At the morning of Feb. 15, 2013, a meteor the scale of a semitrailer shot out from the path of the emerging solar and exploded in a fireball over the town of Chelyabinsk, Russia. In short sparkling brighter than the solar itself, the meteor exploded with 30 occasions extra power than the bomb that destroyed Hiroshima, exploding some 14 miles (22 kilometers) above the bottom. The blast shattered home windows on greater than 7,000 constructions, quickly blinded pedestrians, inflicted instant ultraviolet burns and another way injured greater than 1,600 other folks. Thankfully, no recognized deaths resulted.The Chelyabinsk meteor is considered the largest herbal area object to go into Earth’s environment in additional than 100 years. But no observatory on Earth noticed it coming. Getting back from the path of the solar, the rock remained hidden in our greatest blind spot, till it was once too past due.Occasions like those are, thankfully, unusual. Rocks the scale of the Chelyabinsk meteor — kind of 66 ft (20 meters) large — breach Earth’s environment as soon as each and every 50 to 100 years, consistent with an estimate from the Ecu House Company (ESA). Higher asteroids strike even much less often. Up to now, astronomers have mapped the orbits of greater than 33,000 near-Earth asteroids and located that none pose a chance of hitting our planet for a minimum of the following century.However you’ll be able to’t calculate the danger of an asteroid you’ll be able to’t see — and there are untold 1000’s of them, together with some big enough to damage towns and doubtlessly cause mass-extinction occasions, transferring on unknowable trajectories round our megastar, professionals informed Reside Science. It is a harsh fact that has astronomers each involved concerning the conceivable penalties and motivated to seek out as a lot of our sun gadget’s hidden asteroids as conceivable. When we learn about them, fatal asteroids can both be monitored and deflected if wanted, or if all else fails, populations will also be warned to relocate to keep away from mass casualties.”Essentially the most problematic object is the only you do not know about,” Amy Mainzer, a professor of planetary science on the College of Arizona and foremost investigator for 2 NASA asteroid-hunting missions, informed Reside Science. “If we will know what is available in the market, then we will have a significantly better estimate of the real chance.”Comparable: NASA’s maximum sought after: The 5 most deadly asteroids within the sun systemKillers from the solar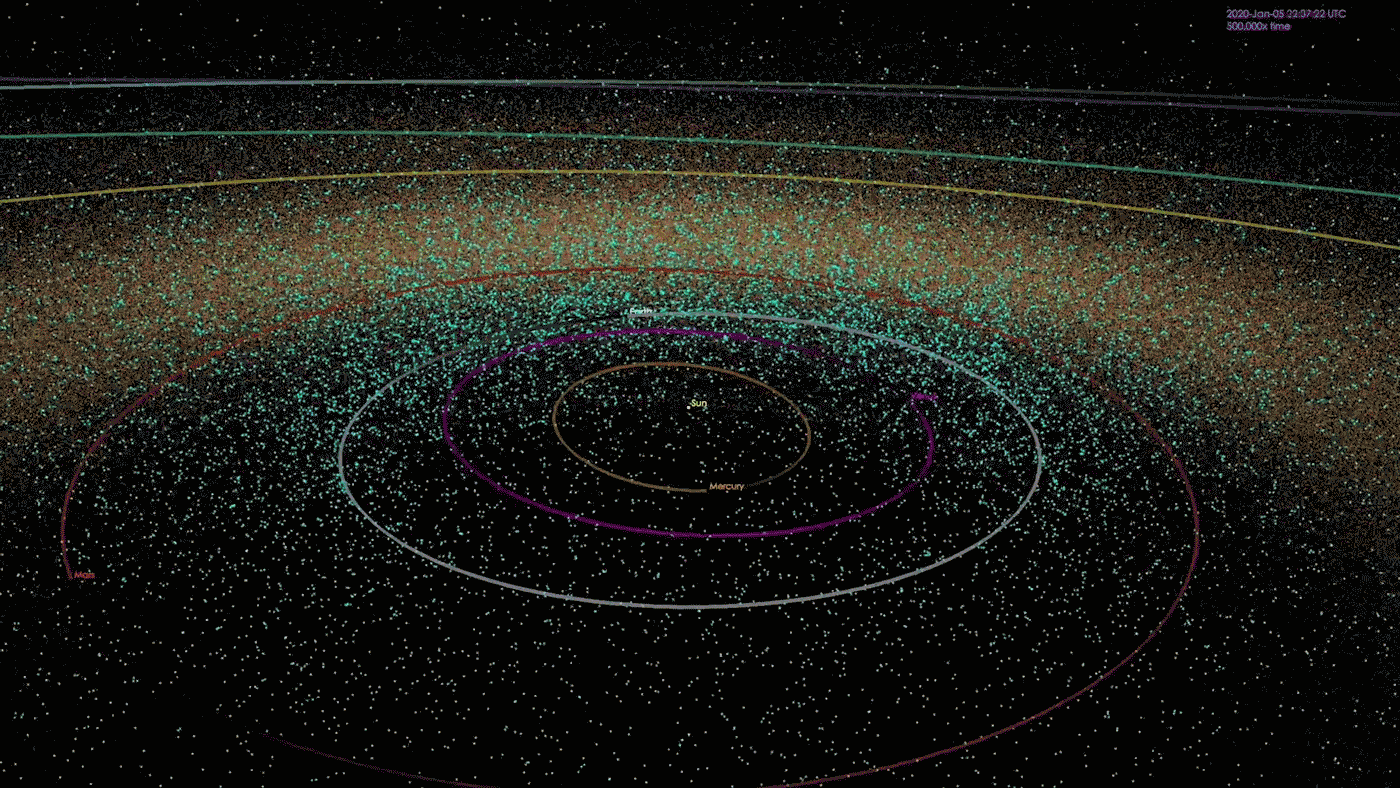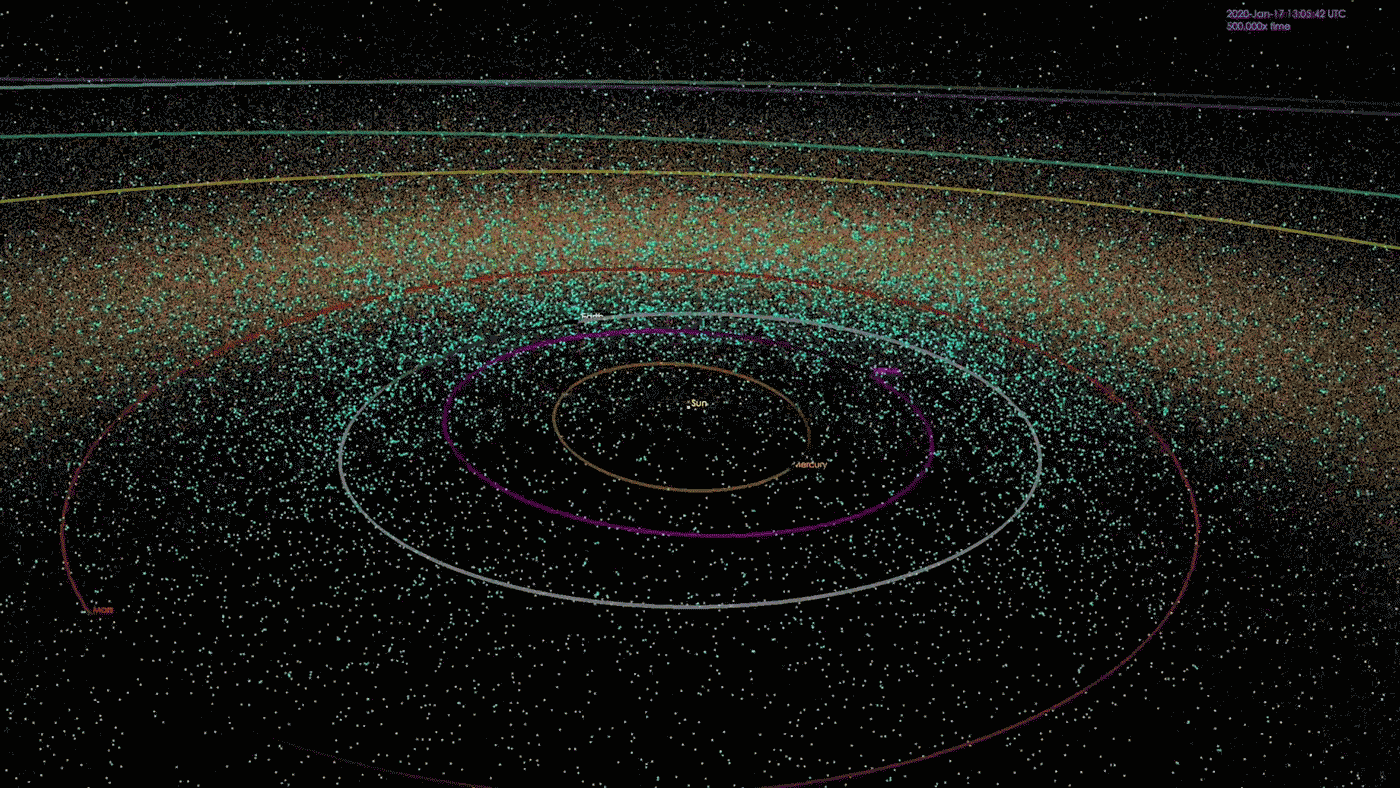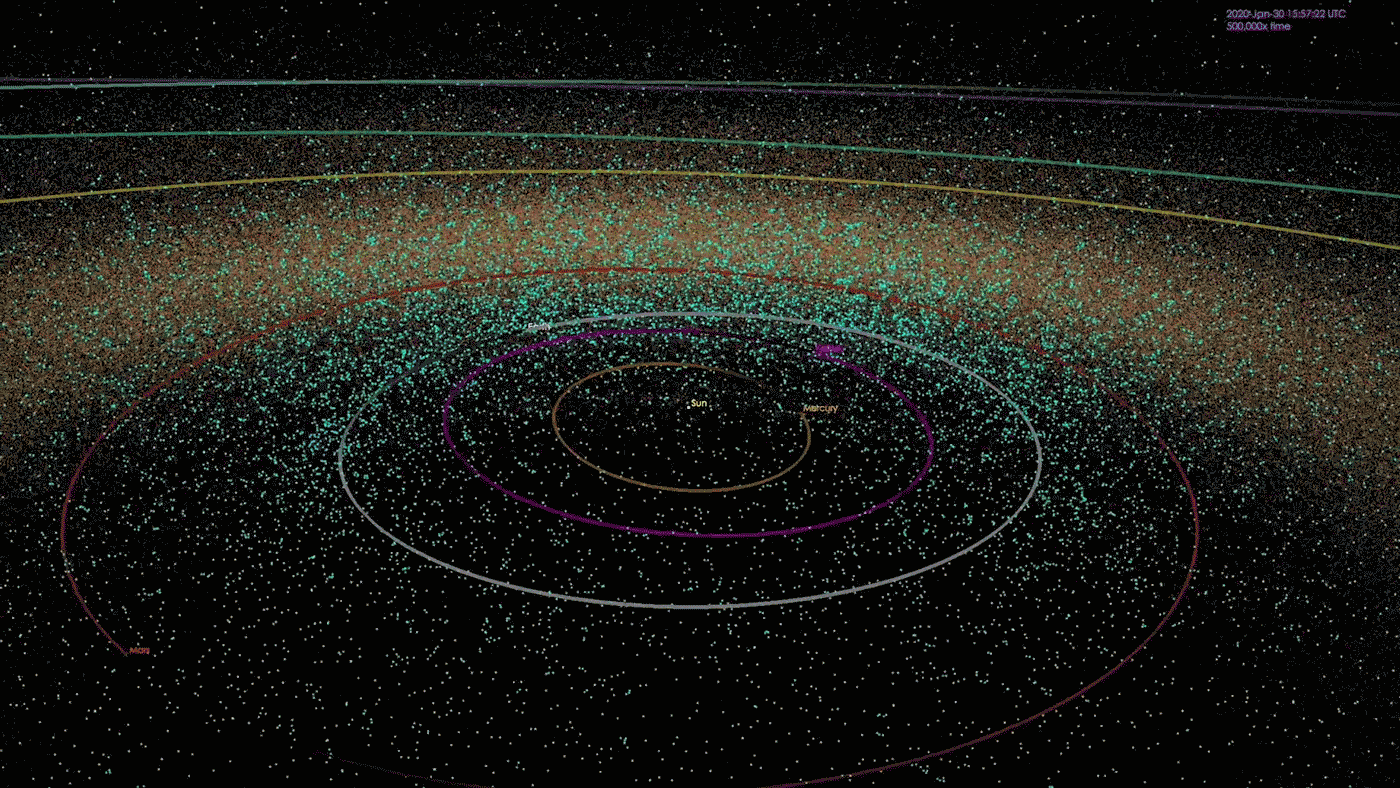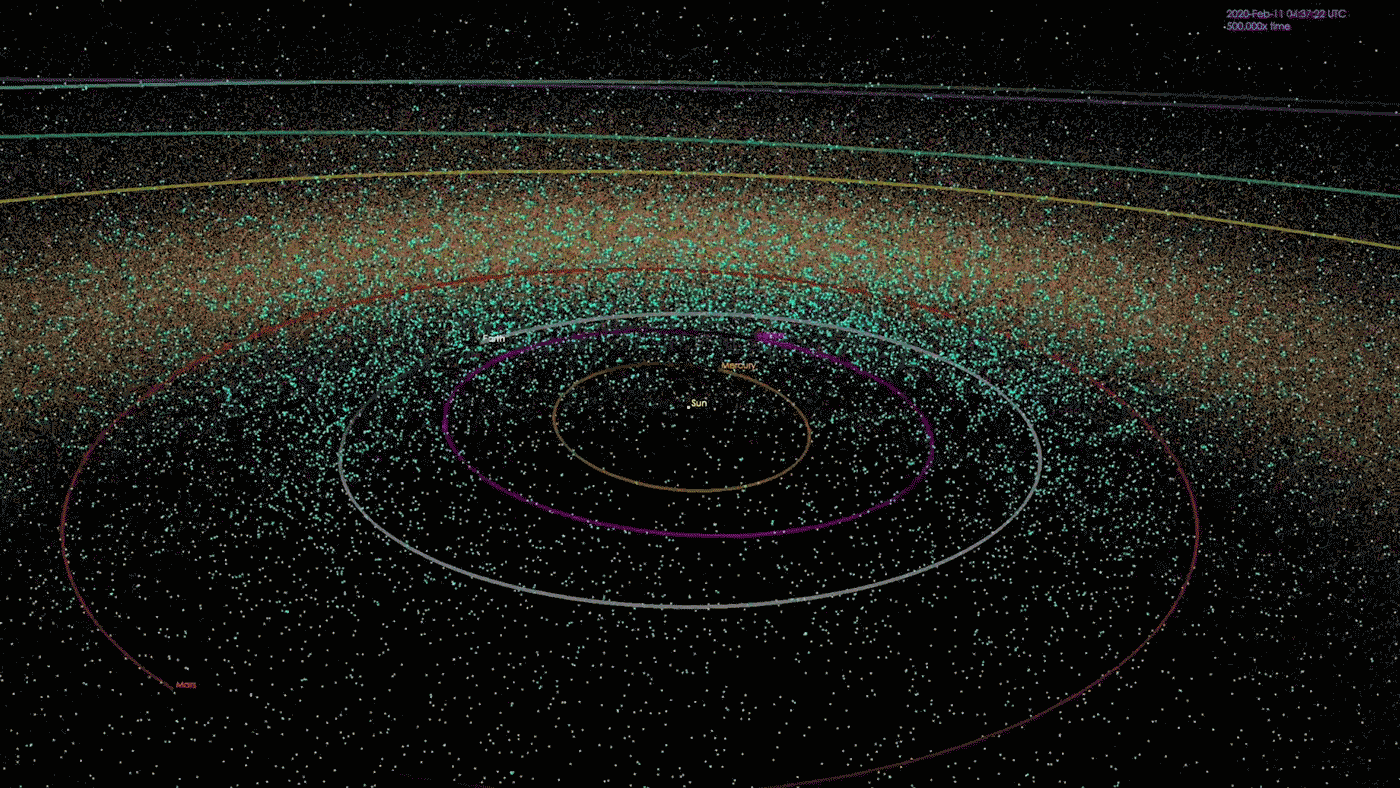 An animation depicting the positions of 1000’s of near-Earth items (NEOs) as of January 2018. As of late, NASA is aware of about greater than 33,000 NEOs, although the area across the solar stays a significant blind spot. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech)At any second, the solar hides numerous asteroids from view. This features a repeatedly rotating solid of Apollo asteroids — near-Earth items that spend maximum in their time some distance past the orbit of Earth however from time to time move our planet’s trail to swoop nearer to the solar — in addition to the mysterious magnificence of asteroids known as the Atens, which orbit nearly solely inside to Earth, ever on the earth’s dayside.”Aten asteroids are essentially the most bad, as a result of they move Earth’s orbit simply slightly at their maximum far-off level,” Scott Sheppard, a team of workers scientist on the Carnegie Establishment for Science, informed Reside Science. “You could by no means see one coming, to some extent, as a result of they are by no means within the darkness of the evening sky.”As with any asteroids, nearly all of those hidden area rocks are most likely sufficiently small to expend utterly in Earth’s environment upon touch. However it is estimated that there also are many undiscovered asteroids measuring greater than 460 ft (140 m) in diameter — big enough to continue to exist the plunge during the environment and purpose catastrophic native harm upon have an effect on, Mainzer mentioned. Asteroids with this damaging doable are on occasion dubbed “town killers.””We predict we’ve got discovered kind of 40% of the ones asteroids within the 140-meter group,” Mainzer mentioned. In step with NASA estimates, that leaves about 14,000 left to be discovered.
An animation depicting the positions of 1000’s of near-Earth items (NEOs) as of January 2018. As of late, NASA is aware of about greater than 33,000 NEOs, although the area across the solar stays a significant blind spot. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech)At any second, the solar hides numerous asteroids from view. This features a repeatedly rotating solid of Apollo asteroids — near-Earth items that spend maximum in their time some distance past the orbit of Earth however from time to time move our planet’s trail to swoop nearer to the solar — in addition to the mysterious magnificence of asteroids known as the Atens, which orbit nearly solely inside to Earth, ever on the earth’s dayside.”Aten asteroids are essentially the most bad, as a result of they move Earth’s orbit simply slightly at their maximum far-off level,” Scott Sheppard, a team of workers scientist on the Carnegie Establishment for Science, informed Reside Science. “You could by no means see one coming, to some extent, as a result of they are by no means within the darkness of the evening sky.”As with any asteroids, nearly all of those hidden area rocks are most likely sufficiently small to expend utterly in Earth’s environment upon touch. However it is estimated that there also are many undiscovered asteroids measuring greater than 460 ft (140 m) in diameter — big enough to continue to exist the plunge during the environment and purpose catastrophic native harm upon have an effect on, Mainzer mentioned. Asteroids with this damaging doable are on occasion dubbed “town killers.””We predict we’ve got discovered kind of 40% of the ones asteroids within the 140-meter group,” Mainzer mentioned. In step with NASA estimates, that leaves about 14,000 left to be discovered.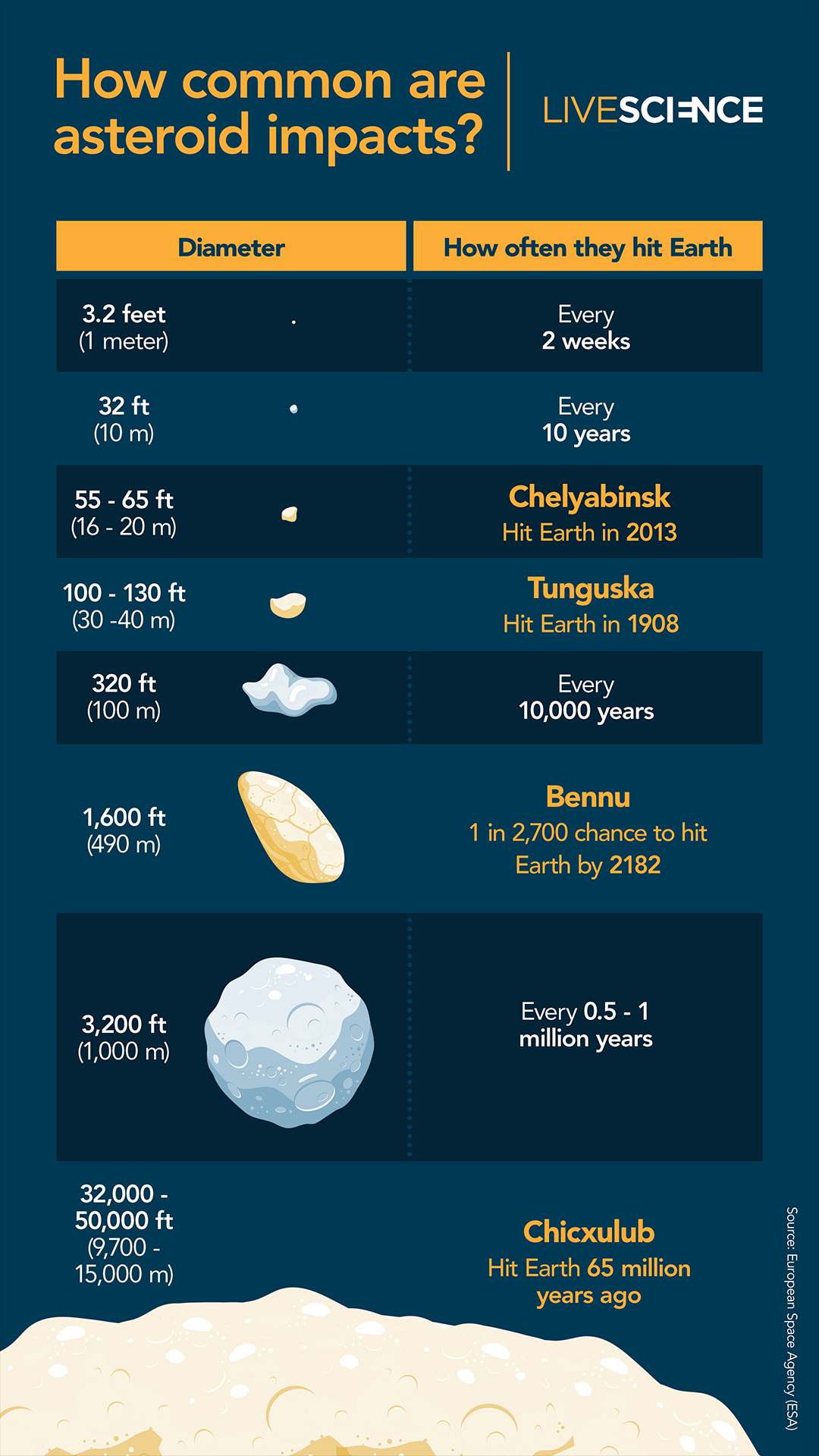 How commonplace are asteroid affects? It is dependent upon the scale. (Symbol credit score: John Strike)There can also be some distance, some distance larger items expecting us within the solar’s glare. Even though exceptionally uncommon, a handful of “planet killer” asteroids — which measure greater than 3,280 ft (1 km) in diameter and are in a position to kicking up sufficient mud to cause an international extinction tournament — would possibly lurk within the solar’s glare, Sheppard mentioned.In 2022, Sheppard and his colleagues found out one such planet killer obscured through the solar, which they described in a paper in The Astronomical Magazine. The researchers had been attempting to find asteroids close to Venus, borrowing time from a number of massive telescopes to scan the horizon for 5 to ten mins each and every evening at twilight, after they found out 2022 AP7 — a mile-wide (1.5 km) behemoth with a unusual five-year orbit that makes the enormous area rock nearly completely invisible to telescopes.”When it is within the evening sky, it is at its furthest level from the solar, and it is very faint,” Sheppard mentioned. “The one time it is moderately vibrant is when it is inside to Earth, close to the solar.”These days, 2022 AP7 crosses Earth’s orbit best when our planet and the asteroid are on reverse facets of the solar, making it innocuous. On the other hand, that hole will slowly slim over 1000’s of years, bringing the 2 items nearer and nearer to a doubtlessly catastrophic collision. And it is most likely no longer the one one.”Thru our survey to this date, we discover that there is surely a number of extra kilometer-size Aten asteroids available in the market to be discovered,” Sheppard added.Comparable: May scientists forestall a ‘planet killer’ asteroid from hitting Earth?A dazzling puzzle
How commonplace are asteroid affects? It is dependent upon the scale. (Symbol credit score: John Strike)There can also be some distance, some distance larger items expecting us within the solar’s glare. Even though exceptionally uncommon, a handful of “planet killer” asteroids — which measure greater than 3,280 ft (1 km) in diameter and are in a position to kicking up sufficient mud to cause an international extinction tournament — would possibly lurk within the solar’s glare, Sheppard mentioned.In 2022, Sheppard and his colleagues found out one such planet killer obscured through the solar, which they described in a paper in The Astronomical Magazine. The researchers had been attempting to find asteroids close to Venus, borrowing time from a number of massive telescopes to scan the horizon for 5 to ten mins each and every evening at twilight, after they found out 2022 AP7 — a mile-wide (1.5 km) behemoth with a unusual five-year orbit that makes the enormous area rock nearly completely invisible to telescopes.”When it is within the evening sky, it is at its furthest level from the solar, and it is very faint,” Sheppard mentioned. “The one time it is moderately vibrant is when it is inside to Earth, close to the solar.”These days, 2022 AP7 crosses Earth’s orbit best when our planet and the asteroid are on reverse facets of the solar, making it innocuous. On the other hand, that hole will slowly slim over 1000’s of years, bringing the 2 items nearer and nearer to a doubtlessly catastrophic collision. And it is most likely no longer the one one.”Thru our survey to this date, we discover that there is surely a number of extra kilometer-size Aten asteroids available in the market to be discovered,” Sheppard added.Comparable: May scientists forestall a ‘planet killer’ asteroid from hitting Earth?A dazzling puzzle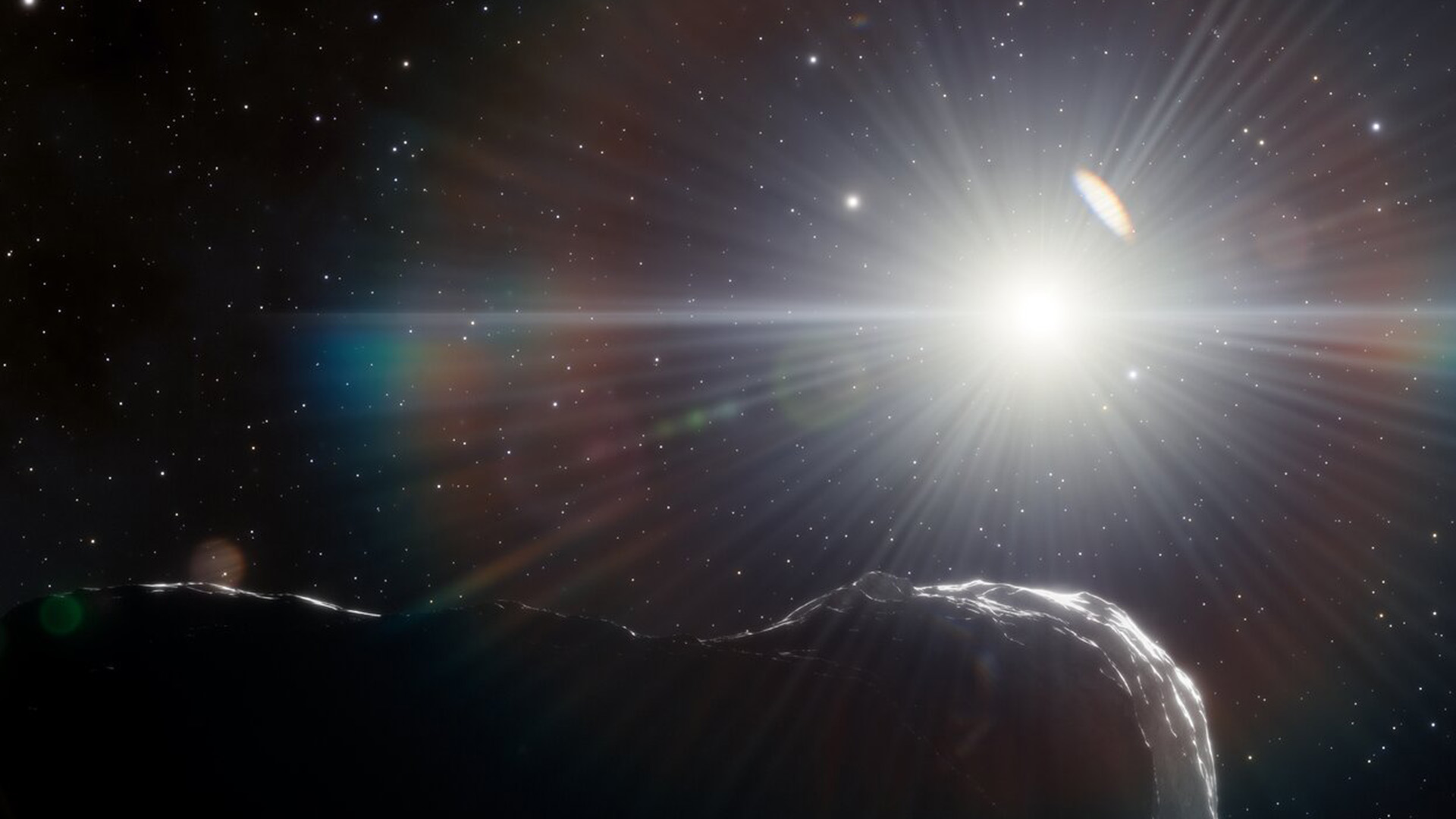 A demonstration of a giant near-Earth asteroid stuck within the solar’s glare. (Symbol credit score: DOE/FNAL/DECam/CTIO/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/J. da Silva/Spaceengine)Surveying asteroids close to the solar poses a singular problem for astronomers. Most room-based telescopes gaze towards the planet’s nightside, to keep away from each sun glare and radiation harm. Floor-based telescopes, in the meantime, face even better restrictions.”Now not best is the glare of the solar an issue, however the timing is a large drawback as neatly,” Sheppard mentioned. “The solar has to set to a undeniable place under the horizon prior to they even can help you open the telescope, and the sky must be simply darkish sufficient the place you’ll be able to take pictures and no longer saturate.”As soon as the solar reaches this fleeting place, ground-based telescopes have lower than half-hour to survey the realm close to the threshold of the solar prior to it dips under the horizon and disappears from view solely, Sheppard added.Right through this transient window, ground-based telescopes have the added problem of peering directly thru Earth’s environment, which seems thickest close to the horizon and reasons mild from far-off items to flicker and diffuse. Gases within the environment additionally take in many wavelengths of infrared mild — the thermal radiation that astronomers use to come across one of the faintest, coolest items within the universe.It is rarely a really perfect state of affairs for recognizing small, darkish, fast-moving chunks of rubble.”That is why you want to visit area,” Luca Conversi, supervisor of ESA’s Close to-Earth Object (NEO) Coordination Centre, informed Reside Science.Salvation in area
A demonstration of a giant near-Earth asteroid stuck within the solar’s glare. (Symbol credit score: DOE/FNAL/DECam/CTIO/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/J. da Silva/Spaceengine)Surveying asteroids close to the solar poses a singular problem for astronomers. Most room-based telescopes gaze towards the planet’s nightside, to keep away from each sun glare and radiation harm. Floor-based telescopes, in the meantime, face even better restrictions.”Now not best is the glare of the solar an issue, however the timing is a large drawback as neatly,” Sheppard mentioned. “The solar has to set to a undeniable place under the horizon prior to they even can help you open the telescope, and the sky must be simply darkish sufficient the place you’ll be able to take pictures and no longer saturate.”As soon as the solar reaches this fleeting place, ground-based telescopes have lower than half-hour to survey the realm close to the threshold of the solar prior to it dips under the horizon and disappears from view solely, Sheppard added.Right through this transient window, ground-based telescopes have the added problem of peering directly thru Earth’s environment, which seems thickest close to the horizon and reasons mild from far-off items to flicker and diffuse. Gases within the environment additionally take in many wavelengths of infrared mild — the thermal radiation that astronomers use to come across one of the faintest, coolest items within the universe.It is rarely a really perfect state of affairs for recognizing small, darkish, fast-moving chunks of rubble.”That is why you want to visit area,” Luca Conversi, supervisor of ESA’s Close to-Earth Object (NEO) Coordination Centre, informed Reside Science.Salvation in area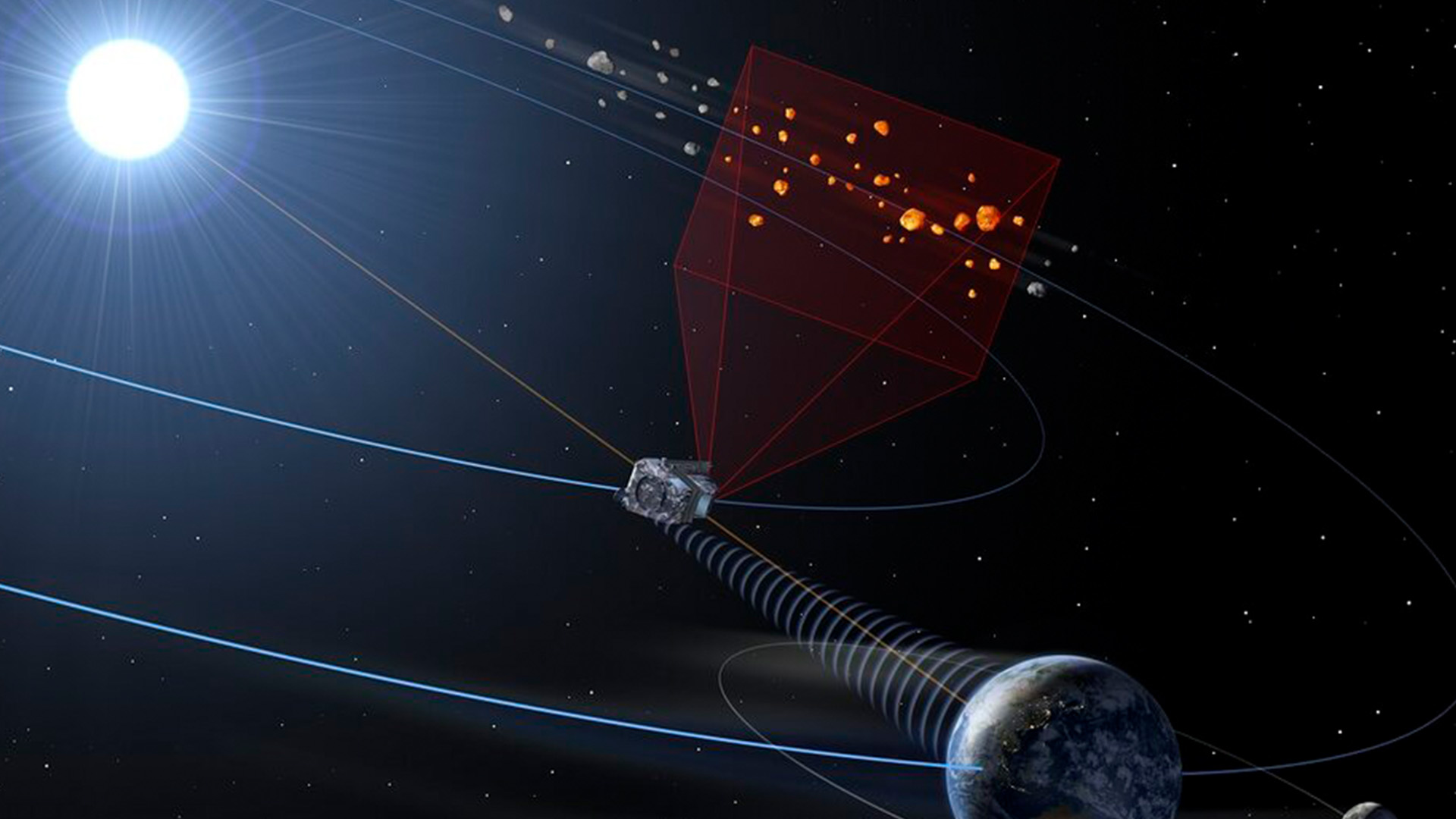 A diagram appearing ESA’s proposed NEOMIR spacecraft in orbit between Earth and the solar. NEOMIR, in conjunction with NASA’s NEO Surveyor, will scan for asteroids obscured through the solar’s glare that ground-based telescopes can not see. (Symbol credit score: ESA)Orbiting masses of miles over Earth and some distance past, area telescopes are unfastened from the distorting results of the planet’s environment. This unlocks a formidable instrument of their arsenals: infrared imaging, or the facility to come across warmth coming off of area items, slightly than simply the mirrored daylight that makes items detectable through visible-light telescopes.”Just a small portion of an asteroid’s floor is illuminated through the solar, even in area,” Conversi mentioned. “So as a substitute of taking a look at daylight mirrored from the skin, [infrared telescopes] have a look at the thermal emission of the asteroid itself, so we are in a position to seek out it.”Which means that even asteroids which might be visually darkish, just like the just lately visited asteroid Bennu, shine “like sparkling coals” when observed in infrared, Mainzer mentioned.These days, there is just one infrared area telescope that is actively searching for near-Earth asteroids — the Close to-Earth Object Vast-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or NEOWISE. Introduced in 2009 as merely WISE, the telescope was once designed to come across items some distance from Earth. However in 2013, after the Chelyabinsk incident, WISE was once roused from a two-year hibernation as NEOWISE, with new device and a brand new challenge to come across doubtlessly difficult near-Earth asteroids.However NEOWISE was once by no means in a position to appear towards the solar — and its challenge is predicted to finish for excellent through July 2024, Mainzer mentioned. That may depart new asteroid detection only within the palms of ground-based surveys till the following technology of space-based telescopes can release later this decade.”Cross glance up.”
A diagram appearing ESA’s proposed NEOMIR spacecraft in orbit between Earth and the solar. NEOMIR, in conjunction with NASA’s NEO Surveyor, will scan for asteroids obscured through the solar’s glare that ground-based telescopes can not see. (Symbol credit score: ESA)Orbiting masses of miles over Earth and some distance past, area telescopes are unfastened from the distorting results of the planet’s environment. This unlocks a formidable instrument of their arsenals: infrared imaging, or the facility to come across warmth coming off of area items, slightly than simply the mirrored daylight that makes items detectable through visible-light telescopes.”Just a small portion of an asteroid’s floor is illuminated through the solar, even in area,” Conversi mentioned. “So as a substitute of taking a look at daylight mirrored from the skin, [infrared telescopes] have a look at the thermal emission of the asteroid itself, so we are in a position to seek out it.”Which means that even asteroids which might be visually darkish, just like the just lately visited asteroid Bennu, shine “like sparkling coals” when observed in infrared, Mainzer mentioned.These days, there is just one infrared area telescope that is actively searching for near-Earth asteroids — the Close to-Earth Object Vast-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or NEOWISE. Introduced in 2009 as merely WISE, the telescope was once designed to come across items some distance from Earth. However in 2013, after the Chelyabinsk incident, WISE was once roused from a two-year hibernation as NEOWISE, with new device and a brand new challenge to come across doubtlessly difficult near-Earth asteroids.However NEOWISE was once by no means in a position to appear towards the solar — and its challenge is predicted to finish for excellent through July 2024, Mainzer mentioned. That may depart new asteroid detection only within the palms of ground-based surveys till the following technology of space-based telescopes can release later this decade.”Cross glance up.”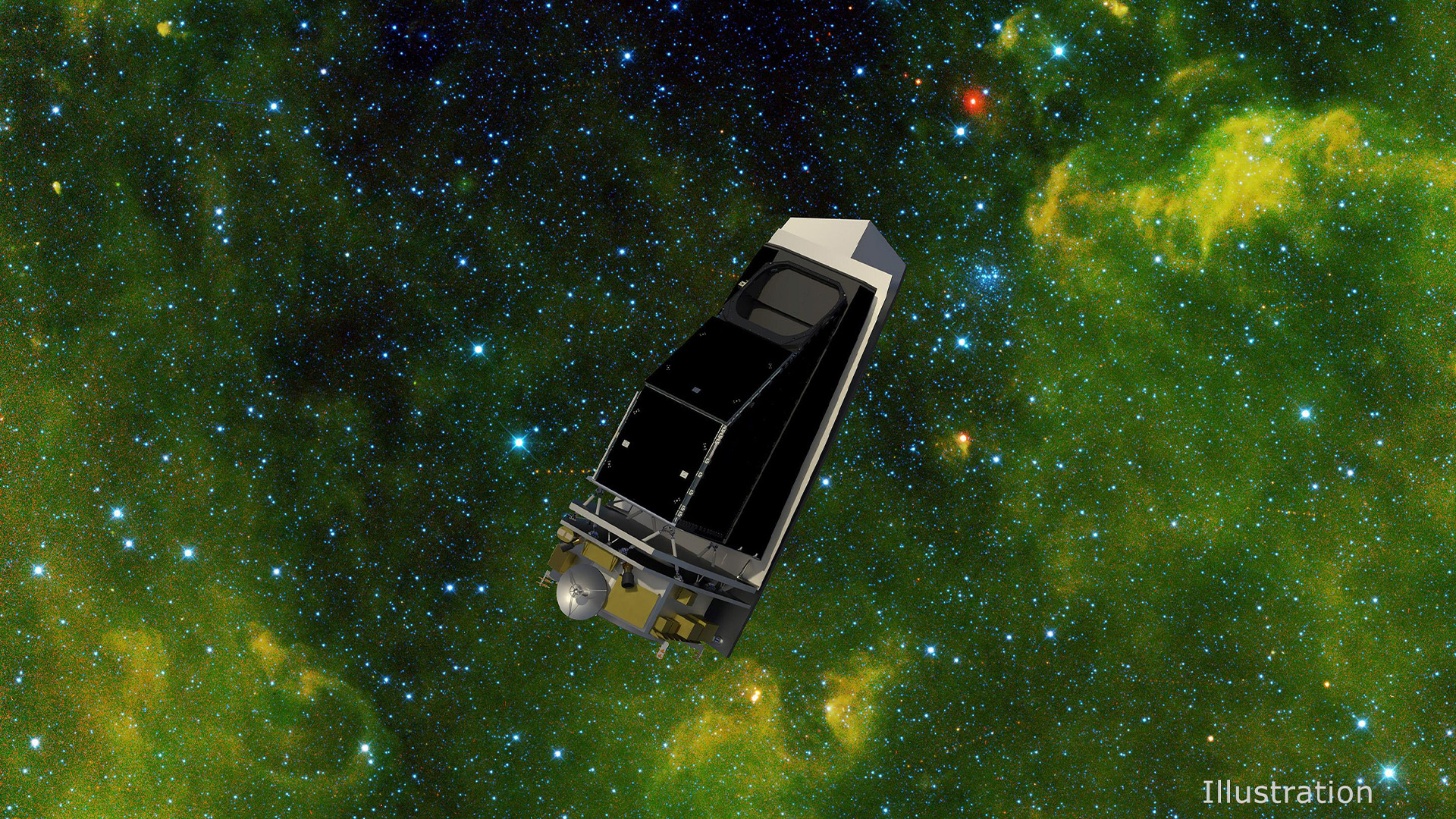 Thought artwork for NASA’s deliberate NEO Surveyor spacecraft, which might release once 2027. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona)Two deliberate spacecraft must assist to noticeably demystify the risks of the sun blind zone: NASA’s NEO Surveyor, these days deliberate to release in 2027, and ESA’s NEOMIR, which continues to be in its early making plans section and can release no quicker than 2030, Conversi mentioned.Each spacecraft will probably be provided with infrared detectors and tall sun sun shades that may let them search for asteroids very just about the solar’s glare, and each will orbit on the first Lagrange level (L1) between Earth and the solar, the place the gravitational pull of the 2 items is balanced. NEO Surveyor will entire a complete scan of the sky each and every two weeks, splitting its focal point calmly between the crack of dawn and nightfall facets of the solar, mentioned Mainzer, the foremost investigator for each NEOWISE and NEO Surveyor. The telescope is predicted to essentially discover near-Earth items starting from 50 to 100 m (164 to 328 ft) large.NEOMIR, in the meantime, would supplement NEO Surveyor through scanning a ring-shaped house across the solar each and every six hours or so, Conversi mentioned. Between the 2 spacecraft, even asteroids as small because the Chelyabinsk meteor must be noticed someplace of their orbits lengthy prior to have an effect on, the researchers mentioned.”In step with our predictions, NEOMIR would have observed the Chelyabinsk meteor about one week prior to have an effect on,” Conversi mentioned. “Greater than sufficient time to alert the inhabitants and take some measures.”Relating to a small, Chelyabinsk-size meteor that explodes prior to achieving the bottom, the ones measures may come with alerting other folks within the have an effect on zone to refuge and avoid home windows. Higher items would optimistically be detected lengthy prior to their date of have an effect on, permitting other folks to evacuate the realm if essential. “Planet killers” require years of making plans to soundly deflect, however also are the very best to identify some distance prematurely.However with each NEO Surveyor and NEOMIR years clear of seeing the sunshine of day, astronomers will proceed to depend on the most efficient ground-based strategies to be had to parse the mysteries of the solar. Even with those spacecraft operational, a small share of near-sun asteroids will most likely stay undetectable, Conversi mentioned. Thankfully, the hazards of a dangerous have an effect on stay low, and can optimistically best decrease as astronomers accumulate extra and higher knowledge.”Cross glance up,” Mainzer mentioned. “Do a greater survey, and you’ll be able to a great deal cut back the uncertainty.”
Thought artwork for NASA’s deliberate NEO Surveyor spacecraft, which might release once 2027. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona)Two deliberate spacecraft must assist to noticeably demystify the risks of the sun blind zone: NASA’s NEO Surveyor, these days deliberate to release in 2027, and ESA’s NEOMIR, which continues to be in its early making plans section and can release no quicker than 2030, Conversi mentioned.Each spacecraft will probably be provided with infrared detectors and tall sun sun shades that may let them search for asteroids very just about the solar’s glare, and each will orbit on the first Lagrange level (L1) between Earth and the solar, the place the gravitational pull of the 2 items is balanced. NEO Surveyor will entire a complete scan of the sky each and every two weeks, splitting its focal point calmly between the crack of dawn and nightfall facets of the solar, mentioned Mainzer, the foremost investigator for each NEOWISE and NEO Surveyor. The telescope is predicted to essentially discover near-Earth items starting from 50 to 100 m (164 to 328 ft) large.NEOMIR, in the meantime, would supplement NEO Surveyor through scanning a ring-shaped house across the solar each and every six hours or so, Conversi mentioned. Between the 2 spacecraft, even asteroids as small because the Chelyabinsk meteor must be noticed someplace of their orbits lengthy prior to have an effect on, the researchers mentioned.”In step with our predictions, NEOMIR would have observed the Chelyabinsk meteor about one week prior to have an effect on,” Conversi mentioned. “Greater than sufficient time to alert the inhabitants and take some measures.”Relating to a small, Chelyabinsk-size meteor that explodes prior to achieving the bottom, the ones measures may come with alerting other folks within the have an effect on zone to refuge and avoid home windows. Higher items would optimistically be detected lengthy prior to their date of have an effect on, permitting other folks to evacuate the realm if essential. “Planet killers” require years of making plans to soundly deflect, however also are the very best to identify some distance prematurely.However with each NEO Surveyor and NEOMIR years clear of seeing the sunshine of day, astronomers will proceed to depend on the most efficient ground-based strategies to be had to parse the mysteries of the solar. Even with those spacecraft operational, a small share of near-sun asteroids will most likely stay undetectable, Conversi mentioned. Thankfully, the hazards of a dangerous have an effect on stay low, and can optimistically best decrease as astronomers accumulate extra and higher knowledge.”Cross glance up,” Mainzer mentioned. “Do a greater survey, and you’ll be able to a great deal cut back the uncertainty.”













