Analysis from Georgia State College presentations that intestine micro organism, specifically segmented filamentous micro organism, play a a very powerful position in protective mice towards respiration viruses by way of influencing immune cells within the lungs. This learn about may have profound implications for working out and managing respiration infections in people.Researchers on the Heart for Translational Antiviral Analysis inside the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State College have found out that the make-up of intestine microbiota impacts mice’s vulnerability to respiration virus infections and the severity of those infections.The findings, printed within the magazine Mobile Host & Microbe, file that segmented filamentous micro organism, a bacterial species discovered within the intestines, secure mice towards influenza virus an infection when those micro organism have been both naturally obtained or administered.
Analysis from Georgia State College presentations that intestine micro organism, specifically segmented filamentous micro organism, play a a very powerful position in protective mice towards respiration viruses by way of influencing immune cells within the lungs. This learn about may have profound implications for working out and managing respiration infections in people.Researchers on the Heart for Translational Antiviral Analysis inside the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State College have found out that the make-up of intestine microbiota impacts mice’s vulnerability to respiration virus infections and the severity of those infections.The findings, printed within the magazine Mobile Host & Microbe, file that segmented filamentous micro organism, a bacterial species discovered within the intestines, secure mice towards influenza virus an infection when those micro organism have been both naturally obtained or administered.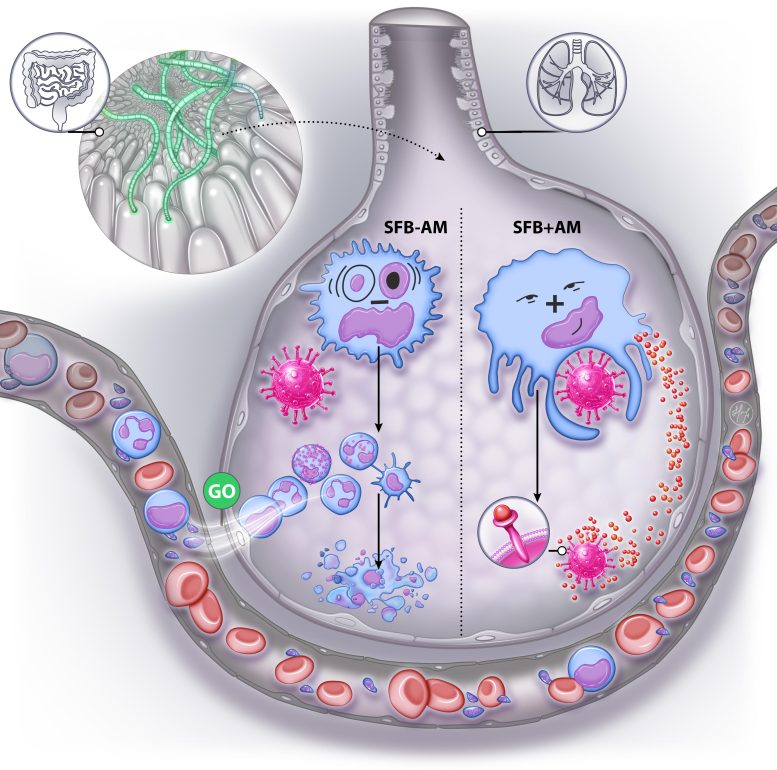 This image illustrates an instance of intestine microbiota composition dictating how resident lung alveolar macrophages (AM) reply to viral an infection. The presence of segmented filamentous micro organism, a commensal microbe found in some mice, reprograms AM gene expression, expanding supplement expression and phagocytosis, thereby enabling AM to engulf and break viral pathogens with out inflammatory signaling. Credit score: Dr. Andrew GewirtzThis coverage towards an infection additionally implemented to respiration syncytial virus (RSV) and critical acute respiration syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that reasons COVID-19. To take care of this coverage, the learn about famous that segmented filamentous micro organism required immune cells within the lungs known as basally resident alveolar macrophages.Learn about Findings
This image illustrates an instance of intestine microbiota composition dictating how resident lung alveolar macrophages (AM) reply to viral an infection. The presence of segmented filamentous micro organism, a commensal microbe found in some mice, reprograms AM gene expression, expanding supplement expression and phagocytosis, thereby enabling AM to engulf and break viral pathogens with out inflammatory signaling. Credit score: Dr. Andrew GewirtzThis coverage towards an infection additionally implemented to respiration syncytial virus (RSV) and critical acute respiration syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that reasons COVID-19. To take care of this coverage, the learn about famous that segmented filamentous micro organism required immune cells within the lungs known as basally resident alveolar macrophages.Learn about Findings Dr. Richard Plemper, co-senior writer of the learn about, Regents’ Professor and director of the Heart for Translational Antiviral Analysis at Georgia State College. Credit score: Georgia State UniversityIn this learn about, the researchers investigated how variations in particular microbial species can have an effect on results of respiration virus infections and the way they may achieve this, which hasn’t been smartly outlined in the past. They studied mice with discrete microbiome variations and mice differing in most effective the presence or absence of segmented filamentous micro organism. Viral titers within the lung have been measured a number of days after an infection and sundry considerably relying at the nature of the microbiome of the other animal teams.“Those findings discover complicated interactions that mechanistically hyperlink the intestinal microbiota with the capability of basally resident alveolar macrophages and severity of respiration virus an infection,” mentioned Dr. Andrew Gewirtz, co-senior writer of the learn about and Regents’ Professor within the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State.The learn about discovered that during segmented filamentous bacteria-negative mice, basally resident alveolar macrophages have been briefly depleted as respiration virus an infection stepped forward. Alternatively, in segmented filamentous bacteria-colonized mice, basally resident alveolar macrophages have been altered to withstand influenza virus an infection depletion and inflammatory signaling.The basally resident alveolar macrophages disabled influenza virus, largely by way of activating an element of the immune machine known as the supplement machine.Implications and Long run Instructions“We discover it exceptional that the presence of a unmarried not unusual commensal bacterial species, amidst the 1000’s of various microbial species that inhabit the mouse intestine, had such sturdy affects in respiration virus an infection fashions and that such affects have been in large part on account of reprogramming of basally resident alveolar macrophages,” mentioned Dr. Richard Plemper, co-senior writer of the learn about, Regents’ Professor and director of the Heart for Translational Antiviral Analysis at Georgia State. “If appropriate to human infections, those findings can have primary implications for the longer term chance overview of a affected person to advance to critical illness.”“We discover it extremely not likely that segmented filamentous micro organism is the one intestine microbe in a position to impacting the phenotype of alveolar macrophages, and in consequence, proneness to respiration virus an infection,” Gewirtz mentioned. “Somewhat, we hypothesize that intestine microbiota composition widely influences proneness to respiration virus an infection. Microbiota mediated programming of basally resident alveolar macrophages won’t most effective affect the severity of acute respiration virus an infection, however can also be a long-term post-respiratory virus an infection well being determinant.”Reference: “Intestinal microbiota programming of alveolar macrophages influences severity of respiration viral an infection” by way of Vu L. Ngo, Carolin M. Lieber, Hae-ji Kang, Kaori Sakamoto, Michal Kuczma, Richard Ok. Plemper and Andrew T. Gewirtz, 30 January 2024, Mobile Host & Microbe.
Dr. Richard Plemper, co-senior writer of the learn about, Regents’ Professor and director of the Heart for Translational Antiviral Analysis at Georgia State College. Credit score: Georgia State UniversityIn this learn about, the researchers investigated how variations in particular microbial species can have an effect on results of respiration virus infections and the way they may achieve this, which hasn’t been smartly outlined in the past. They studied mice with discrete microbiome variations and mice differing in most effective the presence or absence of segmented filamentous micro organism. Viral titers within the lung have been measured a number of days after an infection and sundry considerably relying at the nature of the microbiome of the other animal teams.“Those findings discover complicated interactions that mechanistically hyperlink the intestinal microbiota with the capability of basally resident alveolar macrophages and severity of respiration virus an infection,” mentioned Dr. Andrew Gewirtz, co-senior writer of the learn about and Regents’ Professor within the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State.The learn about discovered that during segmented filamentous bacteria-negative mice, basally resident alveolar macrophages have been briefly depleted as respiration virus an infection stepped forward. Alternatively, in segmented filamentous bacteria-colonized mice, basally resident alveolar macrophages have been altered to withstand influenza virus an infection depletion and inflammatory signaling.The basally resident alveolar macrophages disabled influenza virus, largely by way of activating an element of the immune machine known as the supplement machine.Implications and Long run Instructions“We discover it exceptional that the presence of a unmarried not unusual commensal bacterial species, amidst the 1000’s of various microbial species that inhabit the mouse intestine, had such sturdy affects in respiration virus an infection fashions and that such affects have been in large part on account of reprogramming of basally resident alveolar macrophages,” mentioned Dr. Richard Plemper, co-senior writer of the learn about, Regents’ Professor and director of the Heart for Translational Antiviral Analysis at Georgia State. “If appropriate to human infections, those findings can have primary implications for the longer term chance overview of a affected person to advance to critical illness.”“We discover it extremely not likely that segmented filamentous micro organism is the one intestine microbe in a position to impacting the phenotype of alveolar macrophages, and in consequence, proneness to respiration virus an infection,” Gewirtz mentioned. “Somewhat, we hypothesize that intestine microbiota composition widely influences proneness to respiration virus an infection. Microbiota mediated programming of basally resident alveolar macrophages won’t most effective affect the severity of acute respiration virus an infection, however can also be a long-term post-respiratory virus an infection well being determinant.”Reference: “Intestinal microbiota programming of alveolar macrophages influences severity of respiration viral an infection” by way of Vu L. Ngo, Carolin M. Lieber, Hae-ji Kang, Kaori Sakamoto, Michal Kuczma, Richard Ok. Plemper and Andrew T. Gewirtz, 30 January 2024, Mobile Host & Microbe.
DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2024.01.002The learn about’s number one authors have been virologist Carolin M. Lieber from the Heart for Translational Antiviral Analysis and immunologist Vu L. Ngo from the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State. Different contributing authors have been Hae-ji Kang and Michal Kuczma of the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State and Kaori Sakamoto of the College of Georgia.The learn about is funded by way of the Nationwide Institutes of Well being’s Nationwide Institute of Hypersensitive reaction and Infectious Illnesses.
The Invisible Protection: Intestine Micro organism’s Unexpected Position in Fighting Flu and COVID-19