The lives of galaxies can also be prolonged if their supermassive black holes that supply them with “hearts and lungs” to beef up their “respiring” and save you them from rising too huge.That’s the advice of latest analysis indicating the universe would have elderly a lot sooner and would these days be stuffed with “zombie” galaxies containing lifeless or demise stars had been it no longer for the supermassive black holes idea to sit down on the hearts of all huge galaxies. The astrophysicists in the back of the findings evaluate jets of fuel and radiation that supermassive black holes blow from their poles to the airlines that feed our lungs. The College of Kent workforce thinks pulses from each and every black gap “center” reason surprise fronts that oscillate from side to side throughout each jets. That is very similar to how part of our frame referred to as the thoracic diaphragm strikes up and down within our chest cavities to inflate and deflate our lungs.In galaxies, this respiratory-like motion transmits the power of the supermassive black hole-blown jets to the encircling medium, like how on a chilly iciness morning you’ll breath out heat air into the chillier air. Stars shape when interstellar fuel clouds cool and are allowed to condense. That implies this “respiring out” can sluggish big name formation, curbing galaxies’ enlargement.Similar: James Webb House Telescope sees an historical black gap dance with colliding galaxiesThe crew arrived at this conclusion after examining simulations designed to copy the affect supersonic supermassive black hole-blown jets may play in inhibiting galaxy enlargement. The simulations confirmed that the supermassive black gap center can pulse, developing excessive strain within the jets — virtually like a human affected by hypertension, or “high blood pressure.”When this befell, the crew noticed the jets starting to act like bellows, launching soundwaves that rippled via surrounding subject material of galactic fuel and mud.Breaking house information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!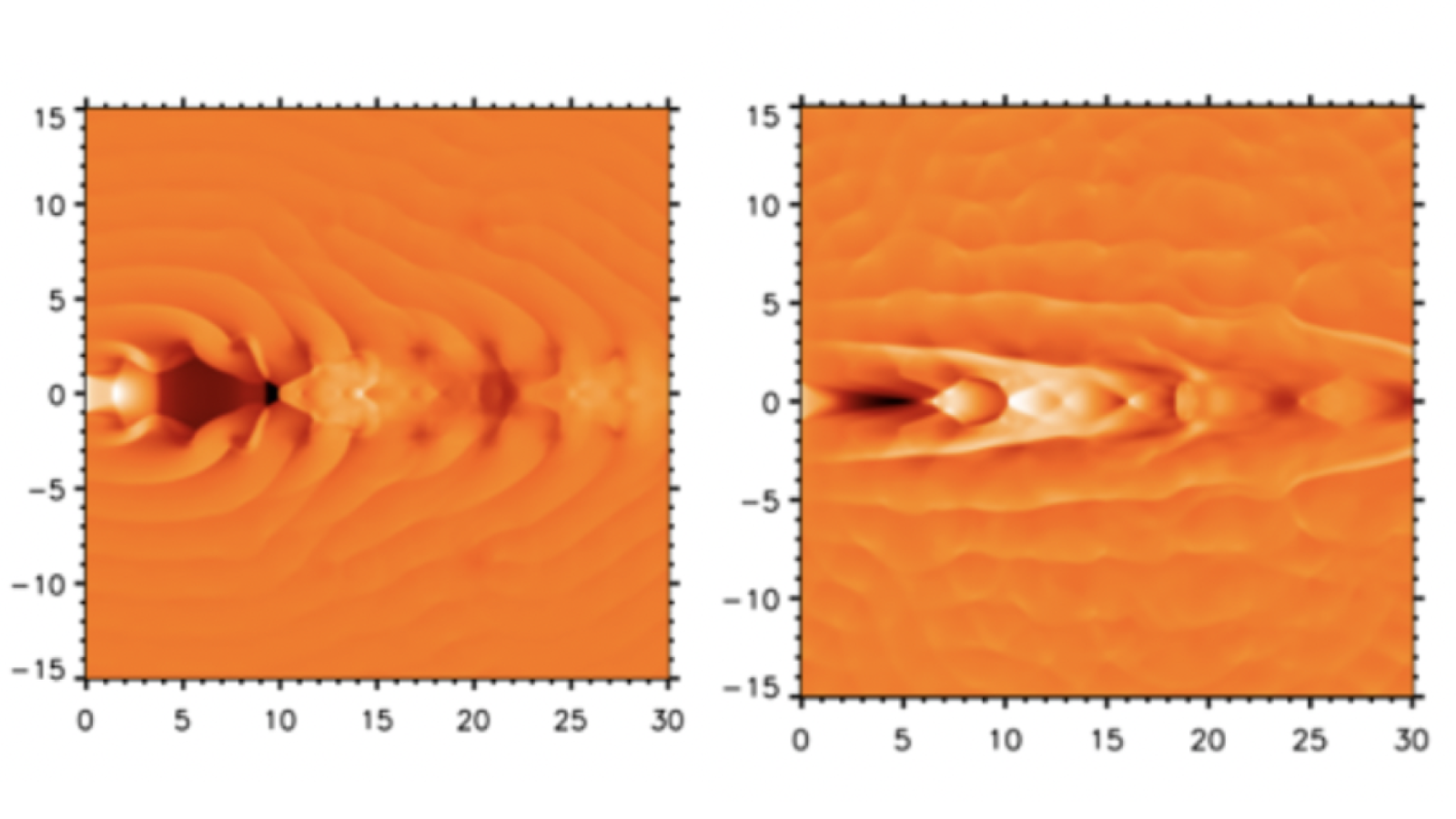 Two other simulations of black gap jets launching into the galactic medium of fuel and mud. (Symbol credit score: C Richards/MD Smith/College of Kent)”We discovered that there would should be some approach for the jets to beef up the frame — the galaxy’s surrounding ambient fuel — and that’s what we came upon in our laptop simulations,” crew member Carl Richards, a Ph.D. scholar on the College of Kent, mentioned in a commentary. “The surprising habits used to be published once we analyzed the pc simulations of excessive strain and allowed the guts to pulse.”This despatched a circulation of pulses into the high-pressure jets, inflicting them to switch form on account of the bellows-like motion of the oscillating jet surprise fronts. The researcher added that those jets expanded “like air-filled lungs.” In doing so, they despatched ripples of strain into the galactic subject material round them, with this preventing the expansion of galaxies within the simulations.
Two other simulations of black gap jets launching into the galactic medium of fuel and mud. (Symbol credit score: C Richards/MD Smith/College of Kent)”We discovered that there would should be some approach for the jets to beef up the frame — the galaxy’s surrounding ambient fuel — and that’s what we came upon in our laptop simulations,” crew member Carl Richards, a Ph.D. scholar on the College of Kent, mentioned in a commentary. “The surprising habits used to be published once we analyzed the pc simulations of excessive strain and allowed the guts to pulse.”This despatched a circulation of pulses into the high-pressure jets, inflicting them to switch form on account of the bellows-like motion of the oscillating jet surprise fronts. The researcher added that those jets expanded “like air-filled lungs.” In doing so, they despatched ripples of strain into the galactic subject material round them, with this preventing the expansion of galaxies within the simulations.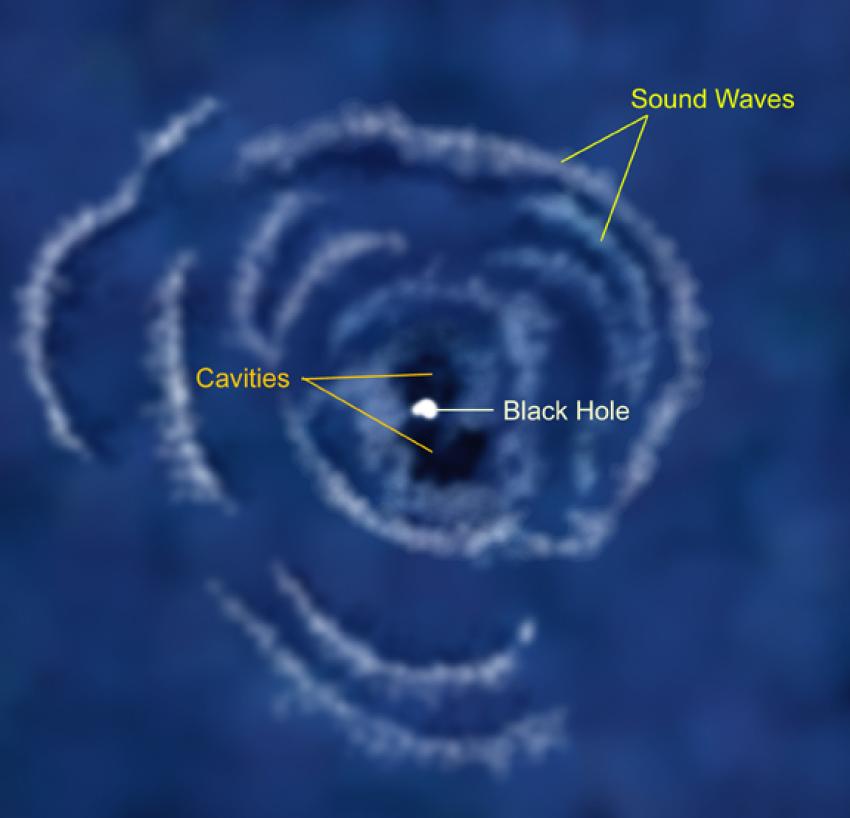 An indication appearing sound waves (ripples) within the sizzling fuel that fills the Perseus cluster. They’re idea to were generated through cavities blown out through jets from a supermassive black gap, the brilliant white spot on the middle of the galaxy. (Symbol credit score: NASA/NASA/CXC/M.Weiss)Clear of the crew’s simulations, there’s every other proof of this phenomenon in actual galaxies. For example, round 240 million light-years from Earth within the Perseus galaxy cluster, astronomers have observed proof of enormous fuel bubbles on this number of hundreds of galaxies immersed in an unlimited cloud of multimillion-degree fuel. Those are believed to be the results of soundwaves rippling throughout the galactic medium on this cluster.The equilibrium between black gap job and the waft of fuel into galaxies is terribly tricky to reach — alternatively, as supermassive black holes require a gradual provide of fuel and mud to create jets.”Respiring too rapid or too sluggish won’t give you the life-giving tremors had to deal with the galaxy medium and, on the identical time, stay the guts provided with gas,” crew member and College of Kent researcher Michael Smith mentioned within the commentary. “To try this isn’t simple, alternatively, and we’ve got constraints on the kind of pulsation, the scale of the black gap, and the standard of the lungs.”The crew concluded {that a} galaxy’s lifespan can also be prolonged with the assistance of its supermassive black gap “center” and that black gap’s jet “lungs” blowing from its core as they inhibit enlargement through restricting the quantity of fuel collapsing into stars from an early degree.With out this mechanism, many galaxies would have exhausted their gas provides wanted for big name formation through now in our 13.8-billion-year-old universe. Consequently, they might have “fizzled out,” with maximum galaxies corresponding to so-called “pink and lifeless” zombie galaxies at this level, stuffed with historical burned-out stars.The crew’s analysis is revealed on July 12 within the magazine Per thirty days Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
An indication appearing sound waves (ripples) within the sizzling fuel that fills the Perseus cluster. They’re idea to were generated through cavities blown out through jets from a supermassive black gap, the brilliant white spot on the middle of the galaxy. (Symbol credit score: NASA/NASA/CXC/M.Weiss)Clear of the crew’s simulations, there’s every other proof of this phenomenon in actual galaxies. For example, round 240 million light-years from Earth within the Perseus galaxy cluster, astronomers have observed proof of enormous fuel bubbles on this number of hundreds of galaxies immersed in an unlimited cloud of multimillion-degree fuel. Those are believed to be the results of soundwaves rippling throughout the galactic medium on this cluster.The equilibrium between black gap job and the waft of fuel into galaxies is terribly tricky to reach — alternatively, as supermassive black holes require a gradual provide of fuel and mud to create jets.”Respiring too rapid or too sluggish won’t give you the life-giving tremors had to deal with the galaxy medium and, on the identical time, stay the guts provided with gas,” crew member and College of Kent researcher Michael Smith mentioned within the commentary. “To try this isn’t simple, alternatively, and we’ve got constraints on the kind of pulsation, the scale of the black gap, and the standard of the lungs.”The crew concluded {that a} galaxy’s lifespan can also be prolonged with the assistance of its supermassive black gap “center” and that black gap’s jet “lungs” blowing from its core as they inhibit enlargement through restricting the quantity of fuel collapsing into stars from an early degree.With out this mechanism, many galaxies would have exhausted their gas provides wanted for big name formation through now in our 13.8-billion-year-old universe. Consequently, they might have “fizzled out,” with maximum galaxies corresponding to so-called “pink and lifeless” zombie galaxies at this level, stuffed with historical burned-out stars.The crew’s analysis is revealed on July 12 within the magazine Per thirty days Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Supermassive black holes supply ‘hearts and lungs’ that assist galaxies reside longer