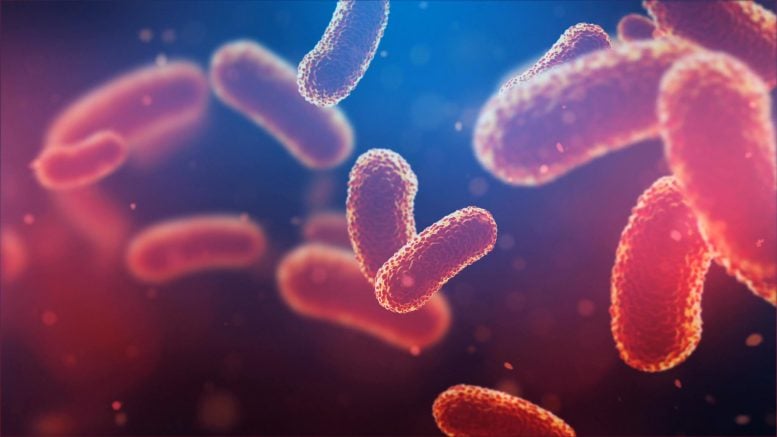
symbol: Evaluate and close-up of cresomycin sure to the bacterial ribosome of Thermus thermophilus.
view extra
Credit score: Yury Polikanov/College of Illinois Chicago
A brand new antibiotic created by means of Harvard researchers overcomes antimicrobial resistance mechanisms that experience rendered many trendy medicine useless and are riding an international public well being disaster.
A staff led by means of Andrew Myers, Amory Houghton Professor of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, stories in Science that their artificial compound, cresomycin, kills many traces of drug-resistant micro organism, together with Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
“Whilst we don’t but know whether or not cresomycin and medicine adore it are protected and efficient in people, our effects display considerably advanced inhibitory process towards a protracted listing of pathogenic bacterial traces that kill greater than one million folks yearly, when compared with clinically licensed antibiotics,” Myers mentioned.
The brand new molecule demonstrates an advanced skill to bind to bacterial ribosomes, that are biomolecular machines that keep watch over protein synthesis. Disrupting ribosomal serve as is a trademark of many present antibiotics, however some micro organism have developed shielding mechanisms that save you legacy medicine from operating.
Cresomycin is one in all a number of promising compounds that Myers’ staff has advanced, with the purpose of serving to win the struggle towards superbugs. They’ll proceed advancing those compounds thru preclinical profiling research, supported by means of a $1.2 million grant from Fighting Antibiotic-Resistant Micro organism Biopharmaceutical Accelerator (CARB-X). A Boston College-based international nonprofit partnership, CARB-X is devoted to supporting early-stage antibacterial analysis and building.
The Harvard staff’s new molecule attracts inspiration from the chemical constructions of lincosamides, a category of antibiotics that incorporates the regularly prescribed clindamycin. Like many antibiotics, clindamycin is made by the use of semisynthesis, by which complicated merchandise remoted from nature are changed at once for drug programs. The brand new Harvard compound, alternatively, is absolutely artificial and lines chemical adjustments that can not be accessed thru present approach.
“The bacterial ribosome is nature’s most well-liked goal for antibacterial brokers, and those brokers are the supply of inspiration for our program,” mentioned co-author Ben Tresco, a Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate College of Arts and Sciences pupil. “Via leveraging the facility of natural synthesis, we’re restricted virtually handiest by means of our creativeness when designing new antibiotics.”
Micro organism can expand resistance to ribosome-targeting antibiotic medicine by means of expressing genes that produce enzymes known as ribosomal RNA methyltransferases. Those enzymes field out the drug elements which might be designed to latch onto and disrupt the ribosome, in the end blockading the drug’s process.
To get round this drawback, Myers and staff engineered their compound right into a rigidified form that intently resembles its binding goal, giving it a more potent grip at the ribosome. The researchers name their drug “pre-organized” for ribosomal binding as it doesn’t wish to deplete as a lot power conforming to its goal as present medicine should do.
The researchers arrived at cresomycin the usage of what they name component-based synthesis, one way pioneered by means of the Myers lab that comes to constructing huge molecular elements of equivalent complexity and bringing them in combination at past due levels – like pre-building sections of a sophisticated LEGO set sooner than assembling them. This modular, totally artificial gadget permits them to make and check now not only one, however masses of goal molecules, a great deal rushing up the drug discovery procedure.
The stakes are transparent. “Antibiotics shape the root on which trendy medication is constructed,” mentioned co-author and graduate pupil Kelvin Wu. “With out antibiotics, many state of the art scientific procedures like surgical procedures, most cancers remedies, and organ transplants, can’t be executed.”
Myers’ component-based synthesis analysis won early toughen from Harvard’s Blavatnik Biomedical Accelerator, a part of the Place of business of Era Construction, which awarded investment to Myers’ lab in 2013 to permit checking out of drug compounds. The Place of business of Era Construction secure the Myers Analysis Team’s inventions and, along side the Blavatnik Biomedical Accelerator, will toughen the analysis staff in the course of the CARB-X settlement. The newly awarded CARB-X investment permits the researchers to proceed profiling and optimizing drug leads.
“Investment and different toughen from teams just like the Blavatnik Biomedical Accelerator and CARB-X are very important for the invention and building of latest antibiotics,” mentioned Curtis Keith, the Harvard accelerator’s leader medical officer. “Those inventions from the Myers Analysis Team have the prospective to yield new medicine that may sooner or later meet an international well being want.”
The broadcast paintings was once supported by means of the Nationwide Institutes of Well being and the Nationwide Science Basis.
Manner of Analysis
Experimental find out about
Topic of Analysis
Cells
Article Identify
An antibiotic preorganized for ribosomal binding overcomes antimicrobial resistance
Article E-newsletter Date
16-Feb-2024
Disclaimer: AAAS and EurekAlert! aren’t liable for the accuracy of stories releases posted to EurekAlert! by means of contributing establishments or for using any data during the EurekAlert gadget.