On the heart of just about each and every huge galaxy within the universe sits a supermassive black hollow — and any surrounding clouds of gasoline, mud, and even stars that wander too shut are ate up as they move over the development horizons of those cosmic monsters.When supermassive black holes gorge on huge volumes of power and subject on this manner, they transform able to developing huge jets of plasma which might be shot out thru area at on the subject of the velocity of sunshine. As an example, one such galaxy, Messier 87, which is more or less 54 million light-years from Earth, is house to a 6.5-billion-solar-mass supermassive black hollow which produces 3,000 light-year-long jets of plasma. And new analysis, in accordance with observations made through the Hubble Area Telescope, has discovered that double-star techniques sitting on the subject of those jets reside lovely dangerous lives. 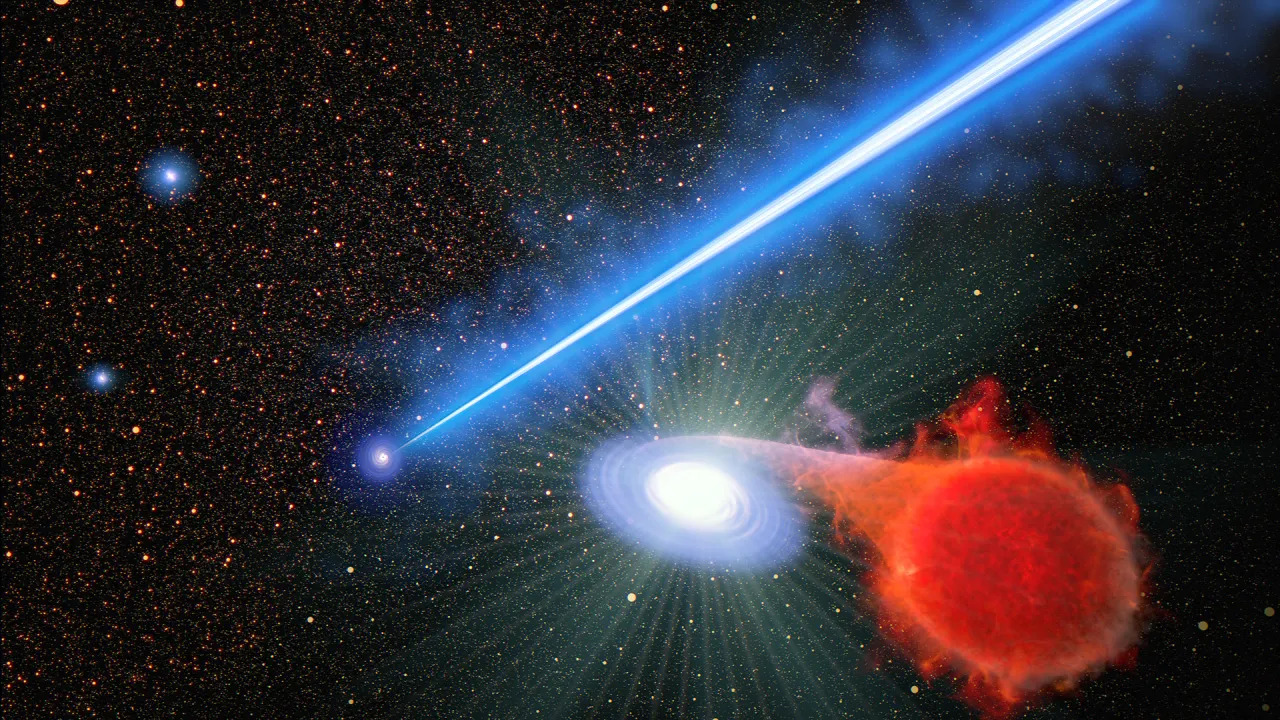 That is an artist’s idea taking a look down into the core of the large elliptical galaxy M87. A supermassive black hollow ejects a three,000-light-year-long jet of plasma, touring at just about the velocity of sunshine. Within the foreground, to the proper is a binary big name machine. (Symbol credit score: NASA, ESA, Joseph Olmsted (STScI))Stars can frequently to find themselves gravitationally certain to each other, forming double-star techniques. And occasionally, an getting older, swelled-up customary big name can to find itself with a white dwarf better half — the lifeless embers of a as soon as lively big name. In such situations, the enlarged big name can shed its fabrics, principally hydrogen, which can be gravitationally interested in the dense white dwarf. Similar: ‘Lacking hyperlink’ black hollow lurks in atypical binary machine with crimson massive starHowever, as hydrogen accumulates at the floor of the white dwarf, the big name can achieve a crucial tipping level. After that time, the method spurs an explosion. You’ll be able to call to mind it like a hydrogen bomb. Such explosions are referred to as nova, and they’re rather not unusual all over the universe. If truth be told, one is anticipated to occur somewhat quickly with a celeb referred to as T Coronae Borealis — and, in an extraordinary flip of occasions, scientists suppose that explosion might be shiny sufficient to make a “new big name” display up in our evening sky.Intriguingly, astronomers discovered that nova eruptions are nearly two times as more likely to happen in double-star techniques positioned within the neighborhood of Messier 87’s supermassive black hollow plasma jets. First of all, astronomers concept one thing in regards to the jets may well be improving the fueling procedure and due to this fact the speed of explosions, and even birthing new double-star techniques in its neighborhood.Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!However Alec Lessing, an astronomer from Stanford College, and lead writer of the paper reporting on those findings, is not somewhat satisfied.”We do not know what is going on, however it is only a very thrilling discovering,” Lessing mentioned in a commentary. “This implies there is something lacking from our working out of the way black hollow jets have interaction with their setting.” No longer lengthy after Hubble used to be introduced in 1990, astronomers pointed the telescope in opposition to the middle of Messier 87, the place the galaxy’s supermassive black hollow dwells. On the time, they noticed atypical blue “brief occasions” close to the black hollow, however the slim box of Hubble’s digital camera on the time intended the scientists could not examine how frequently those occasions had been going on in that location when in comparison to the remainder of the galaxy.”We are not the primary individuals who’ve mentioned that it seems like there may be extra process happening across the M87 jet,” mentioned co-author Michael Shara from the American Museum of Herbal Historical past in a press unencumber. “However Hubble has proven this enhanced process with way more examples and statistical importance than we ever had prior to.”The proof for the jet’s affect at the surrounding stars used to be gathered over a nine-month duration, with Hubble watching with its more moderen, wider-view digital camera each and every 5 days. Regardless of nova eruptions being not unusual occasions in galaxies as an entire, the brand new analysis additional illustrates the affect that supermassive black holes will have on process and evolution of galaxies. The analysis used to be revealed on Sept. 27 in The Astrophysical Magazine.
That is an artist’s idea taking a look down into the core of the large elliptical galaxy M87. A supermassive black hollow ejects a three,000-light-year-long jet of plasma, touring at just about the velocity of sunshine. Within the foreground, to the proper is a binary big name machine. (Symbol credit score: NASA, ESA, Joseph Olmsted (STScI))Stars can frequently to find themselves gravitationally certain to each other, forming double-star techniques. And occasionally, an getting older, swelled-up customary big name can to find itself with a white dwarf better half — the lifeless embers of a as soon as lively big name. In such situations, the enlarged big name can shed its fabrics, principally hydrogen, which can be gravitationally interested in the dense white dwarf. Similar: ‘Lacking hyperlink’ black hollow lurks in atypical binary machine with crimson massive starHowever, as hydrogen accumulates at the floor of the white dwarf, the big name can achieve a crucial tipping level. After that time, the method spurs an explosion. You’ll be able to call to mind it like a hydrogen bomb. Such explosions are referred to as nova, and they’re rather not unusual all over the universe. If truth be told, one is anticipated to occur somewhat quickly with a celeb referred to as T Coronae Borealis — and, in an extraordinary flip of occasions, scientists suppose that explosion might be shiny sufficient to make a “new big name” display up in our evening sky.Intriguingly, astronomers discovered that nova eruptions are nearly two times as more likely to happen in double-star techniques positioned within the neighborhood of Messier 87’s supermassive black hollow plasma jets. First of all, astronomers concept one thing in regards to the jets may well be improving the fueling procedure and due to this fact the speed of explosions, and even birthing new double-star techniques in its neighborhood.Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!However Alec Lessing, an astronomer from Stanford College, and lead writer of the paper reporting on those findings, is not somewhat satisfied.”We do not know what is going on, however it is only a very thrilling discovering,” Lessing mentioned in a commentary. “This implies there is something lacking from our working out of the way black hollow jets have interaction with their setting.” No longer lengthy after Hubble used to be introduced in 1990, astronomers pointed the telescope in opposition to the middle of Messier 87, the place the galaxy’s supermassive black hollow dwells. On the time, they noticed atypical blue “brief occasions” close to the black hollow, however the slim box of Hubble’s digital camera on the time intended the scientists could not examine how frequently those occasions had been going on in that location when in comparison to the remainder of the galaxy.”We are not the primary individuals who’ve mentioned that it seems like there may be extra process happening across the M87 jet,” mentioned co-author Michael Shara from the American Museum of Herbal Historical past in a press unencumber. “However Hubble has proven this enhanced process with way more examples and statistical importance than we ever had prior to.”The proof for the jet’s affect at the surrounding stars used to be gathered over a nine-month duration, with Hubble watching with its more moderen, wider-view digital camera each and every 5 days. Regardless of nova eruptions being not unusual occasions in galaxies as an entire, the brand new analysis additional illustrates the affect that supermassive black holes will have on process and evolution of galaxies. The analysis used to be revealed on Sept. 27 in The Astrophysical Magazine.
Supermassive black hollow jets mysteriously ignite nova explosions, Hubble Telescope reveals











![Samsung launches cloud gaming for Galaxy gadgets, however it is not what you suppose [Gallery] Samsung launches cloud gaming for Galaxy gadgets, however it is not what you suppose [Gallery]](https://9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2024/11/samsung-gaming-hub-cloud-1.jpg?quality=82&strip=all&w=1600)


