Scientists have discovered some planets might migrate towards the hearts in their planetary methods early on of their lives, most likely explaining the loss of planets we see which can be round two times the width of Earth.Through the years, scientists have controlled to look at many exoplanets which can be both smaller or greater than Earth, however planets exactly between 1.6 and a pair of.2 occasions the scale of our international are somewhat scarce. Specifically, exoplanets outlined as super-Earths or mini-Neptunes seem to be lacking in house. They are categorized as such if they are relatively greater than two times the scale of our planet, however nonetheless smaller than the ice large Neptune.The absence of those planets has thus develop into referred to as the “radius valley” or “radius hole,” and has stricken scientists for a very long time.However now, new analysis suggests the “lacking” super-Earths and mini-Neptunes could have simply taken other routes out of the radius valley.”Six years in the past, a reanalysis of information from the Kepler house telescope printed a scarcity of exoplanets with sizes round two Earth radii,” Remo Burn, an exoplanet skilled on the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, stated in a commentary.Comparable: Wonder! Child exoplanets would possibly appear to be Smarties chocolates relatively than spheresScientists have identified for a few years that planets may both transfer towards or clear of their mum or dad stars after formation, however what wasn’t prior to now identified was once simply how efficient this migration could be in developing the radius valley.The commonest reason behind the valley, Burn says, has to do with stars irradiating the planets that carefully encompass them, stripping the atmospheres of the ones worlds and inflicting them to shrink. This concept by itself, on the other hand, wasn’t enough for him. “This rationalization neglects the affect of planetary migration,” he defined.Thus, Burn led a group of researchers that got down to examine whether or not planetary migration may complement the usual rationalization and additional give an explanation for the rationale so few super-Earths and mini-Neptunes are observed orbiting on the subject of their stars.Tremendous-Earths shrink whilst sub-Neptunes growBecause the 2 planets that occupy the radius hole, super-Earths and mini-Neptunes, are each absent from the sun device, scientists cannot moderately learn about both up shut. Howeer, researchers are reasonably positive that super-Earths are rocky or terrestrial planets, whilst the traits of mini-Neptunes are a lot much less sure. What scientists additionally agree on is that mini-Neptunes, sometimes called sub-Neptunes, must have atmospheres that stretch a long way past the ones of rocky planets. Burn and the group sought after to grasp if this truth may play a task in developing the radius valley, and if the very lifestyles of that valley may counsel very other formations and evolutions for super-Earths and mini-Neptunes.Acting a re-analysis of a simulation the group ran in 2020, Burn and co-workers factored in processes within the fuel and mud disks surrounding younger stars that give upward thrust to new planets, the emergence of atmospheres, and the migration of planets.A very powerful to the simulation and to growing a possible answer for the radius valley — that still components in planetary migration — was once working out how water acts over quite a lot of pressures and temperatures. That is as a result of those parameters permit for a extra lifelike calculation of sub-Neptunes’ conduct.”It is exceptional how, as on this case, bodily houses on molecular ranges affect large-scale astronomical processes such because the formation of planetary atmospheres,” group member and MPIA Director, Thomas Henning, stated within the commentary. 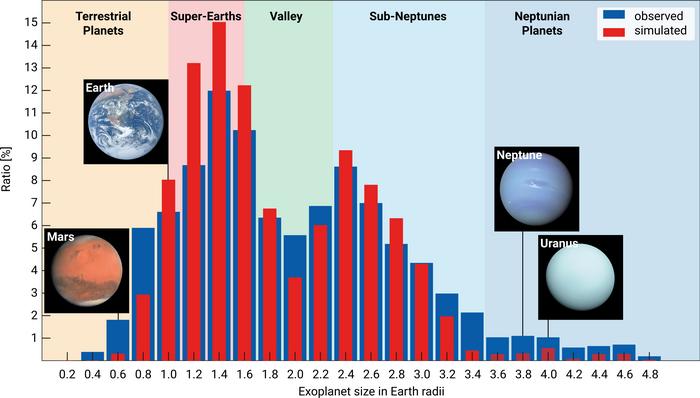 A distribution of exoplanet sizes appearing an opening in planets between 1.6 occasions and a pair of.2 occasions the scale of Earth. (Symbol credit score: R. Burn, C. Mordasini / MPIA)The group discovered that shifting towards a mum or dad superstar had significantly other results on each super-Earths and mini-Neptunes.Mini-Neptunes are born clear of their mum or dad stars within the icy outer areas in their methods. Whilst a few of these planets stay on this native land, receiving low doses of radiation from their superstar, mini-Neptunes that do migrate inwards towards their superstar would have their icy subject material thawed, the group discovered.This might create a thick water surroundings round those exoplanets, thus expanding their radii and moving their widths past planets within the radius hole. That is conceivable as a result of present observations of worlds outdoor the sun device cannot differentiate between an exoplanet’s surroundings and cast portions when calculating width. This impact, the scientists due to this fact estimate, reasons a top in exoplanets 2.4 occasions the scale of Earth. Then again, super-Earths that both migrate towards their host superstar or are born very shut would have their atmospheres stripped via the serious radiation in their stars. That’d power the worlds to lose their surroundings and develop into smaller. This impact, the group says, would create a naked rocky core and motive a top in exoplanet sizes at only one.4 occasions the width of Earth. Put merely, that suggests as mini-Neptunes are shifting out of the radius valley a method, super-Earths are evacuating it by means of the other go out. And each mechanisms lead to a dearth of planets round two times the width of Earth. The group’s simulations used to probably get to the bottom of this thriller may even have an have an effect on in different spaces of exoplanet science.”If we have been to enlarge our effects to cooler areas, the place water is liquid, this would possibly counsel the lifestyles of water worlds with deep oceans,” Christoph Mordasin, group member and head of the Department of Area Analysis and Planetary Sciences on the College of Bern, stated within the commentary. “Such planets may probably host lifestyles and could be somewhat simple objectives for on the lookout for biomarkers because of their dimension.”The group’s analysis was once printed Feb. 9 within the magazine Nature Astronomy.
A distribution of exoplanet sizes appearing an opening in planets between 1.6 occasions and a pair of.2 occasions the scale of Earth. (Symbol credit score: R. Burn, C. Mordasini / MPIA)The group discovered that shifting towards a mum or dad superstar had significantly other results on each super-Earths and mini-Neptunes.Mini-Neptunes are born clear of their mum or dad stars within the icy outer areas in their methods. Whilst a few of these planets stay on this native land, receiving low doses of radiation from their superstar, mini-Neptunes that do migrate inwards towards their superstar would have their icy subject material thawed, the group discovered.This might create a thick water surroundings round those exoplanets, thus expanding their radii and moving their widths past planets within the radius hole. That is conceivable as a result of present observations of worlds outdoor the sun device cannot differentiate between an exoplanet’s surroundings and cast portions when calculating width. This impact, the scientists due to this fact estimate, reasons a top in exoplanets 2.4 occasions the scale of Earth. Then again, super-Earths that both migrate towards their host superstar or are born very shut would have their atmospheres stripped via the serious radiation in their stars. That’d power the worlds to lose their surroundings and develop into smaller. This impact, the group says, would create a naked rocky core and motive a top in exoplanet sizes at only one.4 occasions the width of Earth. Put merely, that suggests as mini-Neptunes are shifting out of the radius valley a method, super-Earths are evacuating it by means of the other go out. And each mechanisms lead to a dearth of planets round two times the width of Earth. The group’s simulations used to probably get to the bottom of this thriller may even have an have an effect on in different spaces of exoplanet science.”If we have been to enlarge our effects to cooler areas, the place water is liquid, this would possibly counsel the lifestyles of water worlds with deep oceans,” Christoph Mordasin, group member and head of the Department of Area Analysis and Planetary Sciences on the College of Bern, stated within the commentary. “Such planets may probably host lifestyles and could be somewhat simple objectives for on the lookout for biomarkers because of their dimension.”The group’s analysis was once printed Feb. 9 within the magazine Nature Astronomy.
The thriller of the lacking super-Earths and mini-Neptunes might in spite of everything be solved