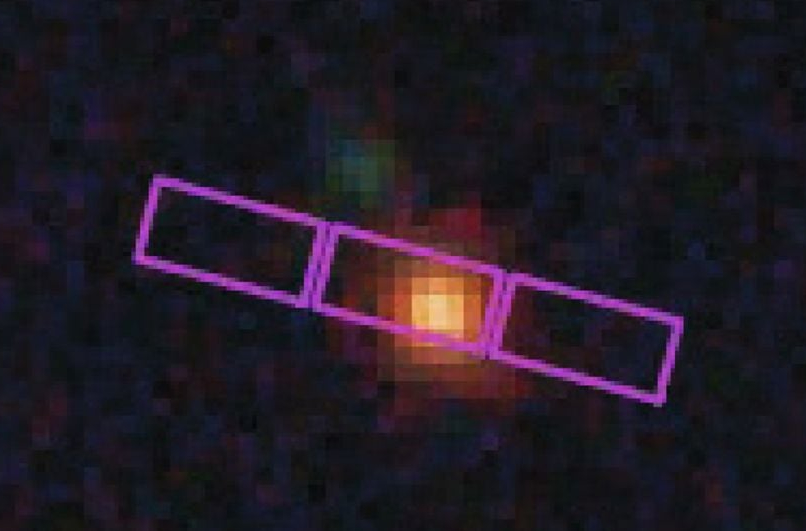
Scientists have lengthy queried how the advanced molecules wanted for existence will have shaped across the tumultuous and violent setting of the solar in its adolescence. A circle of relatives of meteorites known as “chondrites” is theorized to have delivered the appropriate stuff for existence to Earth. However the query is, how did advanced natural molecules containing components like carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen come to be sealed in those meteorites within the first position?New analysis means that the “sizzling spot” for the formation of those macromolecules, the crucial construction blocks of existence, is also so-called “mud traps” in swirling disks of topic round toddler stars. Right here, intense starlight from the central younger big name may just irradiate the collecting ice and dirt to shape carbon-containing macromolecules in simply a long time, which is moderately fast. This could imply the macromolecules may just already be provide when greater planetesimals shape planets, or they may well be sealed in asteroids within the type of small pebbles. Those asteroids will have then be damaged down by means of repeated collisions in area, growing smaller our bodies. A few of these will have arrived at Earth within the type of meteorites. Similar: Spell binding new Hubble Telescope symbol unearths an toddler big name’s sparkle An indication of icy debris harboring advanced molecules (Symbol credit score: ESO/L. Calçada)”It’s fantastic to find a new the most important function of mud traps within the formation of macromolecular topic that planets would possibly want for webhosting existence,” staff member Paola Pinilla of the Mullard House Science Laboratory at College Faculty London instructed House.com. “Mud traps are recommended areas for mud debris to develop to pebbles and planetesimals, which can be the construction blocks of planets.”Pinilla defined that during those areas, very small debris can also be often recreated and replenished by means of ongoing damaging collisions. Those tiny micron-sized grains can simply be lifted to the higher layers of the flattened cloud of star-forming subject matter that surrounds an toddler big name, known as a protoplanetary disk. As soon as right here, Pinilla stated those debris can obtain the appropriate quantity of irradiation from their toddler big name to successfully convert those tiny icy debris into advanced macromolecular topic.Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!Replicating the sun gadget’s early days within the labStars just like the solar are born when overdense patches shape in huge clouds of interstellar gasoline and dirt. First turning into a protostar, the newborn stellar frame gathers topic from what stays of its birthing cloud, piling at the mass had to cause the nuclear fusion of hydrogen to helium in its cores. That is the method that defines a celeb’s “primary collection” lifetime, which for a celeb across the mass of the solar will remaining round 10 billion years.This younger big name is surrounded by means of a protoplanetary disk, which is subject matter that wasn’t ate up all over its introduction and ascension to the principle collection. Because the identify suggests, it’s from this subject matter and throughout the disk that crops shape, however it additionally accounts for the foundation of comets and asteroids.Our sun gadget went via this introduction procedure round 4.5 billion years in the past.Earlier analysis performed in labs right here on Earth has indicated that once those protoplanetary disks are irradiated with starlight, advanced molecules of loads of atoms can shape inside them. Those molecules are constructed most commonly of carbon and are very similar to black soot or graphene.
An indication of icy debris harboring advanced molecules (Symbol credit score: ESO/L. Calçada)”It’s fantastic to find a new the most important function of mud traps within the formation of macromolecular topic that planets would possibly want for webhosting existence,” staff member Paola Pinilla of the Mullard House Science Laboratory at College Faculty London instructed House.com. “Mud traps are recommended areas for mud debris to develop to pebbles and planetesimals, which can be the construction blocks of planets.”Pinilla defined that during those areas, very small debris can also be often recreated and replenished by means of ongoing damaging collisions. Those tiny micron-sized grains can simply be lifted to the higher layers of the flattened cloud of star-forming subject matter that surrounds an toddler big name, known as a protoplanetary disk. As soon as right here, Pinilla stated those debris can obtain the appropriate quantity of irradiation from their toddler big name to successfully convert those tiny icy debris into advanced macromolecular topic.Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!Replicating the sun gadget’s early days within the labStars just like the solar are born when overdense patches shape in huge clouds of interstellar gasoline and dirt. First turning into a protostar, the newborn stellar frame gathers topic from what stays of its birthing cloud, piling at the mass had to cause the nuclear fusion of hydrogen to helium in its cores. That is the method that defines a celeb’s “primary collection” lifetime, which for a celeb across the mass of the solar will remaining round 10 billion years.This younger big name is surrounded by means of a protoplanetary disk, which is subject matter that wasn’t ate up all over its introduction and ascension to the principle collection. Because the identify suggests, it’s from this subject matter and throughout the disk that crops shape, however it additionally accounts for the foundation of comets and asteroids.Our sun gadget went via this introduction procedure round 4.5 billion years in the past.Earlier analysis performed in labs right here on Earth has indicated that once those protoplanetary disks are irradiated with starlight, advanced molecules of loads of atoms can shape inside them. Those molecules are constructed most commonly of carbon and are very similar to black soot or graphene.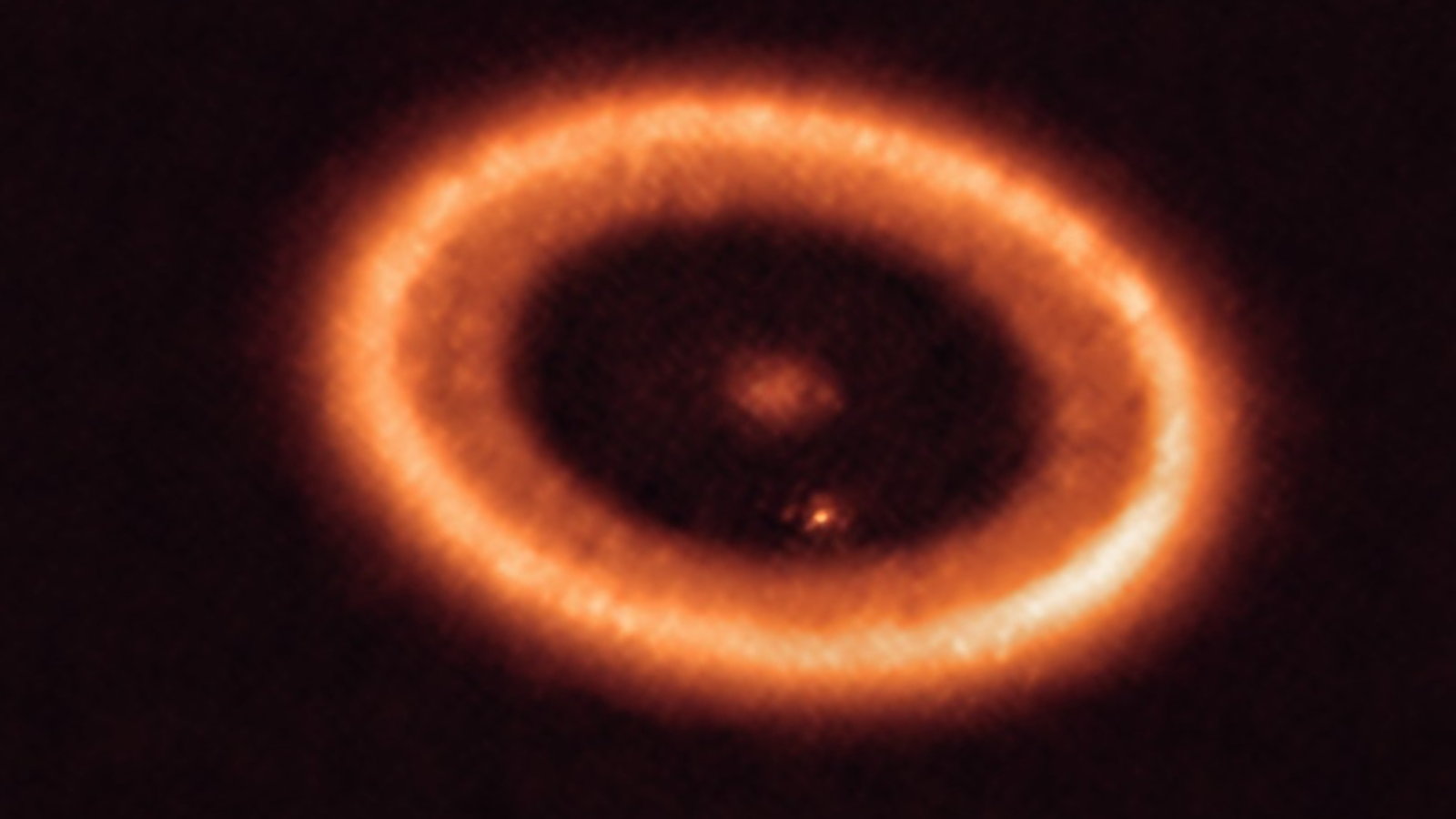  The protoplanetary disk across the toddler big name PDS 70 house to a minimum of two forming planets. (Symbol credit score: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)/Benisty et al.)Mud traps are high-pressure places in protoplanetary disks the place the movement of molecules is slowed, and dirt and ice grains can gather. The slower speeds in those spaces can permit grains to develop and, for essentially the most phase, steer clear of collisions that purpose fragmentation. This implies they may well be crucial to the formation of planets.The staff sought after to grasp if the radiation that starlight brings to those spaces may just purpose advanced macromolecules to shape, the usage of pc modeling to check this concept. The fashion was once in line with observational knowledge amassed by means of the Atacama Massive Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), an array of 66 radio telescopes in northern Chile.”Our analysis is a novel aggregate of astrochemistry, observations with ALMA, laboratory paintings, mud evolution, and the find out about of meteorites from our sun gadget,” staff member Nienke van der Marel of Leiden College stated. “It is truly tremendous cool that we will be able to now use an observation-based fashion to provide an explanation for how huge molecules can shape.”The fashion printed to the staff that the introduction of macromolecules in mud traps is a possible concept.”We had was hoping for this consequence, in fact, however it was once a pleasing wonder that it was once so evident,” staff chief Niels Ligterink of the College of Bern stated. “I am hoping that colleagues can pay extra consideration to the impact of heavy radiation on advanced chemical processes. Maximum researchers focal point on moderately small natural molecules of a couple of dozen atoms in measurement, whilst chondrites include most commonly huge macromolecules.””Within the close to long term, we sit up for trying out those fashions with extra laboratory experiments and observations the usage of robust telescopes just like the Atacama Massive Millimeter Array (ALMA),” Pinilla concluded.The staff’s analysis was once revealed on Tuesday (July 30) within the magazine Nature Astronomy.
The protoplanetary disk across the toddler big name PDS 70 house to a minimum of two forming planets. (Symbol credit score: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)/Benisty et al.)Mud traps are high-pressure places in protoplanetary disks the place the movement of molecules is slowed, and dirt and ice grains can gather. The slower speeds in those spaces can permit grains to develop and, for essentially the most phase, steer clear of collisions that purpose fragmentation. This implies they may well be crucial to the formation of planets.The staff sought after to grasp if the radiation that starlight brings to those spaces may just purpose advanced macromolecules to shape, the usage of pc modeling to check this concept. The fashion was once in line with observational knowledge amassed by means of the Atacama Massive Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), an array of 66 radio telescopes in northern Chile.”Our analysis is a novel aggregate of astrochemistry, observations with ALMA, laboratory paintings, mud evolution, and the find out about of meteorites from our sun gadget,” staff member Nienke van der Marel of Leiden College stated. “It is truly tremendous cool that we will be able to now use an observation-based fashion to provide an explanation for how huge molecules can shape.”The fashion printed to the staff that the introduction of macromolecules in mud traps is a possible concept.”We had was hoping for this consequence, in fact, however it was once a pleasing wonder that it was once so evident,” staff chief Niels Ligterink of the College of Bern stated. “I am hoping that colleagues can pay extra consideration to the impact of heavy radiation on advanced chemical processes. Maximum researchers focal point on moderately small natural molecules of a couple of dozen atoms in measurement, whilst chondrites include most commonly huge macromolecules.””Within the close to long term, we sit up for trying out those fashions with extra laboratory experiments and observations the usage of robust telescopes just like the Atacama Massive Millimeter Array (ALMA),” Pinilla concluded.The staff’s analysis was once revealed on Tuesday (July 30) within the magazine Nature Astronomy.
The construction blocks of existence can shape swiftly round younger stars