In the case of trying to find the explosive deaths of big stars within the early universe, the James Webb Area Telescope (JWST) is rather the cosmic detective. This celestial Sherlock Holmes has discovered proof of 80 new early supernovas in a patch of sky as vast as a grain of rice held at arm’s duration.No longer simplest is that this 10 instances extra supernovas than were exposed prior to in such early cosmic historical past, however the pattern additionally comprises the earliest and furthest supernova ever observed. It is person who exploded when the 13.8 billion-year-old universe used to be simply 1.8 billion years outdated.Knowledge from the JWST Complex Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES) program helped a group of scientists in finding this unparalleled take hold of of supernovas, which additional comprises Kind Ia blasts that astronomers name “same old candles” and will use to measure cosmic distances. Previous to the JWST starting off operations in the summertime of 2022, just a handful of supernovas were discovered relationship again to when the universe used to be simplest 3.3 billion years outdated, equivalent to round 25% its present age. The JADES pattern, then again, accommodates many supernovas that exploded even additional again previously. If truth be told, some erupted when the universe used to be not up to 2 billion years outdated. Similar: Peer inside of remnants of an 800-year-old supernova and spot a ‘zombie’ big name”The JWST is a supernova discovery device,” group member Christa DeCoursey, a third-year graduate pupil on the Steward Observatory and the College of Arizona in Tucson, mentioned in a commentary. “The sheer choice of detections plus the good distances to those supernovas are the 2 most enjoyable results from our survey.”The remarkable infrared sensitivity of the JWST way it’s finding supernovas virtually all over the place it appears to be like within the cosmos.Signal as much as our e-newsletter for the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!The supernova detectiveWhen mild wavelengths commute during the cosmos, the growth of the very cloth of house stretches out the ones wavelengths. This reasons the sunshine to transport additional down the electromagnetic spectrum in relation to classification, inching from the bluer finish in opposition to the redder finish. This phenomenon is referred to as “redshift.” The longer that mild has been touring via house, the extra excessive the stage of redshift it undergoes. Thus, mild from our bodies situated round 12 billion light-years away, like those supernovas, has skilled excessive wavelength lengthening, or “cosmological redshift.”That shifts this supernova mild down into the infrared area of the electromagnetic spectrum, a area the JWST is adept at viewing the universe in.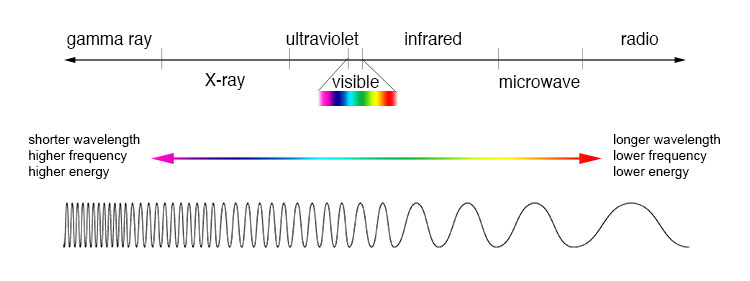 The electromagnetic spectrum appearing the relation between wavelength and quite a lot of varieties of mild. Redshift sees mild shifting from the visual mild spectrum and above all the way down to the infrared area. (Symbol credit score: NASA’s Believe the Universe)The Hubble Area Telescope had in the past allowed astronomers to view supernovas so far-off they existed when the universe used to be in its “younger grownup” section. With JADES and the JWST, then again, astronomers can apply supernovas when the cosmos is in its “teenagers” and even “pre-teens.” Someday, scientists hope to seem again to the “infant” section of the universe — and even again to its cosmic infancy, preferably stumbling upon the deaths of the primary era of big stars.To acquire this new cavalcade of supernova observations, the JADES group took a couple of photographs of the similar patch of the sky at year-long periods. Then, they when put next the pictures. As a result of supernovas are “transients,” which means they brighten and fade over the years, gazing adjustments within the photographs allowed the scientists to differentiate which issues of sunshine had been certainly exploding stars and which have been almost certainly any other phenomena.”That is in reality our first pattern of what the high-redshift universe seems like for temporary science,” JADES group member Justin Pierel, a NASA Einstein Fellow on the Area Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, mentioned within the commentary. “We’re looking to establish whether or not far-off supernovas are basically other from or very similar to what we see within the close by universe.”
The electromagnetic spectrum appearing the relation between wavelength and quite a lot of varieties of mild. Redshift sees mild shifting from the visual mild spectrum and above all the way down to the infrared area. (Symbol credit score: NASA’s Believe the Universe)The Hubble Area Telescope had in the past allowed astronomers to view supernovas so far-off they existed when the universe used to be in its “younger grownup” section. With JADES and the JWST, then again, astronomers can apply supernovas when the cosmos is in its “teenagers” and even “pre-teens.” Someday, scientists hope to seem again to the “infant” section of the universe — and even again to its cosmic infancy, preferably stumbling upon the deaths of the primary era of big stars.To acquire this new cavalcade of supernova observations, the JADES group took a couple of photographs of the similar patch of the sky at year-long periods. Then, they when put next the pictures. As a result of supernovas are “transients,” which means they brighten and fade over the years, gazing adjustments within the photographs allowed the scientists to differentiate which issues of sunshine had been certainly exploding stars and which have been almost certainly any other phenomena.”That is in reality our first pattern of what the high-redshift universe seems like for temporary science,” JADES group member Justin Pierel, a NASA Einstein Fellow on the Area Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, mentioned within the commentary. “We’re looking to establish whether or not far-off supernovas are basically other from or very similar to what we see within the close by universe.”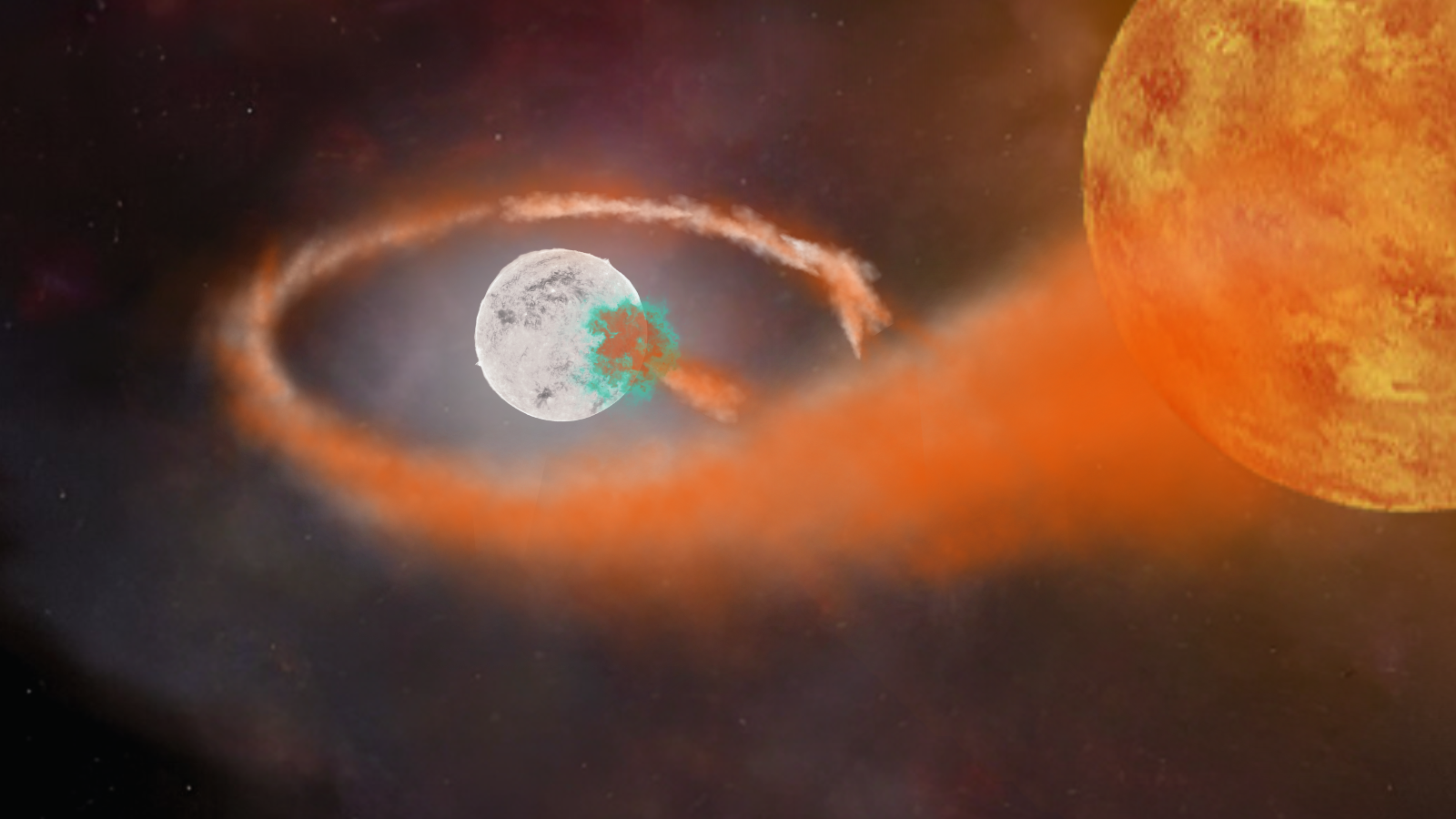 An indication presentations a white dwarf starting to erupt in a kind Ia supernova because it feeds on a significant other big name (Symbol credit score: Robert Lea (created with Canva))No longer all the supernovas observed through the JADES group had been “core cave in” supernovas, induced when huge stars run out of the gasoline provide wanted for nuclear fusion of their cores and cave in below their very own gravity, birthing a black hollow or a neutron big name.As discussed, some had been Kind Ia supernovas induced when stellar corpses referred to as “white dwarfs” cannibalistically feed on subject material stripped from a significant other, or donor, big name. This subject material piles at the white dwarf’s floor till it triggers a runaway thermonuclear explosion that absolutely obliterates the white dwarf.The sunshine outputs of those occasions are uniform with the similar intrinsic brightness, apparently irrespective of distance. This implies they are able to be used as cosmic rulers to measure distance and in addition function markers to gauge the velocity at which the material of house is increasing. Alternatively, must the intrinsic brightness of Kind Ia supernovas trade at excessive redshifts, their application at measuring huge cosmic distances could be restricted.The group’s observations of a Kind Ia that erupted round 11 billion years in the past indicated that its brightness had no longer numerous in spite of its mild present process cosmological redshift.The “pre-teen” universe used to be a hugely other position than we see these days, with way more excessive environments. Moreover, since the universe used to be most commonly hydrogen and helium at those instances, astronomers be expecting to look historical supernovas induced through the deaths of stars that comprise a ways fewer heavy chemical components, or “metals,” than the present era of “metal-rich” stars just like the solar.Thus, evaluating those historical supernovas with huge stars exploding within the native universe may lend a hand scientists higher know how stars are enriched throughout their formation through metals cast through early stars and unfold during the cosmos as they died.”We are necessarily opening a brand new window at the temporary universe,” Matthew Siebert, chief of the spectroscopic research of the JADES supernovas. “Traditionally, on every occasion we’ve got completed that, we’ve got discovered extraordinarily thrilling issues — issues that we did not be expecting.”The group’s findings had been offered at a press convention on the 244th assembly of the American Astronomical Society in Madison, Wisconsin, on Monday (June 10).
An indication presentations a white dwarf starting to erupt in a kind Ia supernova because it feeds on a significant other big name (Symbol credit score: Robert Lea (created with Canva))No longer all the supernovas observed through the JADES group had been “core cave in” supernovas, induced when huge stars run out of the gasoline provide wanted for nuclear fusion of their cores and cave in below their very own gravity, birthing a black hollow or a neutron big name.As discussed, some had been Kind Ia supernovas induced when stellar corpses referred to as “white dwarfs” cannibalistically feed on subject material stripped from a significant other, or donor, big name. This subject material piles at the white dwarf’s floor till it triggers a runaway thermonuclear explosion that absolutely obliterates the white dwarf.The sunshine outputs of those occasions are uniform with the similar intrinsic brightness, apparently irrespective of distance. This implies they are able to be used as cosmic rulers to measure distance and in addition function markers to gauge the velocity at which the material of house is increasing. Alternatively, must the intrinsic brightness of Kind Ia supernovas trade at excessive redshifts, their application at measuring huge cosmic distances could be restricted.The group’s observations of a Kind Ia that erupted round 11 billion years in the past indicated that its brightness had no longer numerous in spite of its mild present process cosmological redshift.The “pre-teen” universe used to be a hugely other position than we see these days, with way more excessive environments. Moreover, since the universe used to be most commonly hydrogen and helium at those instances, astronomers be expecting to look historical supernovas induced through the deaths of stars that comprise a ways fewer heavy chemical components, or “metals,” than the present era of “metal-rich” stars just like the solar.Thus, evaluating those historical supernovas with huge stars exploding within the native universe may lend a hand scientists higher know how stars are enriched throughout their formation through metals cast through early stars and unfold during the cosmos as they died.”We are necessarily opening a brand new window at the temporary universe,” Matthew Siebert, chief of the spectroscopic research of the JADES supernovas. “Traditionally, on every occasion we’ve got completed that, we’ve got discovered extraordinarily thrilling issues — issues that we did not be expecting.”The group’s findings had been offered at a press convention on the 244th assembly of the American Astronomical Society in Madison, Wisconsin, on Monday (June 10).
‘Supernova discovery device’ James Webb Area Telescope unearths maximum far-off big name explosion on report












