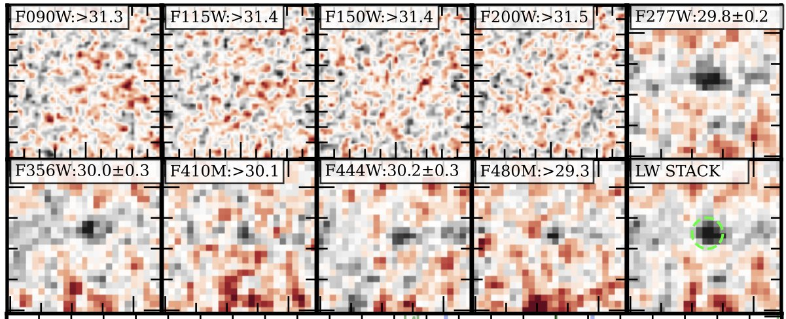
Scientists have ventured to the a ways reaches of the sun gadget, no less than nearly, to collect probably the most actual measurements of the faint glow that fills the universe. The mixed gentle from all assets out of doors of the Milky Manner galaxy is referred to as the cosmic optical background.In a up to date learn about, revealed in The Astrophysical Magazine, mavens analyzed information from NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft, which flew previous Pluto in 2015 and is now just about 5.5 billion miles from Earth. Faint gentle of one trillion galaxies The analysis addresses a apparently easy however profound query, in line with co-author Michael Shull, an astrophysicist on the College of Colorado Boulder: “Is the sky in reality darkish?” “On the break of day of time, the universe used to be a sea of sunshine. However because it expanded, it cooled, dimmed, and topic got here to the fore. Just about 14 billion years after the Large Bang, area is now chilly and darkish,” famous the researchers.“Whilst our horizon encompasses nearly one trillion galaxies that experience shaped over that point, they’re extraordinarily faint, and we’d like our maximum robust telescopes to tally their presence without delay.”Even if area seems black to human eyes, scientists imagine it’s no longer fully devoid of sunshine. Over the process cosmic historical past, trillions of galaxies full of stars have come and long past, leaving in the back of a faint, nearly imperceptible gentle – a kind of cosmic evening gentle.Measuring the glow of the universe Shull and his group, led via Marc Postman from the House Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, calculated the depth of this faint glow. The findings recommend that the cosmic optical background is set 100 billion instances dimmer than the daylight that reaches Earth’s floor – a ways too faint for human eyes to come across.The consequences might assist scientists higher perceive the historical past of the universe because the Large Bang. “We’re more or less like cosmic accountants, including up each supply of sunshine we will account for within the universe,” stated Shull, not anything that this effort to quantify the cosmic optical background has fascinated scientists for just about part a century.Fading gentle all through the universeShull defined that once many years of analysis, astrophysicists imagine they’ve a moderately transparent image of ways the universe developed. Galaxies first shaped all through a duration known as the Cosmic Daybreak, a couple of hundred million years after the Large Bang. The sunshine from those galaxies reached its height brightness about 10 billion years in the past and has been regularly fading ever since.Correct measurements of the cosmic optical background may just assist verify whether or not this working out of the universe is proper – or if there could be hidden, undiscovered items contributing gentle to area. Alternatively, measuring this faint gentle isn’t simple, particularly from Earth.Uncommon alternative to look at the universe’s glow The world round Earth is full of mud and particles. Daylight displays off this subject material, obscuring any indicators from the cosmic optical background.“A metaphor I exploit is if you wish to see the celebs, you want to get out of Denver,” Shull stated. “It’s a must to move approach out, proper to the northeast nook of Colorado the place all you might have forward of you’re South Dakota and Nebraska.”New Horizons has equipped scientists with an extraordinary alternative to succeed in one thing an identical in area.New Horizons missionThe New Horizons undertaking has deep roots in Colorado. Alan Stern, who used to be a graduate pupil on the College of Colorado Boulder below Shull and previous Senior Analysis Affiliate Jack Brandt, leads the undertaking. He’s lately based totally on the Southwest Analysis Institute in Boulder, Colorado. The spacecraft additionally carries the Scholar Mud Counter, an software designed and constructed via scholars at CU Boulder’s Laboratory for Atmospheric and House Physics (LASP).All the way through the summer season of 2023, the analysis group aimed New Horizons’ Lengthy Vary Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) at 25 other patches of sky.Even on the outer edges of the sun gadget, the group nonetheless needed to maintain extra gentle. For example, the Milky Manner galaxy sits inside a halo that, just like the sun gadget, comprises mud. “You’ll be able to’t break out from mud,” Shull famous. “It’s all over the place.”The cosmic optical background The researchers estimated how a lot gentle the Milky Manner’s halo may just give a contribution and subtracted that from the knowledge accumulated via LORRI. After accounting for all different assets of sunshine, they had been left with the faint glow of the cosmic optical background.In medical phrases, this background equates to more or less 11 nanowatts consistent with sq. meter consistent with steradian (a steradian being a piece of the sky with a width about 130 instances the diameter of the moon).Shull defined that this worth aligns smartly with the collection of galaxies scientists imagine have shaped because the Large Bang. In different phrases, there doesn’t seem to be any mysterious items, reminiscent of unique debris, emitting vital quantities of sunshine. Alternatively, the researchers can’t fully rule out the opportunity of such anomalies.Maximum correct estimates of the universe’s glow The measurements are more likely to stay probably the most correct estimates of the universe’s glow for the foreseeable long run. New Horizons is the use of its closing gas for different medical missions, and no different spacecraft are lately deliberate to undertaking into the chilly and far-off portions of area that New Horizons has explored.“In the event that they put a digital camera on a long run undertaking, and all of us wait a few many years for it to get in the market, lets see a extra precise dimension,” Shull concluded.—–Like what you learn? Subscribe to our e-newsletter for attractive articles, unique content material, and the newest updates.Take a look at us out on EarthSnap, a loose app dropped at you via Eric Ralls and Earth.com.—–
The faint glow of the universe is slowly dimming