Within the quest to resolve the mysteries of the way our brains shape and retain reminiscences, a group of scientists from Tokyo College of Science, led via Professor Akiyoshi Saitoh and Junpei Takahashi, has made a groundbreaking discovery. Their analysis, revealed in PLOS One, delves into the function of a naturally going on mind chemical referred to as oxytocin in bettering reminiscence in mice.In particular, they explored how activating oxytocin-producing neurons in a selected space of the mind may just considerably reinforce the animals’ skill to acknowledge gadgets through the years. This find out about no longer best sheds mild at the intricate workings of our cognitive purposes but in addition opens up new avenues for addressing memory-related issues.Oxytocin: A Hormone with A ways-Attaining EffectsOxytocin, incessantly dubbed the “love hormone,” is legendary for its function in fostering bonds between moms and their newborns, in addition to in romantic relationships. However past its emotional affects, oxytocin is a peptide hormone with a fancy function within the mind, influencing quite a lot of cognitive purposes together with studying and reminiscence. Produced within the hypothalamus and performing throughout other mind areas, oxytocin binds to express receptors, triggering a cascade of cell alerts that have an effect on neurotransmitter unlock and neuronal task.The incentive at the back of this newest find out about stems from earlier analysis hinting at oxytocin’s doable as a healing goal for dementia and Alzheimer’s illness. Given the hormone’s involvement in social reminiscence, the researchers aimed to know if and the way endogenous oxytocin — oxytocin produced inside the frame — contributes to non-social sides of reminiscence, corresponding to spotting new gadgets in a single’s setting.“Prior to now we had steered that oxytocin is also a brand new healing candidate for dementia in keeping with research the use of a mouse fashion of Alzheimer’s illness. To research this additional, on this find out about, we tested the function of endogenous OXT in mouse cognitive serve as. This used to be achieved via the use of pharmacogenetic ways to in particular turn on OXT neurons in particular mind areas. The cognitive serve as of mice used to be then evaluated the use of the Novel Object Reputation Process,” Saitoh explainedInvestigating Oxytocin’s Position in MemoryTo read about the results of oxytocin on reminiscence, the researchers hired a complicated chemogenetic solution to selectively turn on oxytocin-producing neurons within the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus in mice. This technique allowed for actual keep watch over over the task of those neurons, offering a transparent image of the way endogenous oxytocin influences cognitive serve as.The find out about concerned 51 male mice, in particular engineered to permit for centered activation of oxytocin neurons. The mice underwent a chain of behavioral checks, together with the Novel Object Reputation Process (NORT) and the Y-maze take a look at, to guage their reminiscence features. Via evaluating the conduct of mice with activated oxytocin neurons to these with commonplace neuron task, the researchers may just discern the precise contribution of oxytocin to reminiscence processes.Findings: Oxytocin Complements Lengthy-term MemoryActivation of oxytocin neurons within the PVN didn’t have an effect on non permanent spatial reminiscence, as proven via the Y-maze take a look at. Alternatively, it considerably progressed long-term object popularity reminiscence within the NORT. This enhancement used to be related to larger task in each the supramammillary nucleus (SuM) and the dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus — spaces of the mind recognized to be enthusiastic about reminiscence formation and retrieval.Additional experiments demonstrated that without delay activating oxytocin-releasing axons within the SuM ended in a marked development within the mice’s skill to acknowledge new gadgets. This means a selected pathway in which oxytocin acts to modulate reminiscence: via influencing neuronal task within the SuM, which in flip impacts reminiscence processing within the hippocampus.“There’s a extensively stated trust that dementia has a tendency to advance extra hastily in settings the place people revel in loneliness or restricted social engagement. Alternatively, the medical underpinnings of this phenomenon have remained in large part elusive. Our analysis seeks to clarify the the most important function of a stimulating setting that turns on oxytocin within the mind, doubtlessly mitigating the development of dementia,” Saitoh mentioned.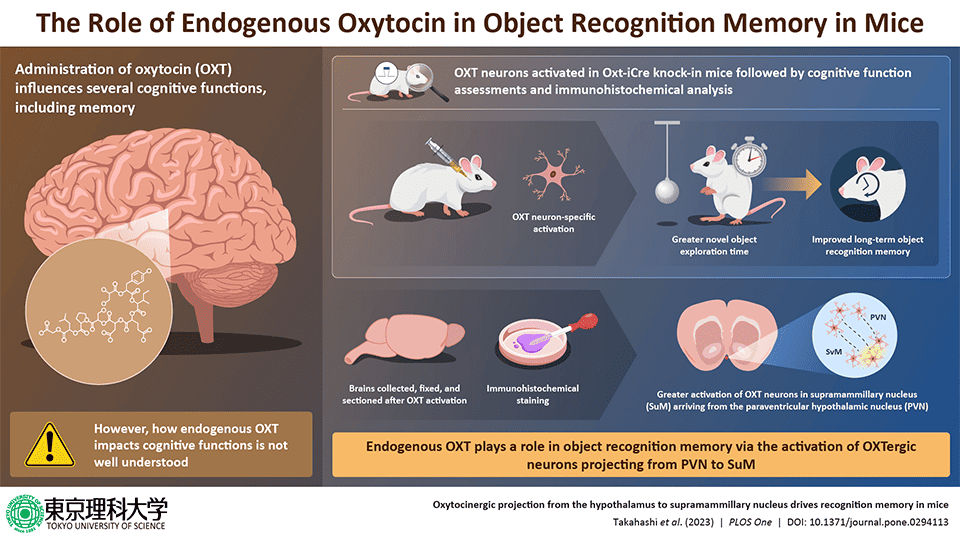 Barriers and Long run DirectionsWhile the find out about provides precious insights into the function of oxytocin in reminiscence, the researchers recognize its boundaries. As an example, the find out about used to be performed completely on male mice, leaving open the query of whether or not an identical mechanisms perform in women. Moreover, the point of interest on chemogenetic activation of oxytocin neurons approach the findings might indirectly translate to herbal prerequisites the place oxytocin unlock is influenced via a mess of things.Long run analysis will want to discover those dynamics additional, doubtlessly increasing the scope to incorporate feminine topics and analyzing the results of oxytocin throughout other phases of reminiscence formation and retrieval. Additionally, working out the interaction between oxytocin and different neurotransmitters enthusiastic about reminiscence may just light up new healing objectives for reminiscence impairment and dementia.The find out about, “Oxytocinergic projection from the hypothalamus to supramammillary nucleus drives popularity reminiscence in mice“, used to be authored via Junpei Takahashi, Daisuke Yamada, Wakana Nagano, Yoshitake Sano, Teiichi Furuichi, and Akiyoshi Saitoh.
Barriers and Long run DirectionsWhile the find out about provides precious insights into the function of oxytocin in reminiscence, the researchers recognize its boundaries. As an example, the find out about used to be performed completely on male mice, leaving open the query of whether or not an identical mechanisms perform in women. Moreover, the point of interest on chemogenetic activation of oxytocin neurons approach the findings might indirectly translate to herbal prerequisites the place oxytocin unlock is influenced via a mess of things.Long run analysis will want to discover those dynamics additional, doubtlessly increasing the scope to incorporate feminine topics and analyzing the results of oxytocin throughout other phases of reminiscence formation and retrieval. Additionally, working out the interaction between oxytocin and different neurotransmitters enthusiastic about reminiscence may just light up new healing objectives for reminiscence impairment and dementia.The find out about, “Oxytocinergic projection from the hypothalamus to supramammillary nucleus drives popularity reminiscence in mice“, used to be authored via Junpei Takahashi, Daisuke Yamada, Wakana Nagano, Yoshitake Sano, Teiichi Furuichi, and Akiyoshi Saitoh.
The “love hormone” holds the important thing to raised reminiscence, in keeping with new neuroscience analysis