Join the Begins With a Bang e-newsletter
Shuttle the universe with Dr. Ethan Siegel as he solutions the most important questions of all
No longer best in the USA, however all internationally, humanity celebrated 2024 because the fifty fifth anniversary of the end result of the Area Race: the search to position a human being at the Moon and safely go back them to Earth. On July 20, 1969, our species completed a dream older than civilization itself, as human beings set foot at the floor of some other international past Earth once they walked at the floor of the Moon, some 380,000 km away. From 1969 via 1972, a complete of 12 American astronauts walked at the lunar floor, marking the primary and best time to this point that human beings have set foot at the forged floor of an international past our personal planet.If any country was once going to do it, maximum concept it was once going to be the Soviet Union. The Soviets had been first to each and every milestone in area prior to that:
the primary satellite tv for pc,
the primary crewed spaceflight,
the primary consumer to orbit the Earth,
the primary lady in area,
the primary spacewalk,
the primary landers on some other international,
and a lot more. After the disastrous Apollo 1 hearth, it gave the impression of a foregone conclusion that the Soviets will be the first to stroll at the Moon. But they by no means even got here shut. Why no longer? The solution lies in a reputation that most of the people have almost certainly by no means heard of: Sergei Korolev. Right here’s what everybody ought to understand.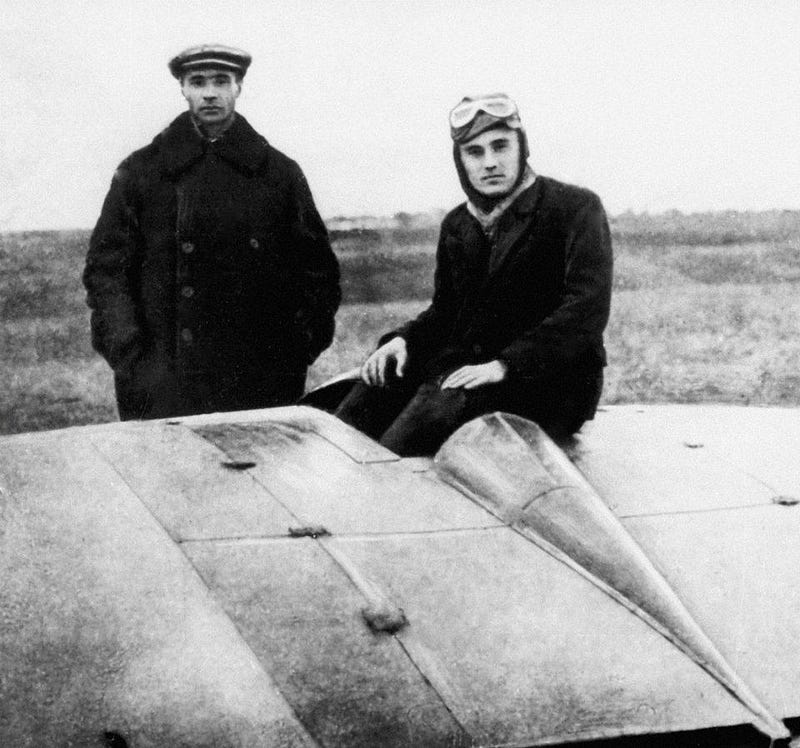 Sergei Korolev, at proper, was once to begin with an aerospace pilot and a pupil of Tsiolkovsky’s paintings prior to changing into a rocket and spacecraft fashion designer. He’s proven right here with fashion designer Boris Cheranovsky close to a BICh-8 glider, in a photograph from 1931.
Sergei Korolev, at proper, was once to begin with an aerospace pilot and a pupil of Tsiolkovsky’s paintings prior to changing into a rocket and spacecraft fashion designer. He’s proven right here with fashion designer Boris Cheranovsky close to a BICh-8 glider, in a photograph from 1931.
Credit score: public area
Lengthy prior to humanity ever broke the gravitational bonds of Earth, there have been a couple of scientists running to pioneer a brand new medical box: theoretical astronautics. Whilst it had a lot in commonplace with standard aeronautics, in accordance with the physics of Newton, there have been further restrictions and issues that got here at the side of the speculation of journeying into area. Not like with terrestrial flight, journeying into area essentially intended:
wanting a gasoline supply that would propel you within the absence of an environment,
the power to frequently boost up for lengthy classes of time,
fabrics that will stay people and kit secure in any respect temperatures and pressures completed all the way through flight,
coverage in opposition to sun and cosmic radiation and the cruel exterior vacuum of area,
and calculating tips on how to maximize the deliverable payload with constraints on gasoline and rocket mass.
Within the early days, all of those issues had been mulled over by means of theorists on my own. A couple of pioneers stand out within the historical past of the early twentieth century: Robert Goddard, who created and introduced the primary liquid-fueled rocket; Robert Esnault-Pelterie, who started designing airplanes and plane engines however later moved directly to rocketry, growing the speculation of rocket maneuvering; and Hermann Oberth, who constructed and introduced rockets, rocket motors, liquid-fueled rockets, and mentored a tender Wernher von Braun.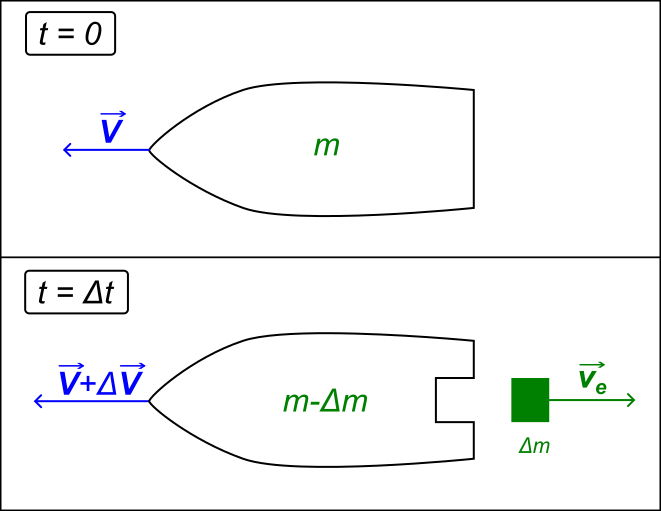 The Tsiolkovsky rocket equation is needed to explain how briskly a spacecraft that burns via a portion of its gasoline to create thrust can finish up touring throughout the Universe. Having to carry your individual gasoline on board is a significantly restricting issue so far as the rate at which we will trip via intergalactic area.
The Tsiolkovsky rocket equation is needed to explain how briskly a spacecraft that burns via a portion of its gasoline to create thrust can finish up touring throughout the Universe. Having to carry your individual gasoline on board is a significantly restricting issue so far as the rate at which we will trip via intergalactic area.
Credit score: Halserach/Wikimedia Commons
However prior to any of them got here Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, who was once the primary to grasp the essential dating between consumable rocket gasoline, mass, thrust, and acceleration. Most likely greater than some other consumer, Tsiolkovsky’s early works influenced the advance of spaceflight and area exploration around the globe. And whilst Goddard was once American, Esnault-Pelterie was once French, and Oberth was once German, Tsiolkovsky lived his complete existence in and round Moscow: first in Russia, and after the October Revolution, the Soviet Union (or USSR).Even if Tsiolkovsky died in 1935, his paintings left an enduring medical legacy, in particular in Russia. Sergey Korolev was once Tsiolkovsky’s pioneering experimental counterpart, who dreamed of touring to Mars and introduced, in 1933, the primary Soviet liquid-fueled rocket and the primary hybrid-fueled rocket. In 1938, then again, he turned into a sufferer of Stalin’s Nice Purge. Korolev was once imprisoned within the Gulag, the place he languished all through maximum of Global Warfare II: till 1944.As soon as Global Warfare II ended, each the US’s and the USSR’s area systems had been boosted by means of the addition of captured German scientists. The US were given many of the best German scientists and a slew of V-2 rockets, however the Soviet Union captured lots of the German information, together with drawings from V-2 manufacturing websites, and likewise the influential scientist Helmut Gröttrup. Not like the US, regardless that, the legacy of Tsiolkovsky gave the Soviets an preliminary edge.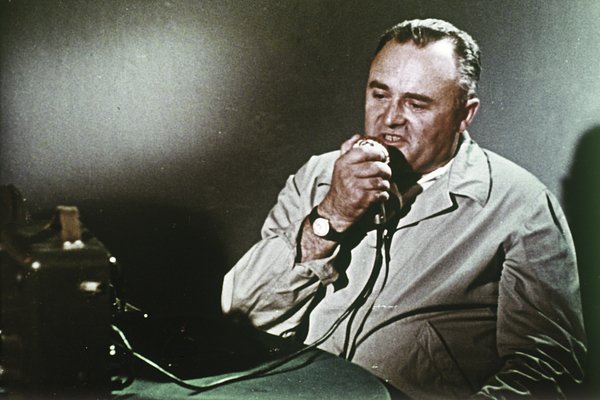 Sergei Korolev, proven right here in 1961, served many purposes within the Soviet area program, together with because the tablet commander from the bottom all the way through lots of the crewed spaceflights of the Sixties.
Sergei Korolev, proven right here in 1961, served many purposes within the Soviet area program, together with because the tablet commander from the bottom all the way through lots of the crewed spaceflights of the Sixties.
Credit score: RIA Novosti
This mixture — of German V-2 generation, Tsiolkovsky’s theoretical paintings, and Korolev’s brainpower and creativeness — proved an implausible recipe for Soviet luck within the mission of area exploration. Korolev’s upward push upon his unlock from the Gulag was once not anything in need of meteoric.In 1945, he was once commissioned as a colonel within the Purple Military, the place he instantly started paintings on growing rocket motors. After being adorned with the Badge of Honor later that 12 months, he was once delivered to Germany to assist recuperate V-2 rocket generation. Through 1946, Korolev was once put accountable for overseeing a workforce of many German consultants, together with Gröttrup, within the enterprise to broaden a countrywide rocket and missile program. Korolev was once appointed as leader fashion designer of long-range missiles, the place by means of 1947, his workforce was once launching R-1 rockets: absolute best replicas of the German V-2 designs.Certain, the USA was once doing one thing very identical: launching V-2 rockets from White Sands missile base in New Mexico within the past due Nineteen Forties, taking complete benefit of post-war German generation. However starting in 1947, the Korolev-led workforce started running on advancing and making improvements to the design of the Soviet R-1 rockets, main to larger missile levels and the implementation of separate-stage payloads, which might simply double as warheads.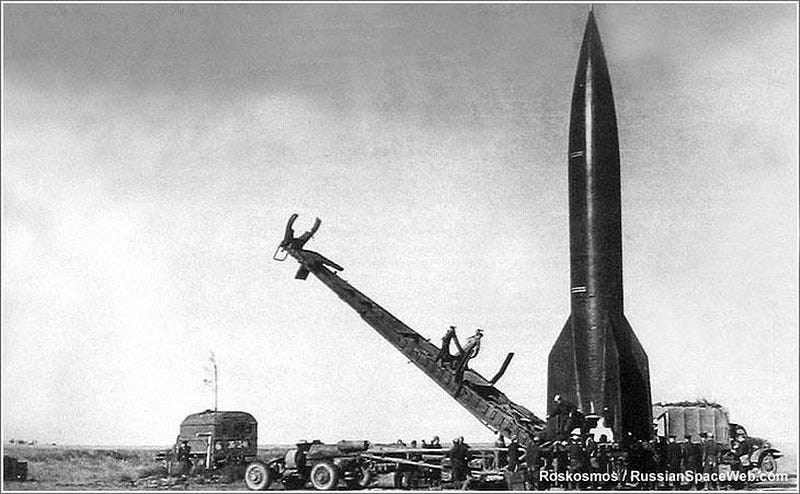 The primary R-1 rocket introduced from Russia befell in September of 1948, from Kapustin Yar. Of the 12 rockets delivered, 9 had been introduced and 7 effectively hit their objectives: about on par with the luck charges of the German V-2 rockets they had been designed to duplicate.
The primary R-1 rocket introduced from Russia befell in September of 1948, from Kapustin Yar. Of the 12 rockets delivered, 9 had been introduced and 7 effectively hit their objectives: about on par with the luck charges of the German V-2 rockets they had been designed to duplicate.
Credit score: Roskosmos/RussianSpaceWeb
Through 1949, the Soviets had been launching R-2 rockets designed by means of Korolev, with double the variety and advanced accuracy over the unique V-2 clones, however Korolev was once already considering additional. As early as 1947, Korolev had get a hold of a completely novel design for an R-3 missile, with a variety of three,000 kilometers: sufficient to succeed in England from Moscow.The incremental enhancements to rocket and missile generation gathered at a staggering tempo beneath Korolev’s steerage. Through 1957, the Soviets had completed the primary a success check flight of the R-7 Semyorka: the sector’s first intercontinental ballistic missile. The R-7 was once a two-stage rocket with a most differ of seven,000 kilometers and a payload of five.4 lots, sufficient to hold a Soviet nuclear bomb from St. Petersburg to New York Town.Those achievements catapulted Korolev to nationwide prominence throughout the Soviet Union. He was once declared totally rehabilitated, and started advocating for the use of the R-7 to release a satellite tv for pc into area, met with utter disinterest from the Communist Birthday celebration. But if the USA media started discussing the chances of making an investment tens of millions of greenbacks to release a satellite tv for pc, Korolev seized his likelihood. In not up to a month, Sputnik 1 was once designed, built, and introduced.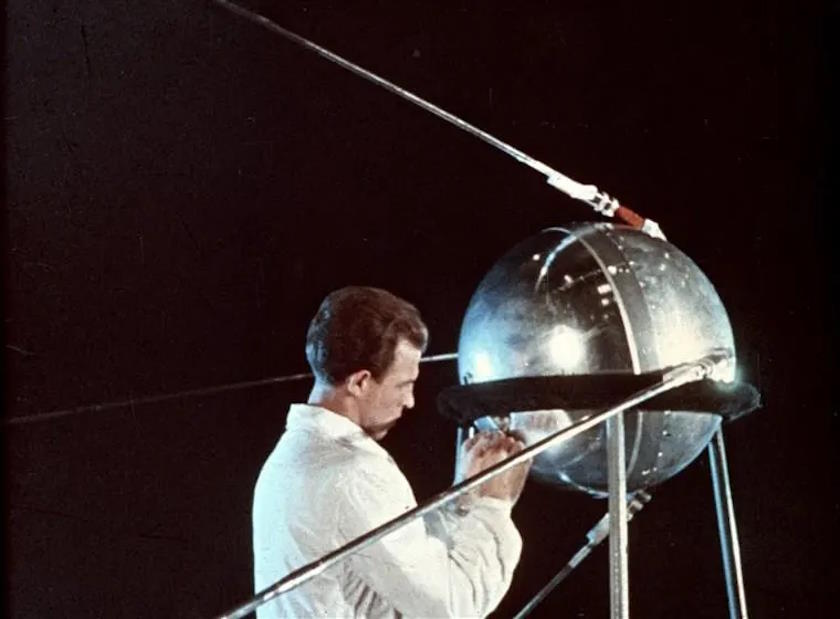 A technician running on Sputnik 1, previous to its release on October 4, 1957. After an insignificant 3 months in area, Sputnik 1 fell again to Earth because of atmospheric drag, an issue that plagues all low-Earth-orbiting satellites even as of late.
A technician running on Sputnik 1, previous to its release on October 4, 1957. After an insignificant 3 months in area, Sputnik 1 fell again to Earth because of atmospheric drag, an issue that plagues all low-Earth-orbiting satellites even as of late.
Credit score: NASA/Asif A. Siddiqi
On October 4, 1957, the distance age formally started. Korolev’s rockets had introduced humanity above the bonds of Earth’s gravity and into orbit. Whilst Khrushchev was once to begin with uninterested in Korolev’s rocket launches, the global reputation for his achievements was once too broad to forget about at the global degree. Not up to a month later, Sputnik 2 — six instances the mass of Sputnik 1 — was once introduced, wearing Laika the canine into orbit.The release of the complicated Sputnik 3, whole with medical tools and a primitive recording tool, befell in Might of 1958, demonstrating the functions of the Soviet area program. However Korolev had his points of interest on a larger goal: the Moon. To start with wanting to make use of the R-7 to hold a package deal there, Korolev changed the rocket’s higher degree to be optimized to be used in outer area and outer area on my own: the primary rocket designed with this type of objective.In spite of a huge loss of investment, time force, and an lack of ability to check {hardware} previous to release, Korolev was once made up our minds to release a payload to the Moon. On January 2, 1959, The Luna 1 project reached the Moon, however flew previous as a substitute of impacting it, which was once the intent. (It ignored by means of not up to 6,000 kilometers.) On September 14, 1959, Luna 2 succeeded: changing into the primary human-made object to reach at the Moon. The unique symbol of the some distance facet of the Moon from the USSR’s Luna 3 project (A), at the side of its fashionable virtual recovery (B), in comparison with a contemporary view of the Moon’s some distance facet from NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (C). Luna 3’s {photograph} of the Moon’s some distance facet was once taken long ago in 1959: some other “first” in area for the USSR.
The unique symbol of the some distance facet of the Moon from the USSR’s Luna 3 project (A), at the side of its fashionable virtual recovery (B), in comparison with a contemporary view of the Moon’s some distance facet from NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (C). Luna 3’s {photograph} of the Moon’s some distance facet was once taken long ago in 1959: some other “first” in area for the USSR.
Credit score: Prasantapalwiki/Wikimedia Commons
Not up to a month later, Luna 3 took the primary {photograph} of the Moon’s some distance facet. Within the realm of area exploration, the Soviets had been attaining new milestones whilst the USA was once compelled to play catch-up. Korolev’s achievements led the way in which, along with his desires rising ever better. He sought to make the primary cushy touchdown at the Moon, and had his points of interest on Mars and Venus as smartly. However his largest dream was once for human spaceflight, and to carry people any place his rockets may take them.Starting in 1958, Korolev started endeavor design research for what would change into the Soviet Vostok spacecraft: a completely computerized tablet able to conserving a human passenger in an area go well with. Through Might of 1960, an uncrewed prototype was once introduced, orbiting the Earth 64 instances prior to failing re-entry. On August 19, 1960, two canines, Beika and Streika, had been introduced into low-Earth orbit and effectively returned, marking the primary time a dwelling creature was once introduced into area and recovered.On April 12, 1961, Korolev’s changed R-7 introduced Yuri Gagarin into area: the primary human to wreck the gravitational bonds of Earth, and likewise the primary human to orbit Earth. The extra Vostok flights, beneath Korolev’s watch (he served because the tablet coordinator), incorporated the primary inter-spacecraft communications and rendezvous, in addition to the primary lady cosmonaut: Valentina Tereshkova.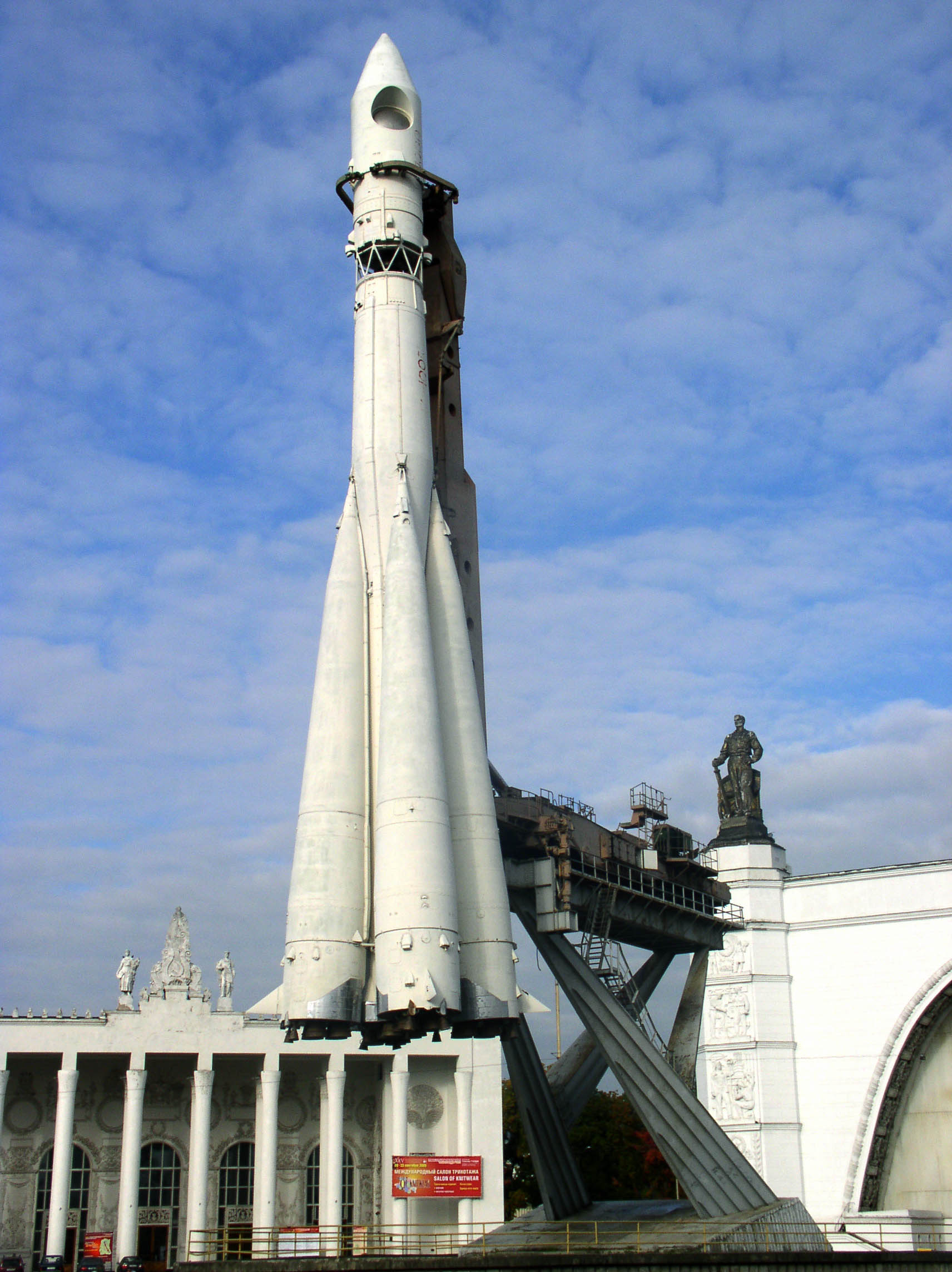 The Soviet rocket R-7 Semyorka, as proven right here, had a twin objective: to function an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) but additionally to permit the supply of large-mass payloads to area. Yuri Gagarin’s notorious flight, the place he turned into the primary human to voyage into area, got here aboard a changed R-7 rocket.
The Soviet rocket R-7 Semyorka, as proven right here, had a twin objective: to function an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) but additionally to permit the supply of large-mass payloads to area. Yuri Gagarin’s notorious flight, the place he turned into the primary human to voyage into area, got here aboard a changed R-7 rocket.
Credit score: Alex Zelenko/Wikimedia Commons
Korolev then started paintings at the Voskhod programme, with without equal objective of sending more than one astronauts into area and sooner or later to the Moon. As early as 1961, Korolev started designing a superheavy release rocket: the N-1, which used an NK-15 liquid gasoline engine and was once of the similar scale because the Saturn V. With the capability for a three-person staff and the aptitude of acting a cushy touchdown upon go back, the Soviets had been poised to take your next step within the Area Race.On October 12, 1964, a staff of 3 Soviet cosmonauts — Vladimir Komarov, Boris Yegorov and Konstantin Feoktistov — finished 16 orbits in area aboard Voskhod 1. 5 months later, Alexei Leonov, aboard Vostok 2, carried out humanity’s first spacewalk. Your next step was once to succeed in for the Moon, and Korolev was once able. With the 1964 fall of Khrushchev, Korolev was once installed sole fee of the crewed area program, with the objective of a lunar touchdown set to happen in October of 1967, which might mark the fiftieth anniversary of the October revolution. The entirety gave the impression smartly inside achieve.Korolev started designing the Soyuz spacecraft that will lift crews to the Moon, in addition to the Luna automobiles that will land softly at the Moon, plus robot missions to Mars and Venus. Korolev additionally sought to satisfy Tsiolkovsky’s dream of placing people on Mars, with plans for closed-loop existence fortify techniques, electric rocket engines, and orbiting area stations to function interplanetary release websites.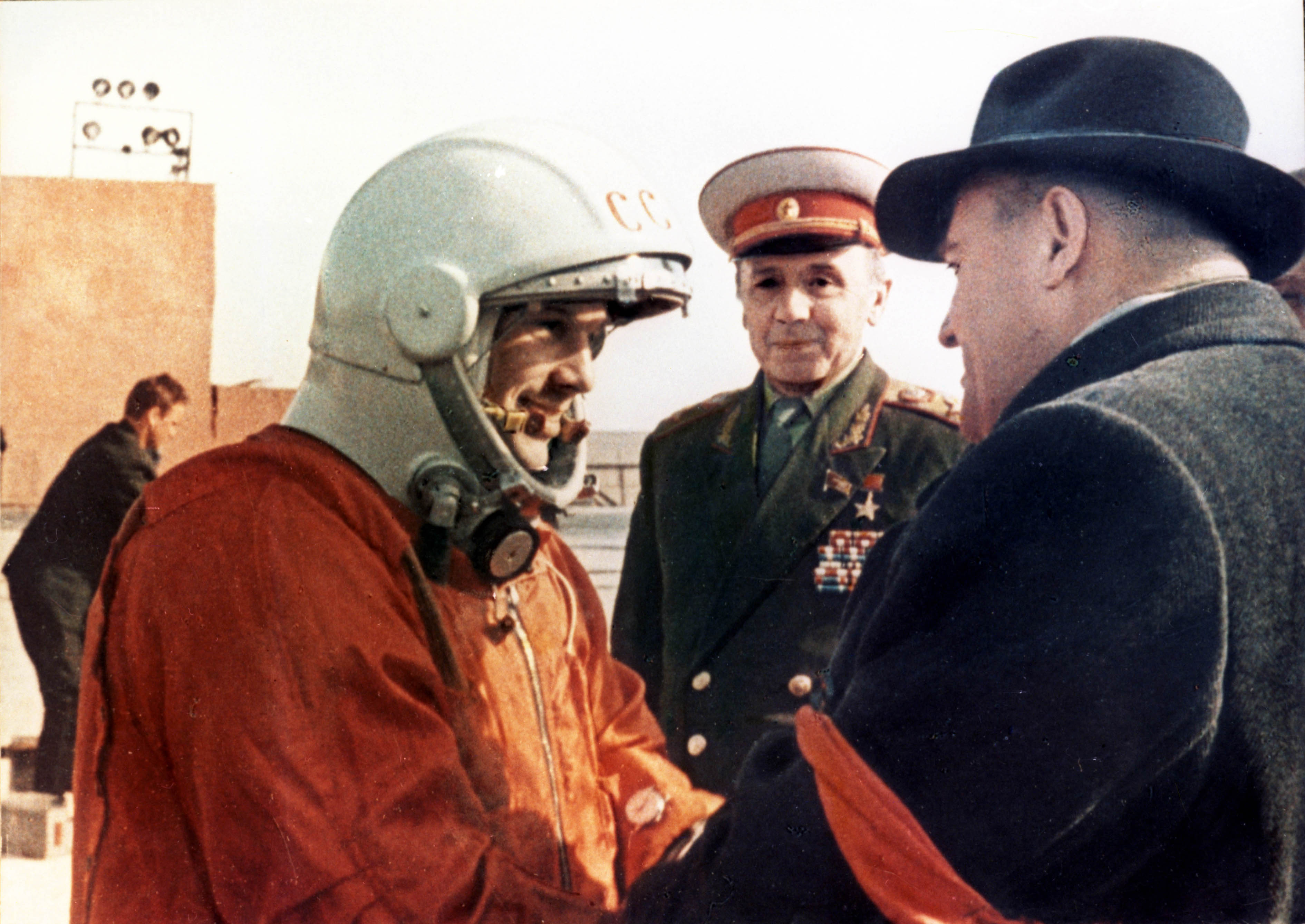 Cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin (left) shaking palms with rocket fashion designer Sergei Korolev (proper) at Baikonur, simply prior to his flight into area, from April 12, 1961. Even if Korolev will not be the family title that Gagarin is, he’s universally heralded (by means of the ones no longer named Khrushchev) because the architect and motive force at the back of the successes of the Soviet crewed area program.
Cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin (left) shaking palms with rocket fashion designer Sergei Korolev (proper) at Baikonur, simply prior to his flight into area, from April 12, 1961. Even if Korolev will not be the family title that Gagarin is, he’s universally heralded (by means of the ones no longer named Khrushchev) because the architect and motive force at the back of the successes of the Soviet crewed area program.
Credit score: Минобороны РФ / РИА Новости
However it was once to not be: Korolev entered the sanatorium on January 5, 1966, for what was once considered regimen intestinal surgical procedure. 9 days later, he was once lifeless from what was once reported as colon most cancers headaches, despite the fact that many to these days suspect foul play. With out Korolev as the manager fashion designer, the whole thing went downhill briefly for the Soviets. Whilst he was once alive, Korolev fended off tried meddling from quite a few rival rocket designers, together with Mikhail Yangel, Vladimir Chhelomei, and Valentin Glushko. However the energy vacuum that arose after his dying proved catastrophic.Vasily Mishin was once selected as Korolev’s successor, and crisis instantly adopted. The Soviet targets for his or her area program remained slightly modified in any respect, with plans to have people orbit the Moon in 1967 and just a bit later to land at the Moon in 1968. Mishin was once beneath super force to reach those targets; failure was once unacceptable. On April 23, 1967, the Soyuz 1 project was once introduced, with Komarov on board: the primary crewed flight because the dying of Korolev.In spite of 203 design faults reported by means of venture engineers, the release nonetheless befell, instantly encountering a chain of disasters. First, one sun panel didn’t spread, resulting in insufficient energy. Then the orientation detectors malfunctioned, the automated stabilization gadget failed, and the release of Soyuz 2, anticipated to rendezvous with Soyuz 1, was once cancelled because of thunderstorms. Komarov’s record at the thirteenth orbit resulted in a project abort; 5 orbits (about 7 hours) later, Soyuz 1 fired its retrorockets and re-entered Earth’s setting. Because of some other defect, the principle parachute by no means opened up, and Komarov’s manually deployed reserve chute turned into tangled.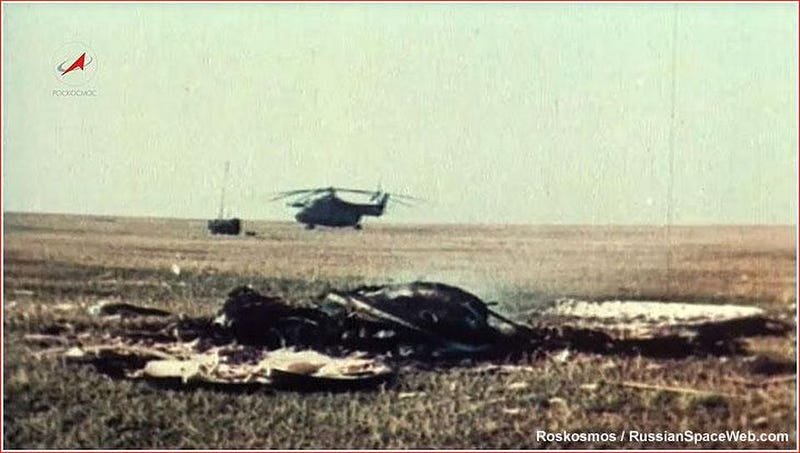 The wreckage of the Soyuz 1 project incorporated a fireplace that was once so catastrophic that it took more than one groups and plenty of makes an attempt to extinguish the flaming wreckage. Komarov was once killed by means of more than one blunt power trauma all the way through the catastrophic descent and re-entry.
The wreckage of the Soyuz 1 project incorporated a fireplace that was once so catastrophic that it took more than one groups and plenty of makes an attempt to extinguish the flaming wreckage. Komarov was once killed by means of more than one blunt power trauma all the way through the catastrophic descent and re-entry.
Credit score: Roskosmos/RussianSpaceWeb
The primary flight beneath Korolev’s successor had ended within the worst crisis possible: the primary in-flight fatality of any area program carried out by means of any area company on Earth. This may end up to not be a one-off tournament, both, as additional setbacks abruptly turned into the norm. Gagarin, the primary human in area, was once tragically killed in a check flight in 1968. Mishin evolved a consuming downside, coincident with more than one N-1 rocket disasters and explosions that adopted the Soviet Area program all through 1969. The lone shiny spots got here in January of 1969, the place the rendezvous, docking, and staff switch of cosmonauts between two Soyuz spacecraft had been completed.However the dying of Korolev, and the mishaps beneath his successors, are the true reason the Soviets misplaced their lead within the area race, and not completed the objective of touchdown people at the Moon. Smaller targets, akin to the primary robot rover at the Moon, in addition to the primary uncrewed landings on Mars and Venus, had been completed by means of the Soviet area program within the Seventies, however the large prize was once already taken off the desk. If no longer for Korolev’s surprising decline in well being and next dying at a vital time, most likely historical past would have grew to become out in a different way. In spite of everything, the management (or lack thereof) by means of a unmarried, competent consumer can in the end be the adaptation between luck and failure.
Join the Begins With a Bang e-newsletter
Shuttle the universe with Dr. Ethan Siegel as he solutions the most important questions of all




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-2155206502-5a8269261f8e477fb14ff4b861a0c5ab.jpg)








