Via Washington College in St. Louis Might 25, 2024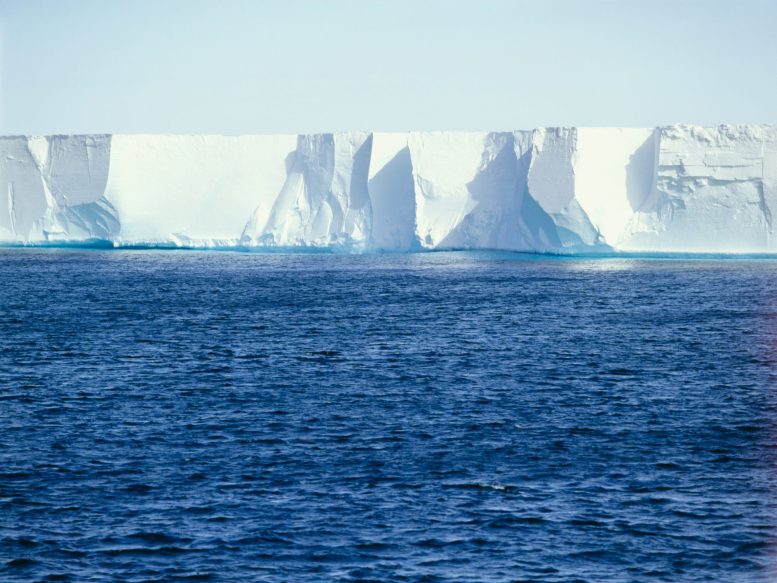 Analysis from Washington College in St. Louis unearths that the Ross Ice Shelf in Antarctica, more or less the scale of France, is dislocated day-to-day through an ice circulate. This motion, induced through a unexpected slip within the ice circulate, may affect icequakes and shelf fractures, elevating considerations about ice shelf balance in a warming international.The task of an ice circulate has induced the Ross Ice Shelf to displace.In Antarctica, large glaciers are continuously moving. Ice streams, which act like conveyor belts, are the pathways of speeded up motion that delivery the vast majority of the ice and sediment particles from those in depth glaciers in opposition to the sea.One such ice circulate jostles all the Ross Ice Shelf misplaced once or more day-to-day, consistent with new analysis from Washington College in St. Louis.This discovering is vital as a result of the size of the Ross Ice Shelf: It’s the greatest ice shelf in Antarctica, about the similar dimension as the rustic of France.“We discovered that the entire shelf strikes about 6 to eight centimeters (or 3 inches) a few times an afternoon, induced through a slip on an ice circulate that flows into the ice shelf,” stated Doug Wiens, the Robert S. Brookings Prominent Professor of earth, environmental and planetary sciences in Arts & Sciences. “Those unexpected actions may doubtlessly play a job in triggering icequakes and fractures within the ice shelf.”The Ross Ice Shelf is a floating lip of ice that extends out over the sea from inland glaciers.Scientists are excited about interactions between ice cabinets and ice streams partly as a result of they’re involved concerning the balance of Antarctica’s ice cabinets in a warming international.Ice cabinets act as brakes for glaciers and ice streams, slowing their adventure to the ocean the place they soften, thus permitting extra ice to amass at the continent. If an ice shelf collapses, this beef up disappears and the glaciers are unfastened to waft quicker. After they waft into the sea, they give a contribution to sea degree upward push.The brand new find out about, in Geophysical Analysis Letters, makes a speciality of motion induced through the Whillans Ice Circulate, considered one of a couple of half-dozen of the massive, fast-moving rivers of ice pouring into the Ross Ice Shelf.“One would no longer come across the motion simply by feeling it,” Wiens stated. “The motion happens over a period of time of a number of mins, so it’s not perceptible with out instrumentation. That’s why the motion has no longer been detected till now, even if other folks were strolling and tenting at the Ross Ice Shelf because the time of the good explorers Robert F. Scott and Roald Amundsen.”Surprising slippingThe motion of the Ross Ice Shelf is induced through a reasonably unexpected — in glacial phrases — motion of the ice circulate referred to as a slip match. It’s reasonably very similar to the “stick-slip” that happens alongside a fault sooner than and all over an earthquake.Beneath the state of affairs that Wiens and his staff seen, a big segment of the Whillans Ice Circulate, measuring greater than 100 km through 100 km, stays desk bound whilst the remainder of the ice circulate creeps ahead. Then, a few times in line with day, the massive segment lurches ahead in opposition to the Ross Ice Shelf.It may transfer up to 40 cm (16 inches) in a couple of mins, Wiens stated.Research of ice streams during the last 50 years display some ice streams rushing up, others slowing down. Scientists can use seismographs to come across the unexpected movement of the ice streams to assist perceive what controls this movement. Wiens and his staff traveled to Antarctica in 2014 to position the seismographs used on this find out about.“I’ve printed a number of papers concerning the Whillans Ice Circulate slip occasions prior to now, however had no longer found out that the entire Ross Ice Shelf additionally strikes till now,” Wiens stated.The researchers don’t assume that those slip occasions are at once associated with human-caused international warming. One idea is that they’re induced through the lack of water within the mattress of the Whillans Ice Circulate, making it extra “sticky.”The tension and traces related to slip occasions is very similar to the tension and pressure seen to cause icequakes below other stipulations.“At this level, icequakes and fractures are simply a part of the traditional lifetime of the ice shelf,” Wiens stated. “There’s a concern that the Ross Ice Shelf will one day fall apart, since different smaller and thinner ice cabinets have carried out so. We additionally know that the Ross Ice Shelf disintegrated all over the remaining interglacial length — about 120,000 years in the past — and that induced fast ice loss to the opposite glaciers and ice streams feeding into it.”Reference: “Ross Ice Shelf Displacement and Elastic Plate Waves Triggered through Whillans Ice Circulate Slip Occasions” through Douglas A. Wiens, Richard C. Aster, Andrew A. Nyblade, Peter D. Bromirski, Peter Gerstoft and Ralph A. Stephen, 27 March 2024, Geophysical Analysis Letters.
Analysis from Washington College in St. Louis unearths that the Ross Ice Shelf in Antarctica, more or less the scale of France, is dislocated day-to-day through an ice circulate. This motion, induced through a unexpected slip within the ice circulate, may affect icequakes and shelf fractures, elevating considerations about ice shelf balance in a warming international.The task of an ice circulate has induced the Ross Ice Shelf to displace.In Antarctica, large glaciers are continuously moving. Ice streams, which act like conveyor belts, are the pathways of speeded up motion that delivery the vast majority of the ice and sediment particles from those in depth glaciers in opposition to the sea.One such ice circulate jostles all the Ross Ice Shelf misplaced once or more day-to-day, consistent with new analysis from Washington College in St. Louis.This discovering is vital as a result of the size of the Ross Ice Shelf: It’s the greatest ice shelf in Antarctica, about the similar dimension as the rustic of France.“We discovered that the entire shelf strikes about 6 to eight centimeters (or 3 inches) a few times an afternoon, induced through a slip on an ice circulate that flows into the ice shelf,” stated Doug Wiens, the Robert S. Brookings Prominent Professor of earth, environmental and planetary sciences in Arts & Sciences. “Those unexpected actions may doubtlessly play a job in triggering icequakes and fractures within the ice shelf.”The Ross Ice Shelf is a floating lip of ice that extends out over the sea from inland glaciers.Scientists are excited about interactions between ice cabinets and ice streams partly as a result of they’re involved concerning the balance of Antarctica’s ice cabinets in a warming international.Ice cabinets act as brakes for glaciers and ice streams, slowing their adventure to the ocean the place they soften, thus permitting extra ice to amass at the continent. If an ice shelf collapses, this beef up disappears and the glaciers are unfastened to waft quicker. After they waft into the sea, they give a contribution to sea degree upward push.The brand new find out about, in Geophysical Analysis Letters, makes a speciality of motion induced through the Whillans Ice Circulate, considered one of a couple of half-dozen of the massive, fast-moving rivers of ice pouring into the Ross Ice Shelf.“One would no longer come across the motion simply by feeling it,” Wiens stated. “The motion happens over a period of time of a number of mins, so it’s not perceptible with out instrumentation. That’s why the motion has no longer been detected till now, even if other folks were strolling and tenting at the Ross Ice Shelf because the time of the good explorers Robert F. Scott and Roald Amundsen.”Surprising slippingThe motion of the Ross Ice Shelf is induced through a reasonably unexpected — in glacial phrases — motion of the ice circulate referred to as a slip match. It’s reasonably very similar to the “stick-slip” that happens alongside a fault sooner than and all over an earthquake.Beneath the state of affairs that Wiens and his staff seen, a big segment of the Whillans Ice Circulate, measuring greater than 100 km through 100 km, stays desk bound whilst the remainder of the ice circulate creeps ahead. Then, a few times in line with day, the massive segment lurches ahead in opposition to the Ross Ice Shelf.It may transfer up to 40 cm (16 inches) in a couple of mins, Wiens stated.Research of ice streams during the last 50 years display some ice streams rushing up, others slowing down. Scientists can use seismographs to come across the unexpected movement of the ice streams to assist perceive what controls this movement. Wiens and his staff traveled to Antarctica in 2014 to position the seismographs used on this find out about.“I’ve printed a number of papers concerning the Whillans Ice Circulate slip occasions prior to now, however had no longer found out that the entire Ross Ice Shelf additionally strikes till now,” Wiens stated.The researchers don’t assume that those slip occasions are at once associated with human-caused international warming. One idea is that they’re induced through the lack of water within the mattress of the Whillans Ice Circulate, making it extra “sticky.”The tension and traces related to slip occasions is very similar to the tension and pressure seen to cause icequakes below other stipulations.“At this level, icequakes and fractures are simply a part of the traditional lifetime of the ice shelf,” Wiens stated. “There’s a concern that the Ross Ice Shelf will one day fall apart, since different smaller and thinner ice cabinets have carried out so. We additionally know that the Ross Ice Shelf disintegrated all over the remaining interglacial length — about 120,000 years in the past — and that induced fast ice loss to the opposite glaciers and ice streams feeding into it.”Reference: “Ross Ice Shelf Displacement and Elastic Plate Waves Triggered through Whillans Ice Circulate Slip Occasions” through Douglas A. Wiens, Richard C. Aster, Andrew A. Nyblade, Peter D. Bromirski, Peter Gerstoft and Ralph A. Stephen, 27 March 2024, Geophysical Analysis Letters.
DOI: 10.1029/2023GL108040
The Biggest Ice Shelf in Antarctica Is Behaving Oddly