Seeds have helped crops evolve into a panoramic number of paperwork that fill our international with colour and supply us with meals and medication. It is tricky to consider the place crops can be lately with out seeds. That raises a query: The place did the primary seeds come from?Crops began the use of seeds to breed towards the top of the Devonian duration (419 million to 359 million years in the past). Scientists are nonetheless learning the precise evolutionary origins of seeds, however the earliest showed seeding-plant fossils are from the Famennian age, which started round 372 million years in the past.For instance, Famennian fossils of the plant Elkinsia polymorpha came upon in West Virginia expose seed-bearing shoots, in line with the College of California, Berkeley Museum of Paleontology. Researchers have additionally discovered different examples of historic seeds in Europe and China.Gerhard Leubner, a plant biochemistry professor whose staff specializes in seed science analysis at Royal Holloway, College of London, mentioned crops most probably developed seeds quickly once they began rising on land.”They emerged from the ocean about 450 million years in the past,” Leubner informed Are living Science. “Slightly later, there’s a section the place ferns ruled the arena, and so they had spores, and from those spores, it’s believed plant seeds developed.”Similar: How do crops with seedless fruit reproduce?Some crops — together with mosses, algae and ferns — proceed to make use of spores, slightly than seeds, to breed, in line with a 2019 article in The Dialog via Marjorie Lundgren, a senior analysis fellow in plant environmental body structure at Lancaster College within the U.Ok.Get the arena’s most attractive discoveries delivered directly for your inbox.A spore is made up of a unmarried mobile with the DNA of 1 mum or dad plant, whilst a seed is a extra advanced multicellular organism that generally calls for two oldsters. A single-parent spore should first turn into one of those pre-plant degree referred to as a gametophyte, most effective turning into a plant when two of those gametophytes sign up for for fertilization. Seeds, in contrast, skip this degree as a result of a feminine plant produces seeds from a male plant’s pollen after fertilization.Leubner defined that seeds have plenty of benefits over spores. They are able to be a lot greater and feature laborious, protecting shells, making them extra resilient. They are able to additionally retailer meals to give you the new plant with a direct power supply.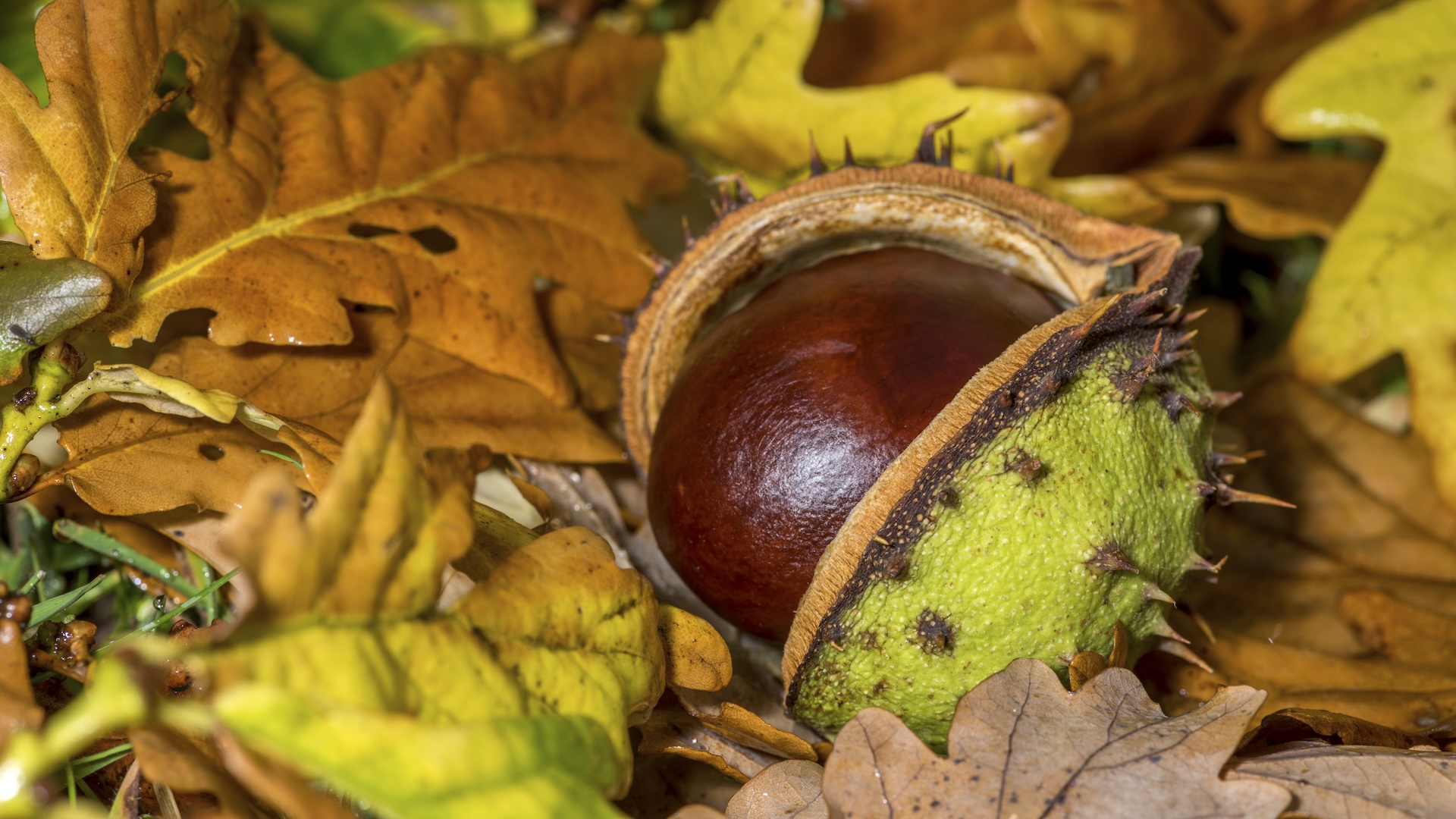 A conker, a fallen seed from a horse chestnut tree (Aesculus hippocastanum). (Symbol credit score: Michael Roberts by way of Getty Photographs)Spores additionally generally require a large number of moisture to forestall them from drying out, whilst seeds are able to adapting to plenty of other environments, which is most probably what drove their evolution, Leubner famous. “It isn’t that spores don’t seem to be tailored, however seeds was extra refined,” Leubner mentioned.Each spores and seeds can input a state referred to as dormancy, which comes to delaying their germination — construction right into a plant — till prerequisites are optimum. Leubner famous that seeds’ talent to live to tell the tale in several habitats, blended with dormancy, allowed them to be versatile and diversify.Dormancy used to be an enormous benefit to crops and made seeds able to one of those “multidimensional shuttle,” mentioned Charles Knight, a plant evolutionary biologist at California Polytechnic State College.Seeds are “multidimensional in that they are able to shuttle lengthy distances with their variations to be addicted to fur or to be carried via the wind,” Knight informed Are living Science. “However they are able to additionally shuttle thru time. They are able to shuttle thru generations as a result of they are able to stay dormant within the soil after which germinate masses, if no longer 1000’s, of years later.”
A conker, a fallen seed from a horse chestnut tree (Aesculus hippocastanum). (Symbol credit score: Michael Roberts by way of Getty Photographs)Spores additionally generally require a large number of moisture to forestall them from drying out, whilst seeds are able to adapting to plenty of other environments, which is most probably what drove their evolution, Leubner famous. “It isn’t that spores don’t seem to be tailored, however seeds was extra refined,” Leubner mentioned.Each spores and seeds can input a state referred to as dormancy, which comes to delaying their germination — construction right into a plant — till prerequisites are optimum. Leubner famous that seeds’ talent to live to tell the tale in several habitats, blended with dormancy, allowed them to be versatile and diversify.Dormancy used to be an enormous benefit to crops and made seeds able to one of those “multidimensional shuttle,” mentioned Charles Knight, a plant evolutionary biologist at California Polytechnic State College.Seeds are “multidimensional in that they are able to shuttle lengthy distances with their variations to be addicted to fur or to be carried via the wind,” Knight informed Are living Science. “However they are able to additionally shuttle thru time. They are able to shuttle thru generations as a result of they are able to stay dormant within the soil after which germinate masses, if no longer 1000’s, of years later.”