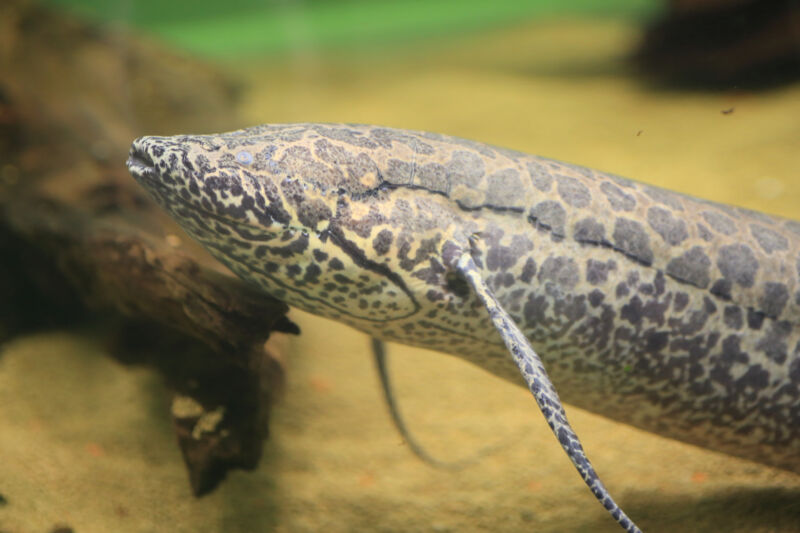
Amplify / The African Lungfish, appearing it is skinny, wispy fins.
When it used to be first came upon, the coelacanth brought about a large number of pleasure. It used to be a dwelling instance of a gaggle of fish that used to be concept to simply exist as fossils. And no longer simply any staff of fish. With their lengthy, stalk-like fins, coelacanths and their relatives are concept to incorporate the ancestors of all vertebrates that don’t seem to be fish—the tetrapods, or vertebrates with 4 limbs. Which means, amongst a large number of different issues, us.
Since then, on the other hand, proof has piled up that we are extra intently associated with lungfish, which are living in freshwater and are present in Africa, Australia, and South The us. However lungfish are just a little bizarre. The African and South American species have observed the limb-like fins in their ancestors decreased to skinny, floppy strands. And getting some point of view on their evolutionary historical past has confirmed tough as a result of they have got the biggest genomes identified in animals, with the South American lungfish genome containing over 90 billion base pairs. That is 30 instances the quantity of DNA now we have.
However new sequencing era has made tackling that kind of problem manageable, and a world collaboration has now finished the biggest genome ever, one the place all however one chromosome elevate extra DNA than is located within the human genome. The paintings issues to a historical past the place the South American lungfish has been including 3 billion further bases of DNA each and every 10 million years for the ultimate 200 million years, all with out including an important selection of new genes. As a substitute, it kind of feels to have misplaced the power to stay junk DNA in test.
Going lengthy
The paintings used to be enabled by means of a era generically termed “long-read sequencing.” Lots of the genomes that have been finished have been carried out the usage of quick reads, generally within the house of 100–200 base pairs lengthy. The name of the game used to be to do sufficient sequencing that, on moderate, each and every base within the genome will have to be sequenced a couple of instances. For the reason that, a cleverly designed pc program may just work out the place two bits of collection overlapped and sign in that as a unmarried, longer piece of collection, repeating the method till the pc spit out lengthy strings of contiguous bases.
The issue is that almost all non-microbial species have stretches of repeated collection (assume masses of copies of the bases G and A in a row) that have been longer than a couple of hundred bases lengthy—and just about an identical sequences that display up in a couple of places of the genome. Those could be not possible to check to a novel location, and so the output of the genome meeting instrument would have loads of gaps of unknown duration and collection.
This creates excessive issue for genomes like that of the lungfish, which is full of non-functional “junk” DNA, all of which is generally repetitive. The instrument has a tendency to provide a genome that is extra hole than collection.
Lengthy-read era will get round that by means of doing precisely what its identify implies. Somewhat than with the ability to collection fragments of 200 bases or so, it might probably generate sequences which can be 1000’s of base pairs lengthy, simply protecting all the repeat that will have another way created an opening. One early model of long-read era concerned stuffing lengthy DNA molecules thru pores and staring at for various voltage adjustments around the pore as other bases handed thru it. Any other had a DNA copying enzyme make a reproduction of an extended strand and look ahead to fluorescence adjustments as other bases have been added. Those early variations tended to be just a little error-prone however have since been advanced, and several other more recent competing applied sciences at the moment are available on the market.
Again in 2021, researchers used this era to finish the genome of the Australian lungfish—the one who maintains the limb-like fins of the ancestors that gave upward push to tetrapods. Now they are again with the genomes from African and South American species. Those species appear to have long gone their separate techniques all the way through the breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana, a procedure that began just about 200 million years in the past. And having the genomes of all 3 will have to give us some point of view at the options which can be not unusual to all lungfish species, and thus are much more likely to had been shared with the far-off ancestors that gave upward push to tetrapods.