Whilst our frame shuts down in shut eye on a daily basis, the mind stays busy at paintings, submitting in the course of the day’s recordings and making sense of them with admire to previous stories.Simply how contemporary recollections are processed with out blurring into outdated memories hasn’t ever been transparent, with scientists hypothesizing other strategies of preserving our recollections separate whilst we sleep.
Researchers from Cornell College in america strapped brain-scanning electrodes and tiny eye-tracking cameras to mice, tracking them as they discovered new duties within the day, equivalent to navigating a maze, and slept right through the night time. (A laugh truth: mice can sleep with their eyes open.)
The staff discovered two substages taking place right through non-rapid eye motion (NREM) sleep, that restorative length an important to forming recollections. One replayed new recollections, coinciding with a constriction of the pupils. The opposite substage featured recall of older recollections, with the pupils dilated. Every section came about in fast succession.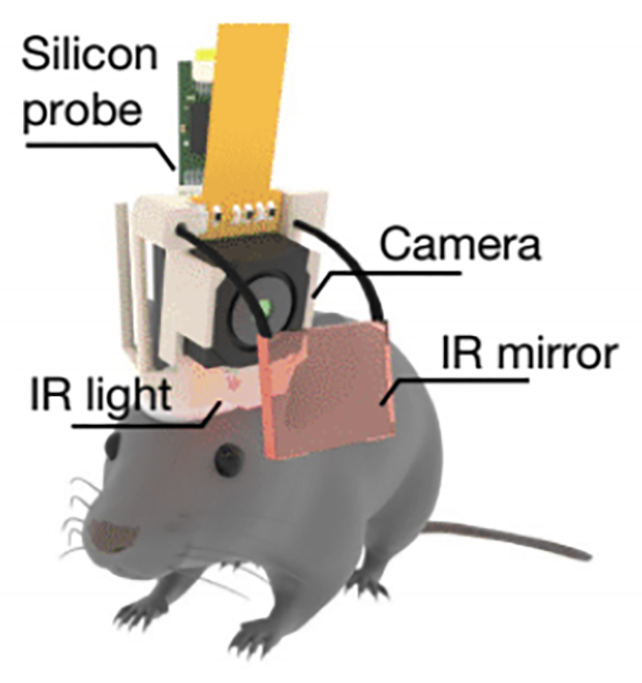 Researchers tracked mouse mind and eye job for a month. (Chang et al., Nature, 2025)The findings assist resolution the query of why consolidation of latest recollections does not erase outdated ones; for instance, finding out to play the piano with out forgetting the best way to journey a motorcycle. A equivalent research will want to be performed in people to make sure the effects, despite the fact that we do proportion numerous mind similarities with mice.
Researchers tracked mouse mind and eye job for a month. (Chang et al., Nature, 2025)The findings assist resolution the query of why consolidation of latest recollections does not erase outdated ones; for instance, finding out to play the piano with out forgetting the best way to journey a motorcycle. A equivalent research will want to be performed in people to make sure the effects, despite the fact that we do proportion numerous mind similarities with mice.
“Our effects recommend that the mind can multiplex distinct cognitive processes right through sleep to facilitate steady finding out with out interference,” write the researchers of their revealed paper.
Earlier research have known hyperlinks between student measurement and sleep state, and between sleep state and reminiscence formation, however this learn about provides an entire new stage of element to these connections.
Prior to now, there were numerous debate over how the mind fitted new recollections in among the outdated ones right through sleep – particularly, simply how separated and intentional those processes are.
The staff additionally discovered that blockading sharp-wave ripples (SWRs) – recognized to have an effect on reminiscence garage – right through reduced in size student phases within the mice restricted their functions to keep in mind anything else new.
“It is like new finding out, outdated wisdom, new finding out, outdated wisdom, and that’s fluctuating slowly all over the sleep,” says neuroscientist Azahara Oliva, from Cornell College.
“We’re proposing that the mind has this intermediate timescale that separates the brand new finding out from the outdated wisdom.”
The consequences of the learn about are far-reaching: having a non-invasive method of tracking mind serve as would possibly assist within the remedy of reminiscence problems or the boosting of reminiscence, for instance.
The findings additionally lend weight to hypotheses on how our brains and pc techniques have the possible to disregard outdated knowledge on a vital scale. In AI, it is referred to as catastrophic forgetting, and is one space the place the machines are nonetheless method in the back of biology.
“This discovering supplies a possible resolution for the long-standing drawback in each organic and synthetic neural networks of forestalling catastrophic interference whilst additionally enabling reminiscence integration,” write the researchers.The analysis has been revealed in Nature.
The Measurement of Your Pupils Whilst You Sleep May just Disclose The Reminiscences You might be Reliving