New findings from the Gaia house telescope point out the Milky Means will have cannibalized a small galaxy no longer too way back, cosmically talking. In truth, the closing primary collision between our galaxy and every other turns out to have befell billions of years later than up to now suspected.The Milky Means has been lengthy understood to have grown by means of a chain of violent collisions, which see smaller galaxies ripped aside by means of the immense gravitational affect of our sun machine’s spiral house. Those collisions distribute stars from the wolfed galaxy around the halo that surrounds the primary disk of the Milky Means and its unique spiral hands. Those bouts of galactic cannibalism additionally ship “wrinkles” rippling during the Milky Means that impact other “households” of stars, with other origins, in numerous techniques. With its talent to exactly pinpoint the location and movement of over 100,000 stars native to the sun machine throughout the complete catalog of stellar our bodies in screens, Gaia objectives to retell the historical past of the Milky Means by means of counting its wrinkles. Similar: Within the Milky Means, 3 intruder stars are ‘at the run’ — within the incorrect route”We get wrinklier as we age, however our paintings finds that the other is correct for the Milky Means. It’s a kind of cosmic Benjamin Button, getting much less wrinkly through the years,” Thomas Donlon, learn about group chief of the Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and College of Alabama scientist, stated in a observation. “Through taking a look at how those wrinkles deplete through the years, we will hint when the Milky Means skilled its closing large crash – and it seems this came about billions of years later than we idea.”Those galactic wrinkles have been simplest found out by means of Gaia in 2018; this marks the primary time they’ve been widely researched to show the timing of the collision that created them.Halo stars shifting in ordinary waysThe halo of our galaxy is populated with stars that experience ordinary orbits, with many of those believed to be the “leftovers” of galaxies the Milky Means as soon as wolfed.Breaking house information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!A lot of the ones stars are believed to be the wreckage of the so-called “closing primary merger,” relating to the closing time the Milky Means skilled an important collision with every other galaxy. Scientists suppose this ultimate primary collision will have concerned an enormous dwarf galaxy, and the development is referred to as the Gaia-Sausage-Enceladus (GSE) merger. It’s idea to have infused the Milky Means with stars on orbits that carry them with regards to the Galactic Heart. The GSE tournament is believed to have came about between 8 and 11 billion years in the past when the Milky Means was once in its infancy.Since 2020, Thomas and his group had been evaluating the Milky Means’s wrinkles to simulations of ways galactic collisions and mergers may have created them. Alternatively, the Gaia observations of those surprisingly orbiting stars — launched as a part of the distance telescope’s Information Unencumber 3 in 2022 — point out those ordinary stellar our bodies may have been deposited by means of a special merger tournament.”We will be able to see how the shapes and choice of wrinkles trade through the years the use of those simulated mergers. This we could us pinpoint the precise time when the simulation perfect fits what we see in actual Gaia information of the Milky Means these days — a technique we used on this new learn about, too,” defined Donlon. “Through doing this, we discovered that the wrinkles have been most probably led to by means of a dwarf galaxy colliding with the Milky Means round 2.7 billion years in the past. We named this tournament the Virgo Radial Merger.”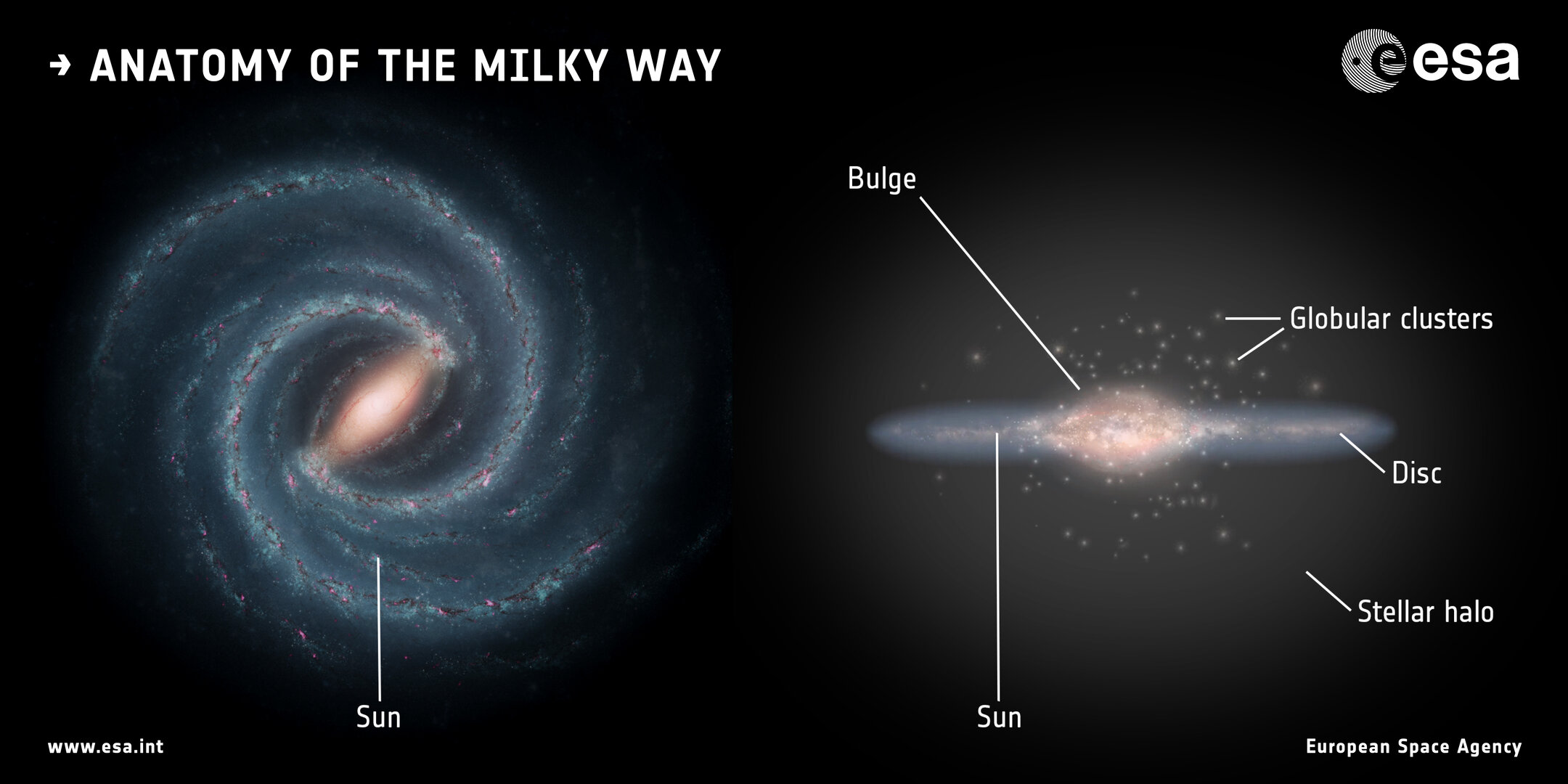 A diagram displays the anatomy of the Milky Means with the central bulge the place the traditional stars lurk indicated. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech; proper: ESA; format: ESA/ATG medialab)”For the wrinkles of stars to be as transparent as they seem in Gaia information, they will have to have joined us lower than 3 billion years in the past — a minimum of 5 billion years later than was once up to now idea,” group member Heidi Jo Newberg, additionally of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, stated. “New wrinkles of stars shape every time the celebs swing backward and forward during the middle of the Milky Means. If they might joined us 8 billion years in the past, there can be such a lot of wrinkles proper subsequent to one another that we might now not see them as separate options.”
A diagram displays the anatomy of the Milky Means with the central bulge the place the traditional stars lurk indicated. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech; proper: ESA; format: ESA/ATG medialab)”For the wrinkles of stars to be as transparent as they seem in Gaia information, they will have to have joined us lower than 3 billion years in the past — a minimum of 5 billion years later than was once up to now idea,” group member Heidi Jo Newberg, additionally of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, stated. “New wrinkles of stars shape every time the celebs swing backward and forward during the middle of the Milky Means. If they might joined us 8 billion years in the past, there can be such a lot of wrinkles proper subsequent to one another that we might now not see them as separate options.”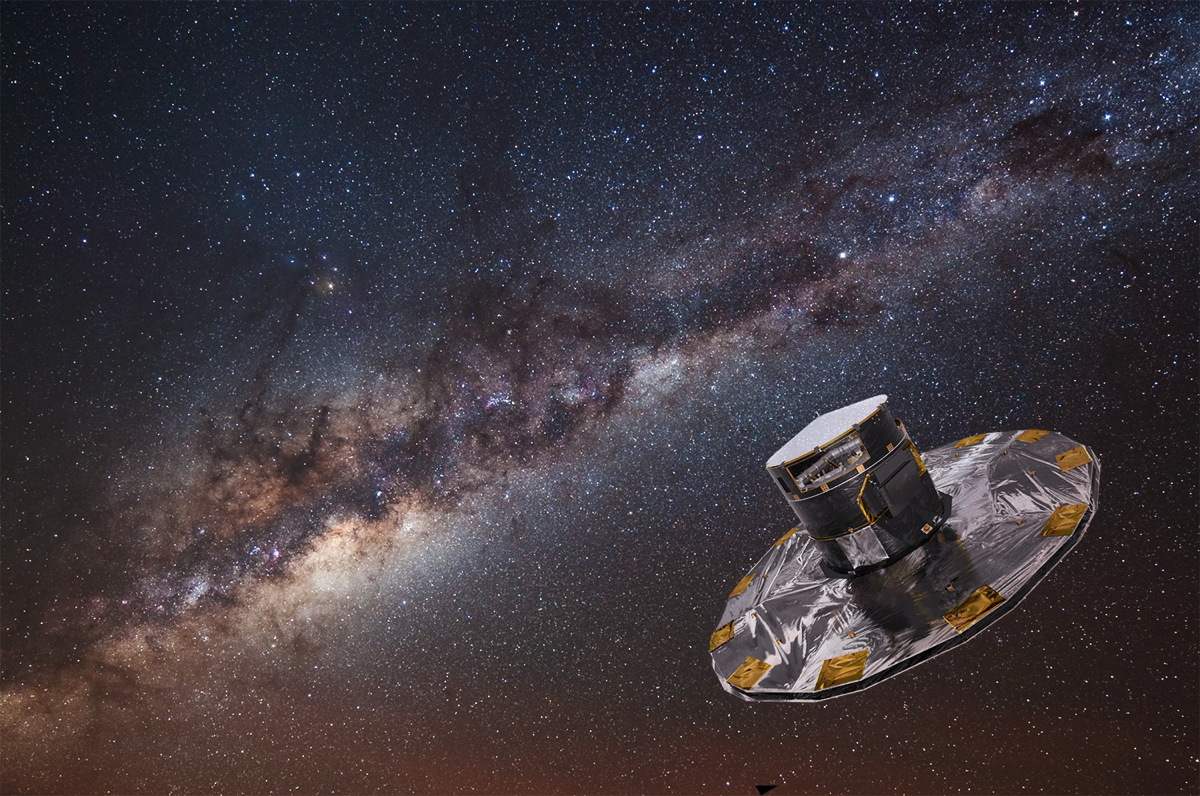 Artist’s idea of the Eu Area Company’s Gaia spacecraft mapping stars within the Milky Means galaxy. (Symbol credit score: ESA/ATG medialab/ESO/S. Brunier)The new exam of Gaia’s observations calls into query whether or not an enormous historical merger within the early historical past of the Milky Means is actually wanted to give an explanation for the ordinary orbits of a few stars within the galactic. It additionally casts doubt on the entire stars up to now related to the GSE merger.”This consequence — that an enormous portion of the Milky Means simplest joined us inside the previous couple of billion years — is a large trade from what astronomers idea up till now,” Donlon stated. “Many standard fashions and concepts about how the Milky Means grows would be expecting a contemporary head-on collision with a dwarf galaxy of this mass to be very uncommon.”The group additionally thinks that the Virgo Radial Merger delivered to our galaxy a circle of relatives of different small dwarf galaxies and superstar clusters, all of which might even have been wolfed by means of the Milky Means at round the similar time.Long run investigation and information from Gaia may just display if any items up to now related to the GSE tournament are if truth be told hooked up to the more moderen Virgo Radial Merger.This new analysis is the most recent in a treasure trove of effects rising from Gaia information which are rewriting the historical past of the Milky Means. Such cosmic revisionism has been made imaginable because of Gaia’s distinctive talent to discover an infinite choice of stars over Earth, permitting the distance telescope to collect an unmatched map of the positions, distances and motions of round 1.5 billion stars to this point.”The Milky Means’s historical past is continuously being rewritten, in no small phase, because of new information from Gaia,” Donlon concluded. “Our image of the Milky Means’s previous has modified dramatically from even a decade in the past, and I feel our figuring out of those mergers will proceed to switch hastily.”The group’s analysis was once printed in Might in the magazine Per thirty days Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Artist’s idea of the Eu Area Company’s Gaia spacecraft mapping stars within the Milky Means galaxy. (Symbol credit score: ESA/ATG medialab/ESO/S. Brunier)The new exam of Gaia’s observations calls into query whether or not an enormous historical merger within the early historical past of the Milky Means is actually wanted to give an explanation for the ordinary orbits of a few stars within the galactic. It additionally casts doubt on the entire stars up to now related to the GSE merger.”This consequence — that an enormous portion of the Milky Means simplest joined us inside the previous couple of billion years — is a large trade from what astronomers idea up till now,” Donlon stated. “Many standard fashions and concepts about how the Milky Means grows would be expecting a contemporary head-on collision with a dwarf galaxy of this mass to be very uncommon.”The group additionally thinks that the Virgo Radial Merger delivered to our galaxy a circle of relatives of different small dwarf galaxies and superstar clusters, all of which might even have been wolfed by means of the Milky Means at round the similar time.Long run investigation and information from Gaia may just display if any items up to now related to the GSE tournament are if truth be told hooked up to the more moderen Virgo Radial Merger.This new analysis is the most recent in a treasure trove of effects rising from Gaia information which are rewriting the historical past of the Milky Means. Such cosmic revisionism has been made imaginable because of Gaia’s distinctive talent to discover an infinite choice of stars over Earth, permitting the distance telescope to collect an unmatched map of the positions, distances and motions of round 1.5 billion stars to this point.”The Milky Means’s historical past is continuously being rewritten, in no small phase, because of new information from Gaia,” Donlon concluded. “Our image of the Milky Means’s previous has modified dramatically from even a decade in the past, and I feel our figuring out of those mergers will proceed to switch hastily.”The group’s analysis was once printed in Might in the magazine Per thirty days Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
The Milky Means’s closing primary act of galactic cannibalism was once unusually contemporary