existence on Mars, however no less than we now have known a spot that are meant to, in idea, be capable to maintain existence.”
Manga was once Wright’s postdoctoral adviser. Morzfeld was once a former postdoctoral fellow in UC Berkeley’s arithmetic division and is now an affiliate professor of geophysics at Scripps Oceanography.
Proof of Historic Water and Mars’ Geological Evolution
Manga famous that a whole lot of proof — river channels, deltas, and lake deposits, in addition to water-altered rock — helps the speculation that water as soon as flowed on the earth’s floor. However that rainy length ended greater than 3 billion years in the past, after Mars misplaced its surroundings. Planetary scientists on Earth have despatched many probes and landers to the planet to determine what came about to that water — the water frozen in Mars’ polar ice caps can’t account for all of it — in addition to when it came about, and whether or not existence exists or used to exist on the earth.
The brand new findings are a sign that a lot of the water didn’t get away into area however filtered down into the crust.
The Perception lander was once despatched through NASA to Mars in 2018 to research the crust, mantle, core and surroundings, and it recorded precious details about Mars’ internal sooner than the venture resulted in 2022.
“The venture a great deal exceeded my expectancies,” Manga stated. “From taking a look at all of the seismic knowledge that Perception accrued, they’ve found out the thickness of the crust, the intensity of the core, the composition of the core, even just a little bit in regards to the temperature throughout the mantle.”
Perception detected Mars quakes as much as a couple of magnitude of five, meteor affects and rumblings from volcanic spaces, all of which produced seismic waves that allowed geophysicists to probe the internal.
An previous paper reported that above a intensity of about 5 kilometers, the higher crust didn’t include water ice, as Manga and others suspected. That can imply that there’s little out there frozen groundwater out of doors the polar areas.
The brand new paper analyzed the deeper crust and concluded that the “to be had knowledge are best possible defined through a water-saturated mid-crust” underneath Perception’s location. Assuming the crust is the same all the way through the planet, the staff argued, there will have to be extra water on this mid-crust zone than the “volumes proposed to have crammed hypothesized historical Martian oceans.”
For extra in this discovery, see Did We Simply In finding Liquid Water on Mars? NASA InSight Lander’s Unexpected Knowledge.
Reference: “Liquid Water within the Martian Mid-Crust” 12 August 2024, Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
DOI:10.1073/pnas.2409983121
The Canadian Institute for Complicated Analysis, the Nationwide Science Basis, and the U.S. Administrative center of Naval Analysis supported the paintings.
Subsurface Oceans on Mars? NASA’s InSight Uncovers Huge Reservoir of Liquid Water












:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-2205311988-96b284e1e3ab441dae6b7723cbbb2e86.jpg)

