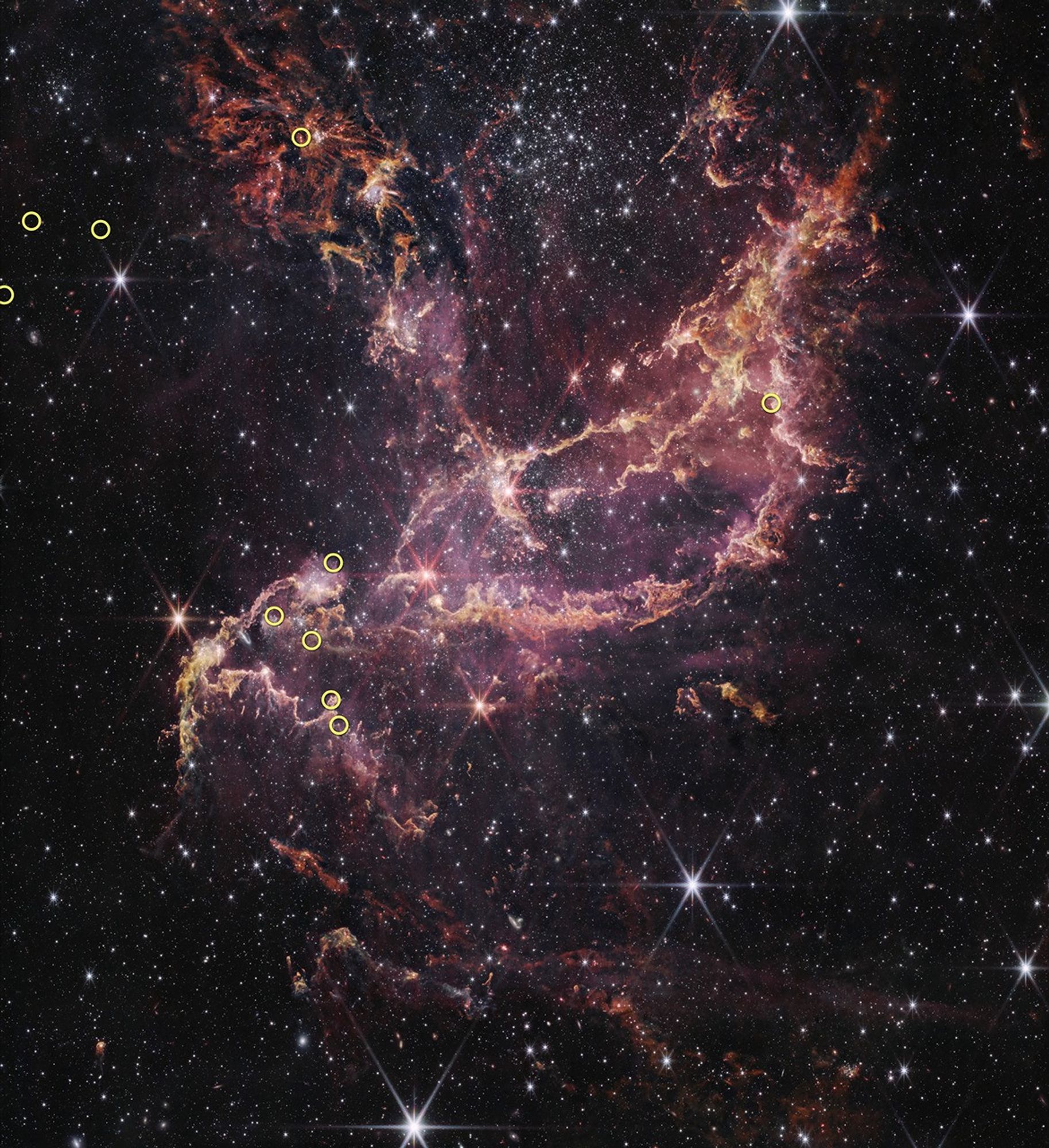
Astronomers have got the first-ever detailed perspectives of turbulent job in a celebrity rather than our personal solar.A time-lapse video launched Sep 11 displays monumental fuel bubbles roiling on a close-by superstar referred to as R Doradus, a purple large about 300 occasions larger than our solar that lies kind of 180 light-years away, within the southern constellation Dorado. Like a boiling soup on a stovetop, the superstar’s sizzling subject material erupts on its floor in bubbles, which astronomers estimate swell to a whopping 75 occasions our solar’s dimension.”It’s impressive that we will now immediately symbol the main points at the floor of stars thus far away,” Behzad Bojnodi Arbab, a doctoral pupil on the Chalmers College of Generation in Sweden and a co-author of a brand new find out about concerning the observations, revealed Wednesday within the magazine Nature, mentioned in a commentary. Due to the newest photographs, astronomers can now “practice physics that till now used to be most commonly most effective observable in our solar,” Arbab added. Those best-yet photographs of the within reach superstar R Doradus display large plasma bubbles 75 occasions larger than our solar emerging and sinking on its floor. (Symbol credit score: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)/W. Vlemmings et al.)The video is pieced in combination from the all time photographs of the superstar’s chaotic floor, which have been captured by means of a community of radio telescopes in Chile referred to as the Atacama Huge Millimeter/submillimeter Array, or ALMA for brief. The photographs display the plasma bubbles, which can be pushed by means of warmth emerging from the superstar’s core, crashing on its floor so violently that they seem to moderately deform the superstar.Comparable: Betelgeuse, Betelgeuse? One of the most brightest stars within the sky might in fact be 2 stars, find out about hints”We had by no means anticipated the knowledge to be of such top quality that shall we see such a lot of main points of the convection at the stellar floor,” find out about lead writer Wouter Vlemmings, a professor at Chalmers College of Generation, mentioned within the commentary.From the newest snapshots of R Doradus, which ALMA captured from early July to August of remaining yr, Vlemmings and his colleagues estimate the superstar’s plasma bubbles upward thrust and fall on a one-month cycle, which is quicker than the timeline adopted by means of an identical convective cells ample on our solar’s floor.Get the sector’s most enticing discoveries delivered immediately in your inbox.”We do not but know what’s the explanation why for the adaptation,” mentioned Vlemmings.Although R Doradus is amazingly bloated, its mass is very similar to that of our solar. So find out about group participants suspect the superstar displays how our solar will glance in about 5 billion years, when it’ll input its purple large section by means of ballooning as much as the purpose of swallowing Mercury and Venus.”It sort of feels that convection adjustments as a celebrity will get older in ways in which we do not but perceive,” mentioned Vlemmings.Earlier ALMA observations confirmed that R Doradus is spinning no less than two orders of magnitude sooner than anticipated for a purple large. Within the new find out about, Vlemmings and his group dominated out the likelihood that the top spin is an phantasm created by means of the superstar’s boiling floor, a speculation that used to be not too long ago put forth by means of a special group of astronomers finding out Betelgeuse, some other purple large within the constellation Orion identified to spin 100 occasions sooner than anticipated.Vlemmings and his colleagues argue that R Doradus’ rotation fee is for much longer than the one-month cycle they discovered its convective bubbles to function in, thus ruling out the percentages of telescopes being tricked by means of the sort of probability alignment of fuel bubbles.In the beginning posted on House.com.
Those best-yet photographs of the within reach superstar R Doradus display large plasma bubbles 75 occasions larger than our solar emerging and sinking on its floor. (Symbol credit score: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)/W. Vlemmings et al.)The video is pieced in combination from the all time photographs of the superstar’s chaotic floor, which have been captured by means of a community of radio telescopes in Chile referred to as the Atacama Huge Millimeter/submillimeter Array, or ALMA for brief. The photographs display the plasma bubbles, which can be pushed by means of warmth emerging from the superstar’s core, crashing on its floor so violently that they seem to moderately deform the superstar.Comparable: Betelgeuse, Betelgeuse? One of the most brightest stars within the sky might in fact be 2 stars, find out about hints”We had by no means anticipated the knowledge to be of such top quality that shall we see such a lot of main points of the convection at the stellar floor,” find out about lead writer Wouter Vlemmings, a professor at Chalmers College of Generation, mentioned within the commentary.From the newest snapshots of R Doradus, which ALMA captured from early July to August of remaining yr, Vlemmings and his colleagues estimate the superstar’s plasma bubbles upward thrust and fall on a one-month cycle, which is quicker than the timeline adopted by means of an identical convective cells ample on our solar’s floor.Get the sector’s most enticing discoveries delivered immediately in your inbox.”We do not but know what’s the explanation why for the adaptation,” mentioned Vlemmings.Although R Doradus is amazingly bloated, its mass is very similar to that of our solar. So find out about group participants suspect the superstar displays how our solar will glance in about 5 billion years, when it’ll input its purple large section by means of ballooning as much as the purpose of swallowing Mercury and Venus.”It sort of feels that convection adjustments as a celebrity will get older in ways in which we do not but perceive,” mentioned Vlemmings.Earlier ALMA observations confirmed that R Doradus is spinning no less than two orders of magnitude sooner than anticipated for a purple large. Within the new find out about, Vlemmings and his group dominated out the likelihood that the top spin is an phantasm created by means of the superstar’s boiling floor, a speculation that used to be not too long ago put forth by means of a special group of astronomers finding out Betelgeuse, some other purple large within the constellation Orion identified to spin 100 occasions sooner than anticipated.Vlemmings and his colleagues argue that R Doradus’ rotation fee is for much longer than the one-month cycle they discovered its convective bubbles to function in, thus ruling out the percentages of telescopes being tricked by means of the sort of probability alignment of fuel bubbles.In the beginning posted on House.com.