The use of the James Webb House Telescope (JWST), astronomers have came upon far-off, overly huge supermassive black holes within the early universe. The black holes appear means too huge in comparison to the mass of the celebs within the galaxies that host them.Within the fashionable universe, for galaxies with regards to our personal Milky Approach, supermassive black holes have a tendency to have plenty equivalent to round 0.01% of the stellar mass in their host galaxy. Thus, for each 10,000 sun plenty attributed to stars in a galaxy, there’s round one sun mass of a central supermassive black gap.Within the new learn about, researchers statistically calculated that supermassive black holes in one of the most early galaxies noticed by way of JWST have plenty of 10% in their galaxies’ stellar mass. That suggests for each 10,000 sun plenty in stars in every of those galaxies, there are 1,000 sun plenty of a supermassive black gap.”The mass of those supermassive black holes may be very top in comparison to the stellar mass of the galaxies that host them,” group chief Jorryt Matthee, a scientist on the Institute of Science and Era Austria (ISTA), instructed House.com. “At face price, our measurements indicate that the supermassive black gap mass is 10% of the stellar mass within the galaxies we studied.””In probably the most excessive situation, this may indicate that the black holes are 1,000 instances too heavy.”The invention may just carry astronomers a step nearer to fixing the thriller of ways supermassive black holes with plenty hundreds of thousands and even billions of instances that of the solar grew so briefly within the early universe.”Relatively than pronouncing this discovery is ‘troubling,’ I’d say it’s ‘promising,’ as the massive discrepancy means that we’re about to be informed one thing new,” Matthee added.Breaking house information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!Comparable: Black holes: The whole thing you wish to have to knowThe tale starts with little purple dotsSince JWST began beaming information again to Earth in the summertime of 2022, the $10 billion telescope has helped astronomers refine their figuring out of the early cosmos.This has integrated the invention of supermassive black holes with hundreds of thousands of sun plenty when the universe used to be not up to a thousand million years previous. That is problematic, as a result of scientists have estimated that the merger chains of step by step higher black holes and the voracious feeding on surrounding topic that leads black holes to supermassive sizes are concept to take greater than one billion years.Some other vital side of this investigation of the early universe by way of JWST has been the invention of “little purple dot galaxies,” a few of which existed simply 1.5 billion years after the Large Bang, when the universe used to be round 11% of its present age. The purple colour of those strangely vivid early galaxies is believed to come back from fuel and dirt in a flattened cloud of topic round supermassive black holes referred to as an accretion disk. As the large black holes feed in this topic, they emit large quantities of electromagnetic power, from a compact area referred to as an lively galactic nucleus (AGN).”In 2023 and 2024, we and different teams came upon a in the past hidden inhabitants of AGNs within the early universe within the first information units from the JWST,” Matthee stated. “The sunshine that we see from those gadgets, specifically the redder mild, originates from accretion disks round supermassive black holes.”Those gadgets turned into referred to as ‘little purple dots’ as a result of that is how they seem in JWST pictures.”These days, this early galactic inhabitants may be very thrilling, albeit poorly understood. As an example, within the early universe, little purple dots appear to be way more a large number of in comparison to in the past recognized populations of AGNs noticed from Earth as supermassive black hole-powered quasars.Comparable: What’s the Large Bang concept?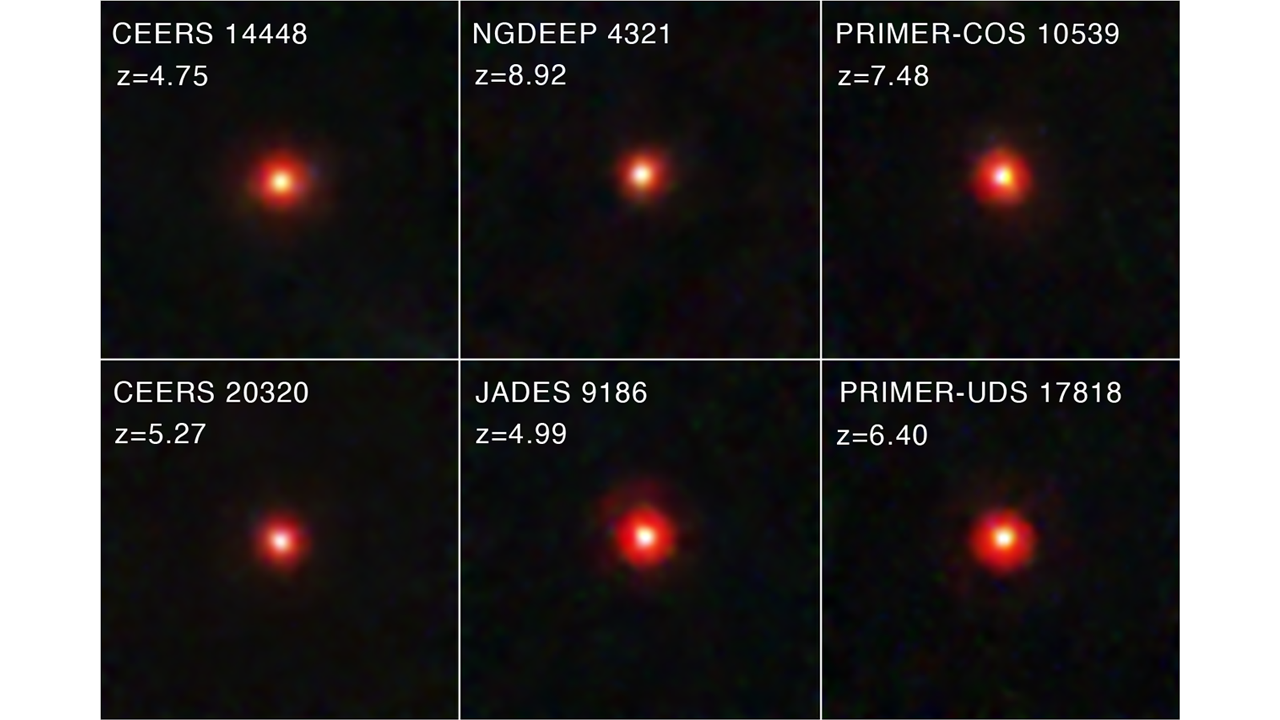 A picture presentations six of the “little purple dot” galaxies noticed by way of JWST within the early universe. (Symbol credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Dale Kocevski (Colby School))”The little purple dots additionally display some very exceptional homes, such because the faintness in X-ray emission, which is beautiful odd for AGNs, and the infrared emission could also be odd,” Matthee stated. “Because of those headaches, we’re suffering to interpret the sunshine that we follow from the little purple dots, which means that that it is extremely tough to check their homes.”That is the place Matthee and associates’ new paintings is available in. The use of a knowledge set from the JWST 12 months 2 (cycle 2) “All of the Little Issues (ALT)” survey, the group constructed an exact 3-d map of all galaxies in a selected area within the sky.”Inside of that area, now we have known seven little purple dots, very similar to earlier research, however now now we have been in a position to match the places of those little purple dots within the 3-d galaxy map,” Matthee stated.The group’s little purple dots are situated up to now away that their mild has been touring to us for round 12.5 billion years. They’re clustered within the so-called cosmic internet of galaxies, with their positioning being of paramount significance.Little purple dot galaxies are morsels on a cosmic webThe place of galaxies within the cosmic internet relies on the kind of galaxy. Extra developed, huge galaxies are present in over-dense areas such because the nodes the place the strands of the internet attach. More youthful and lower-mass galaxies have a tendency to be present in much less dense areas of the cosmic internet, alongside the duration of person strands clear of nodes.”We now have discovered that the little purple dots are in environments that resemble low-mass, younger galaxies,” Matthee stated. “This means that the little purple dot galaxies also are low-mass younger galaxies.”The reality those little purple dot galaxies include AGNs has equipped proof that early black holes are actively rising in galaxies with stellar plenty as little as round 100 million instances that of the solar.
A picture presentations six of the “little purple dot” galaxies noticed by way of JWST within the early universe. (Symbol credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Dale Kocevski (Colby School))”The little purple dots additionally display some very exceptional homes, such because the faintness in X-ray emission, which is beautiful odd for AGNs, and the infrared emission could also be odd,” Matthee stated. “Because of those headaches, we’re suffering to interpret the sunshine that we follow from the little purple dots, which means that that it is extremely tough to check their homes.”That is the place Matthee and associates’ new paintings is available in. The use of a knowledge set from the JWST 12 months 2 (cycle 2) “All of the Little Issues (ALT)” survey, the group constructed an exact 3-d map of all galaxies in a selected area within the sky.”Inside of that area, now we have known seven little purple dots, very similar to earlier research, however now now we have been in a position to match the places of those little purple dots within the 3-d galaxy map,” Matthee stated.The group’s little purple dots are situated up to now away that their mild has been touring to us for round 12.5 billion years. They’re clustered within the so-called cosmic internet of galaxies, with their positioning being of paramount significance.Little purple dot galaxies are morsels on a cosmic webThe place of galaxies within the cosmic internet relies on the kind of galaxy. Extra developed, huge galaxies are present in over-dense areas such because the nodes the place the strands of the internet attach. More youthful and lower-mass galaxies have a tendency to be present in much less dense areas of the cosmic internet, alongside the duration of person strands clear of nodes.”We now have discovered that the little purple dots are in environments that resemble low-mass, younger galaxies,” Matthee stated. “This means that the little purple dot galaxies also are low-mass younger galaxies.”The reality those little purple dot galaxies include AGNs has equipped proof that early black holes are actively rising in galaxies with stellar plenty as little as round 100 million instances that of the solar.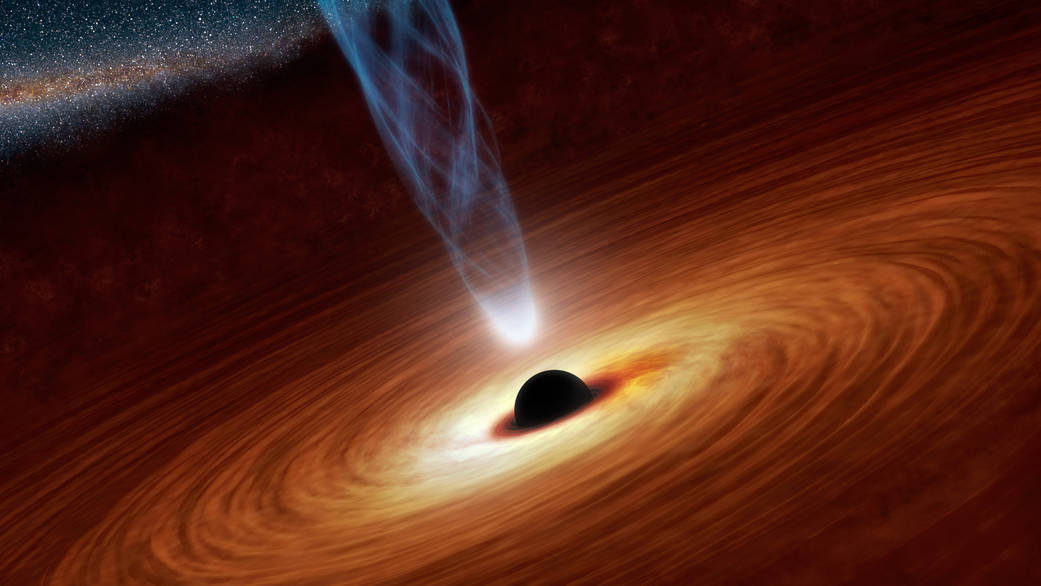 An Representation presentations a supermassive black gap on the center of a area referred to as an AGN (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech)One conceivable cause of that is that supermassive black holes within the early universe controlled to shape and develop a lot more successfully than the ones within the present-day universe. This might be because of the extra speedy intake of surrounding fuel and topic.”Personally, the possibly rationalization is the extraordinarily speedy expansion of supermassive black holes nurtured by way of the top fuel densities of galaxies within the early universe,” Matthee stated. “Those densities concurrently result in top stellar densities, which promotes supermassive black gap formation thru facilitating runaway collisions of remnant black holes.”If that is true, then the formation of stars and supermassive black holes in galaxies are intrinsically related, with those processes relying on every different. Despite the fact that supermassive black holes develop sooner in early galaxies, megastar formation catches up, resulting in the 1:100 mass ratio noticed nowadays.This does not but verify speedy expansion theories over different supermassive black gap expansion explanations, similar to the concept that those cosmic titans develop from huge black gap seeds created by way of the direct cave in of large clouds of fuel and dirt.Then again, Matthee added that it is going to now be laborious for theorists to get round low host galaxy plenty when competing theories are regarded as.Matthee defined that the following steps for each the group and for the broader astronomical group are to do away with the chance that the stellar mass/black gap mass ratio they discovered isn’t the results of misguided measurements or a spread bias that can have liked probably the most lively and thus huge supermassive black holes.This will likely most likely contain the invention of extra little purple dot galaxies, a hunt that the JWST will certainly be on the center of.”The JWST has been necessary for 2 primary causes: With out it, we shouldn’t have came upon the ones populations of faint AGNs,” Matthee concluded. “Additionally, with out the JWST, we shouldn’t have been in a position to make the correct 3-d map of galaxy distributions that we used to deduce the homes of the galaxies web hosting the faint AGNs.”It’s an excessively thrilling analysis box this present day!”The group’s analysis has no longer but been revealed in a peer-reviewed magazine. It’s been posted at the paper repository website online arXiv.
An Representation presentations a supermassive black gap on the center of a area referred to as an AGN (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech)One conceivable cause of that is that supermassive black holes within the early universe controlled to shape and develop a lot more successfully than the ones within the present-day universe. This might be because of the extra speedy intake of surrounding fuel and topic.”Personally, the possibly rationalization is the extraordinarily speedy expansion of supermassive black holes nurtured by way of the top fuel densities of galaxies within the early universe,” Matthee stated. “Those densities concurrently result in top stellar densities, which promotes supermassive black gap formation thru facilitating runaway collisions of remnant black holes.”If that is true, then the formation of stars and supermassive black holes in galaxies are intrinsically related, with those processes relying on every different. Despite the fact that supermassive black holes develop sooner in early galaxies, megastar formation catches up, resulting in the 1:100 mass ratio noticed nowadays.This does not but verify speedy expansion theories over different supermassive black gap expansion explanations, similar to the concept that those cosmic titans develop from huge black gap seeds created by way of the direct cave in of large clouds of fuel and dirt.Then again, Matthee added that it is going to now be laborious for theorists to get round low host galaxy plenty when competing theories are regarded as.Matthee defined that the following steps for each the group and for the broader astronomical group are to do away with the chance that the stellar mass/black gap mass ratio they discovered isn’t the results of misguided measurements or a spread bias that can have liked probably the most lively and thus huge supermassive black holes.This will likely most likely contain the invention of extra little purple dot galaxies, a hunt that the JWST will certainly be on the center of.”The JWST has been necessary for 2 primary causes: With out it, we shouldn’t have came upon the ones populations of faint AGNs,” Matthee concluded. “Additionally, with out the JWST, we shouldn’t have been in a position to make the correct 3-d map of galaxy distributions that we used to deduce the homes of the galaxies web hosting the faint AGNs.”It’s an excessively thrilling analysis box this present day!”The group’s analysis has no longer but been revealed in a peer-reviewed magazine. It’s been posted at the paper repository website online arXiv.
Supermassive black holes in ‘little purple dot’ galaxies are 1,000 instances higher than they will have to be, and astronomers have no idea why




/wion/media/media_files/2025/03/30/B1xgUHuPTxMh8iNXB0N4.png)