Join the Begins With a Bang publication
Trip the universe with Dr. Ethan Siegel as he solutions the most important questions of all
Right here in our cosmic community, galaxies are available all varieties of sizes, lots, and shapes. The biggest, maximum huge galaxies within the Native Crew are the Milky Approach and our giant sister, Andromeda: two galaxies consultant of recent broad spirals. Whilst galaxies like our personal are simple to seek out all all over the Universe, they’re now not the commonest form of galaxy in any respect. As a substitute, it’s smaller, lower-mass galaxies which might be a long way and away the commonest, with an estimated 30-to-100 tiny dwarf galaxies discovered all over the Universe for each and every one Milky Approach-like galaxy in the market. Whilst the most important, brightest, maximum huge galaxies are the perfect ones to identify, it’s in reality the smaller, extra commonplace, lower-mass galaxies which might be basically answerable for blowing away the intergalactic impartial fuel and making the cosmos visual.One of the small galaxies that we discover have broad reservoirs of fuel inside of them, the place they proceed to shape stars all over their lives, whilst others are just about gas-free, having fashioned all in their stars in only one main burst that took place way back. Then again, the small galaxies which were tested maximum studiously are the nearest ones: those contained inside of our personal Native Crew, situated not more than about 3 million light-years from us.What would we discover, then, once we tested — first with Hubble after which with JWST — a tiny, low-mass, remoted galaxy situated in deep intergalactic house? Proof for unstoppable expansion that took place over billions of years. Right here’s what we realized.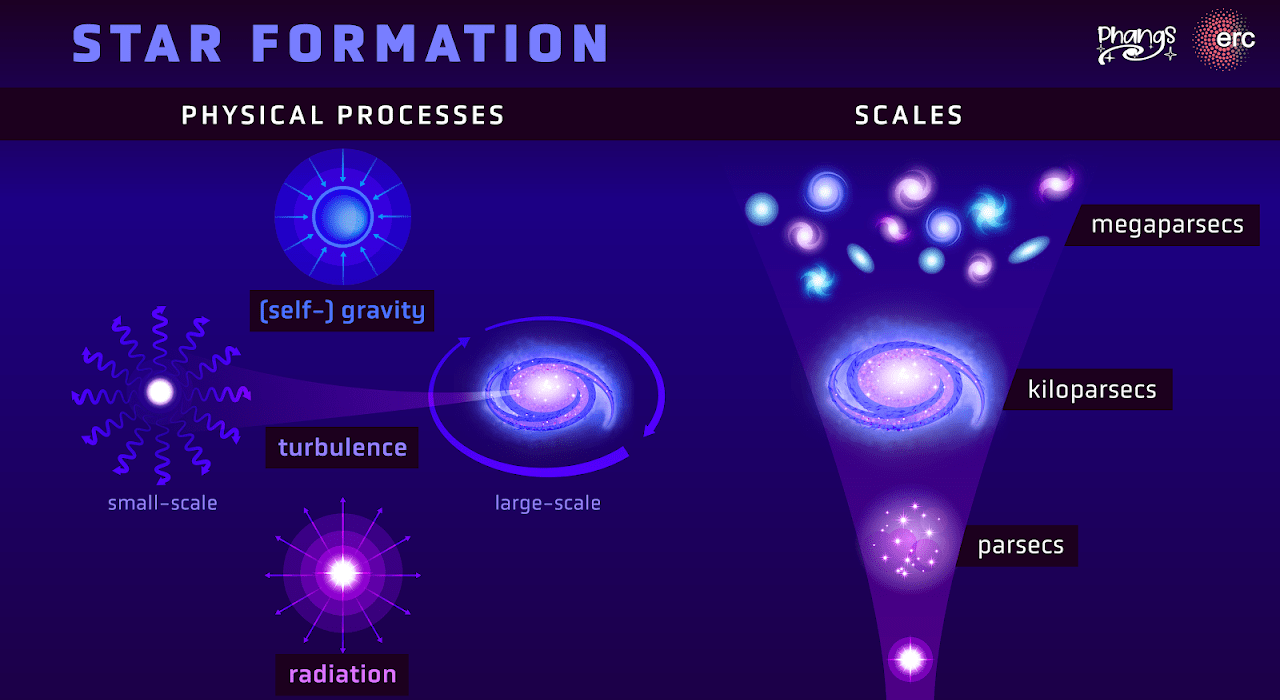 Celebrity forming areas are pushed by way of gravitational cave in, turbulent flows, and effort bobbing up from radiation, carving small-scale and large-scale options into spiral galaxies. On stellar/star-forming area scales as much as galactic and galaxy crew/cluster scales, its results may also be felt and noticed by way of cosmic constructions. Remoted, low-mass galaxies, alternatively, are simplest starting to be studied.
Celebrity forming areas are pushed by way of gravitational cave in, turbulent flows, and effort bobbing up from radiation, carving small-scale and large-scale options into spiral galaxies. On stellar/star-forming area scales as much as galactic and galaxy crew/cluster scales, its results may also be felt and noticed by way of cosmic constructions. Remoted, low-mass galaxies, alternatively, are simplest starting to be studied.
Credit score: PHANGS collaboration, Design: Daniela Leitner
There were a sequence of necessary classes we’ve realized about cosmic historical past right here within the JWST generation: classes for now not simply what’s within the Universe, however for the way the Universe grew up. Very early on, there have been no stars or galaxies; it took tens to masses of thousands and thousands of years for the primary stars to shape. In no time, the star-formation price inside the Universe larger, as the most important, brightest galaxies abruptly grew to comprise thousands and thousands, masses of thousands and thousands, after which billions of sun lots price of stars inside of. Then again, those vivid, early behemoths aren’t basically answerable for generating the ultraviolet gentle that ionizes impartial atoms all over intergalactic house; it’s the a lot more plentiful low-mass galaxies which might be answerable for reionizing the Universe.After we read about the tiniest, lowest-mass galaxies discovered inside of our Native Crew, we discover that their evolution is a great deal suffering from the presence of enormous, close by galaxies such because the Milky Approach and Andromeda. As they pace via house, any impartial atoms (akin to fuel) which might be provide inside the tiny galaxy collide with debris at the outskirts of those greater galactic halos, stripping that intervening subject away. Streams of chilly fuel from the distance between galaxies, moreover, will get preferentially funneled into the bigger, higher-mass galaxies, fighting those tiny dwarf galaxies from proceeding to shape stars through the years.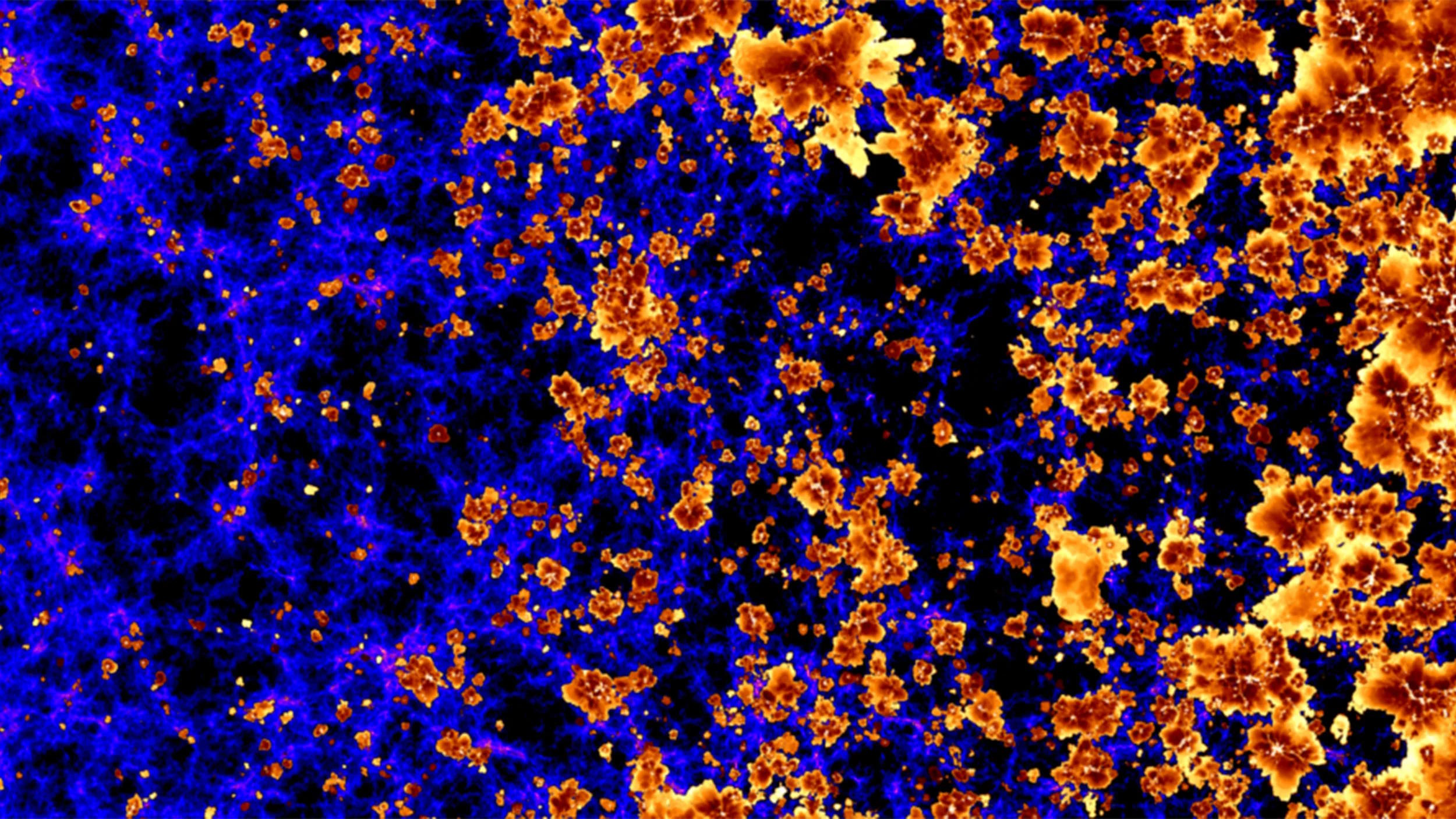 To start with, at left, the Universe is stuffed with impartial, light-blocking subject again sooner than any stars have fashioned. When stars start to shape, alternatively, they devise ionizing ultraviolet photons, which result in wallet that behave as despite the fact that they’re clear to visual gentle, as proven in purple. Through the years, as we transfer to the appropriate, an increasing number of of the Universe turns into reionized, till reionization completes round 550 million years after the Giant Bang. This epoch of reionization, opposite to previous ideas, used to be most commonly illuminated, reasonably than being part of our true “darkish age” previous, the place a minimum of 80% of the reionizing photons got here from small, low-mass galaxies.
To start with, at left, the Universe is stuffed with impartial, light-blocking subject again sooner than any stars have fashioned. When stars start to shape, alternatively, they devise ionizing ultraviolet photons, which result in wallet that behave as despite the fact that they’re clear to visual gentle, as proven in purple. Through the years, as we transfer to the appropriate, an increasing number of of the Universe turns into reionized, till reionization completes round 550 million years after the Giant Bang. This epoch of reionization, opposite to previous ideas, used to be most commonly illuminated, reasonably than being part of our true “darkish age” previous, the place a minimum of 80% of the reionizing photons got here from small, low-mass galaxies.
Credit score: Thesan Collaboration
Since the Native Crew is the place we are living, it’s the galaxies inside of it which might be the perfect, closest ones to review. And we will measure the homes of stars and fuel inside of the ones tiny, low-mass galaxies. A few of them fashioned stars suddenly early on, after which by no means once more in all of the billions of years since. A few of them show off more than one populations of stars that fashioned at a number of other epochs all over cosmic historical past. Then again, as a result of there are broad, huge galaxies close by — once more, the Milky Approach and Andromeda — it’s tough to know the way such things as mergers and galactic interactions affected the ones histories. Many confounding components make it tough to grasp why the items we see close by have the homes that they do.
Did galaxies that experience only one inhabitants of stars inside of acquire that inhabitants as a result of they fashioned stars suddenly after which expelled their impartial subject? Or would they’ve persisted to shape stars in the event that they had been remoted, however interactions with the massive, neighboring galaxy’s halo stripped that subject away?
Have galaxies that show off a number of populations of stars inside of accreted subject from intergalactic house to feed their fuel reservoirs through the years, or have they resulted from more than one smaller galaxies that experience merged in combination through the years?
And do galaxies that shape stars repeatedly achieve this as a result of inside processes by myself, or had been they induced by way of gravitational interactions with greater neighboring galaxies?
If we need to solution those questions, we’re pressured to take a look at remoted low-mass galaxies: galaxies that lack those headaches.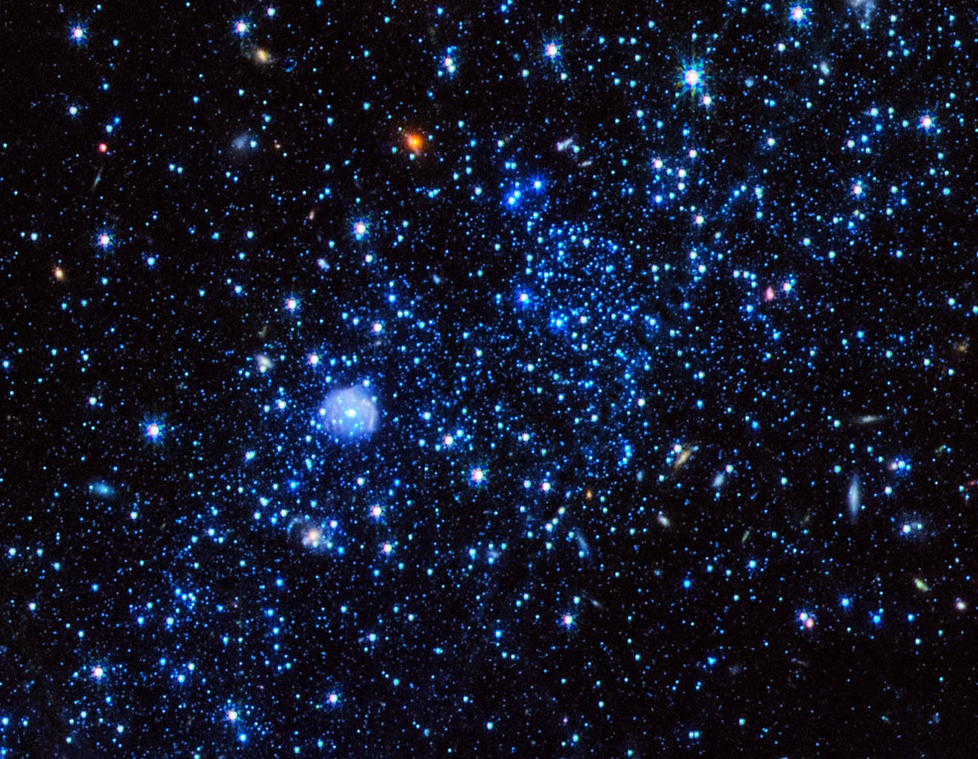 The dwarf galaxy, Leo P, is an engaging mixture of a close-by, low-mass galaxy, with simply 200,000 stars inside of at a distance of five.3 million light-years away. Then again, its remoted location, and its loss of interplay with greater or comparably massed galaxies, lets in it to provide us distinctive insights into the star-formation historical past of our Universe.
The dwarf galaxy, Leo P, is an engaging mixture of a close-by, low-mass galaxy, with simply 200,000 stars inside of at a distance of five.3 million light-years away. Then again, its remoted location, and its loss of interplay with greater or comparably massed galaxies, lets in it to provide us distinctive insights into the star-formation historical past of our Universe.
Credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, Kristen McQuinn (STScI); Processing: Joseph DePasquale (STScI)
That’s the place the tiny, remoted galaxy referred to as Leo P is available in. Positioned 5.3 million light-years from Earth, Leo P used to be simplest found out quite lately: again in 2013. Not like galaxies inside of our Native Crew, Leo P is situated a long way away — about one million light-years away — from even the nearest different tiny galaxies in its neighborhood. With out a big halo of subject material close by, or a scorching area the place starlight and/or star-formation took place in nice abundance, it must have skilled only a few exterior components that may have contributed to disrupt its herbal star-forming historical past over cosmic time.With simplest about 200,000 sun lots price of stars inside of (fewer stars than even many of the globular clusters discovered littered all over the Milky Approach), it’s the very best laboratory for learning how star-formation took place in very remoted low-mass galaxies all over the Universe. Although galaxies akin to Leo P may well be very tough to seek out and find out about within the close by Universe, it’s galaxies akin to this one which might be considered those basically answerable for generating the ultraviolet gentle when the Universe used to be simplest about ~500 million years previous. Since that’s the epoch in cosmic historical past the place the Universe turns into reionized — i.e., when the impartial atoms fashioned in a while after the Giant Bang turned into ionized, permitting starlight to circulation freely all over house — learning the historical past of galaxies akin to that is of paramount significance. Many close by galaxies, together with all of the galaxies of the native crew (most commonly clustered on the excessive left), show a dating between their mass and pace dispersion that signifies the presence of darkish subject. NGC 1052-DF2 is the primary recognized galaxy that seems to be made of ordinary subject by myself, and used to be later joined by way of DF4 in 2019. Galaxies like Segue 1 and Segue 3, alternatively, are specifically darkish matter-rich; there are a large variety of homes, and the darkish matter-free galaxies are simplest poorly understood.
Many close by galaxies, together with all of the galaxies of the native crew (most commonly clustered on the excessive left), show a dating between their mass and pace dispersion that signifies the presence of darkish subject. NGC 1052-DF2 is the primary recognized galaxy that seems to be made of ordinary subject by myself, and used to be later joined by way of DF4 in 2019. Galaxies like Segue 1 and Segue 3, alternatively, are specifically darkish matter-rich; there are a large variety of homes, and the darkish matter-free galaxies are simplest poorly understood.
Credit score: S. Danieli et al., ApJL, 2019
This galaxy, Leo P, is in some ways similar to what we all know as ultra-faint dwarf galaxies: a inhabitants of galaxies that would possibly have as few as a number of hundred stars inside of it, however could have as much as a few hundred thousand stars as neatly. They aren’t like globular clusters within the sense that globular clusters have little-to-no darkish subject inside of them, as their dynamics are ruled by way of stars and different kinds of common subject (i.e., stuff fashioned from protons, neutrons, and electrons). After we practice those ultra-faint dwarf galaxies, we discover that the celebrities inside of them transfer round in no time: a lot more temporarily than the volume of stars inside of them would permit.With such rapid speeds for the celebrities and so little stellar mass inside of, they will have to be ruled by way of darkish subject. On a cosmic scale, darkish subject outmasses common subject by way of a 5-to-1 ratio, and this ratio seems in maximum puts: within the cosmic internet, in galaxy clusters, in teams of galaxies, and in particular person broad, huge galaxies. However as we move to decrease mass galaxies, we discover that the darkish matter-to-normal subject ratio seems to extend precipitously. The ultra-faint dwarf galaxies are probably the most excessive, with ratios of a number of hundred to at least one, considered brought about by way of star-formation “kicking” the standard subject out of those items, leaving simplest the celebrities and the standard subject in the back of.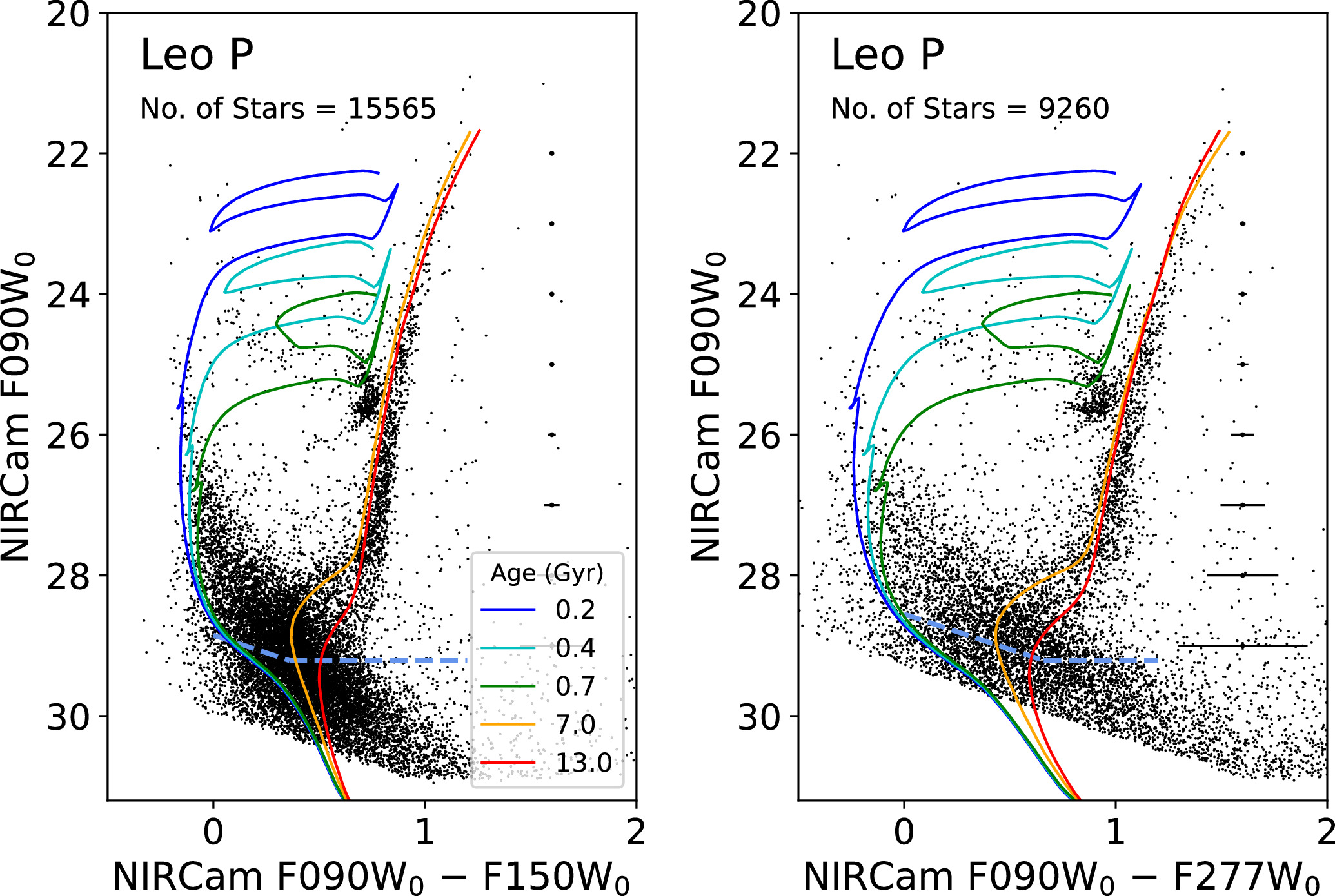 The colour-difference diagram (x-axis) plotted in opposition to the brightness (y-axis) of the celebrities inside of Leo P disclose proof for a number of other populations of stars fashioned in punctuated bursts at quite a lot of epochs in cosmic historical past. Remarkably, the primary burst took place greater than 13 billion years in the past, and used to be adopted by way of a “quiet length” the place no new stars fashioned for 3-4 billion years thereafter.
The colour-difference diagram (x-axis) plotted in opposition to the brightness (y-axis) of the celebrities inside of Leo P disclose proof for a number of other populations of stars fashioned in punctuated bursts at quite a lot of epochs in cosmic historical past. Remarkably, the primary burst took place greater than 13 billion years in the past, and used to be adopted by way of a “quiet length” the place no new stars fashioned for 3-4 billion years thereafter.
Credit score: Okay.B.W. McQuinn et al., Astrophysical Magazine, 2024
So what would we discover, so far as its historical past went, as we appeared to the galaxy Leo P with our trendy arsenal of house telescopes? 5.3 million light-years might appear to be a a long way distance to us, however to a telescope like Hubble or JWST, it’s shut sufficient that we will unravel particular person stars inside of this galaxy. When Hubble considered this galaxy years in the past, it used to be in a position to show us that the celebrities on this galaxy aren’t all previous; as an alternative, it discovered proof for quite recently-formed populations of stars. Hubble excels at revealing the brightest, bluest stars, which can be additionally the shortest-lived stars. The truth that it noticed a big inhabitants of vivid blue stars tells us that star-formation didn’t happen suddenly, way back, after which by no means took place once more. As a substitute, it signifies a historical past the place star-formation took place in numerous bursts, together with a number of bursts that took place simplest within the fresh previous.However JWST, with its:
greater aperture,
larger solution,
and infrared-optimized features,
is adept at measuring older, redder, fainter populations of stars inside of galaxies akin to this one. Despite the fact that we had strongly suspected that there can be a mixture of old-and-young stellar populations inside of, it used to be JWST information that used to be required for unveiling the total star-formation historical past of this galaxy, appearing us when it did — and importantly, when it didn’t — shape stars inside of it over the process its existence. 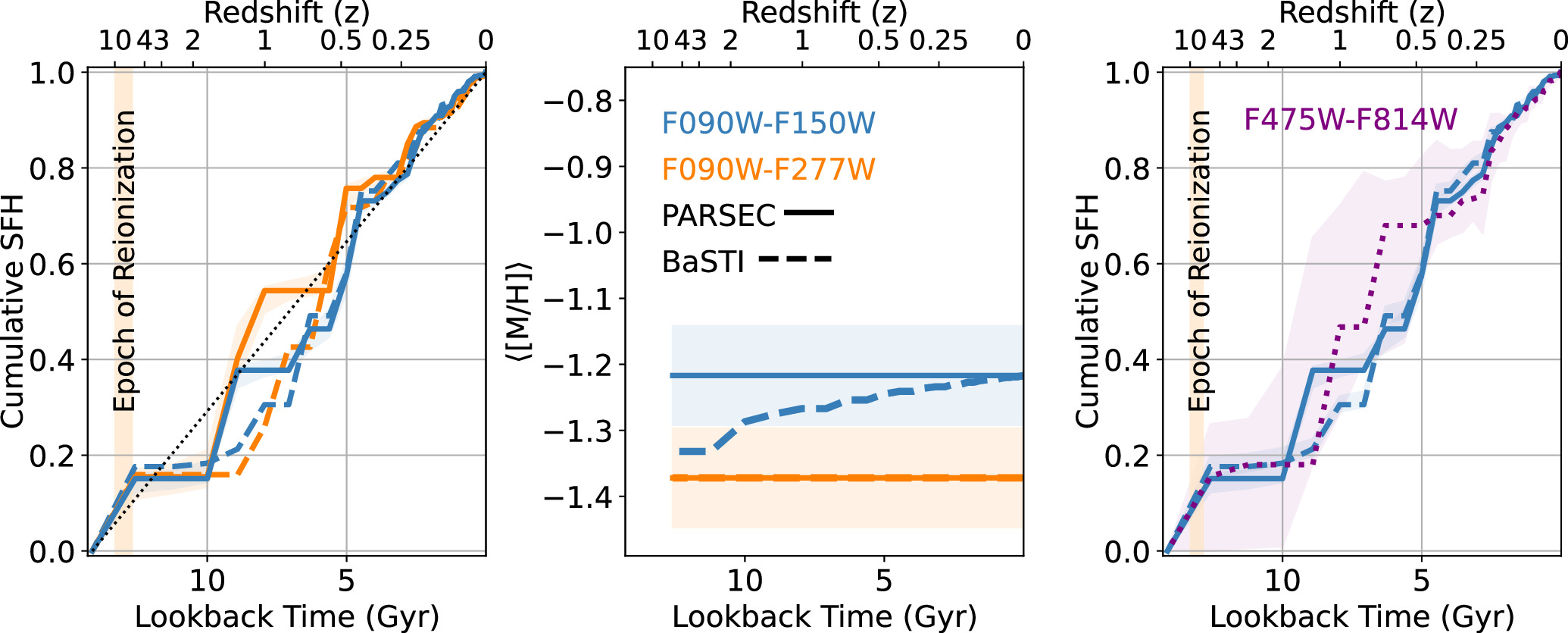 This determine, taken from a paper that studied galaxy Leo P with JWST, finds when stars fashioned inside of this galaxy, appearing the way it affected reionization and the way it frequently, however in bursts, fashioned stars due to this fact all over its historical past.
This determine, taken from a paper that studied galaxy Leo P with JWST, finds when stars fashioned inside of this galaxy, appearing the way it affected reionization and the way it frequently, however in bursts, fashioned stars due to this fact all over its historical past.
Credit score: Okay.B.W. McQuinn et al., Astrophysical Magazine, 2024
What used to be discovered inside of used to be exceptional. As you’ll see from the above chart, there are a number of other stellar populations inside of. In chronological order:
the primary inhabitants fashioned ~500-600 million years after the Giant Bang, representing simplest about 15-20% of the celebrities discovered inside of,
then the whole lot used to be quiet, without a star-formation in any respect, for the following 3-4 billion years,
after which every other, greater, longer-lasting burst of star-formation took place, spanning a few billion years and forming about two times as many stars as the unique burst,
after which after every other quiet length, with every other 3-4 million years of state of no activity, star-formation picked up once more,
with an enormous burst happening about 5 billion years in the past (larger, fairly, than the primary authentic starburst),
after which with star-formation step by step proceeding to trickle in frequently over the last 5 billion years.
Now, what’s maximum exceptional about that is how other it’s from the star-formation historical past we discover in close by ultra-faint dwarf galaxies. Both all of them shape stars in a single burst, early on, after which by no means once more, or they show off a wealthy historical past of star-formation, however provided that their lots are a lot better. In different phrases, one thing will have to be taking place inside of this remoted galaxy that doesn’t occur for galaxies inside of our Native Crew, or for any of the opposite ultra-faint dwarf galaxies that we all know of.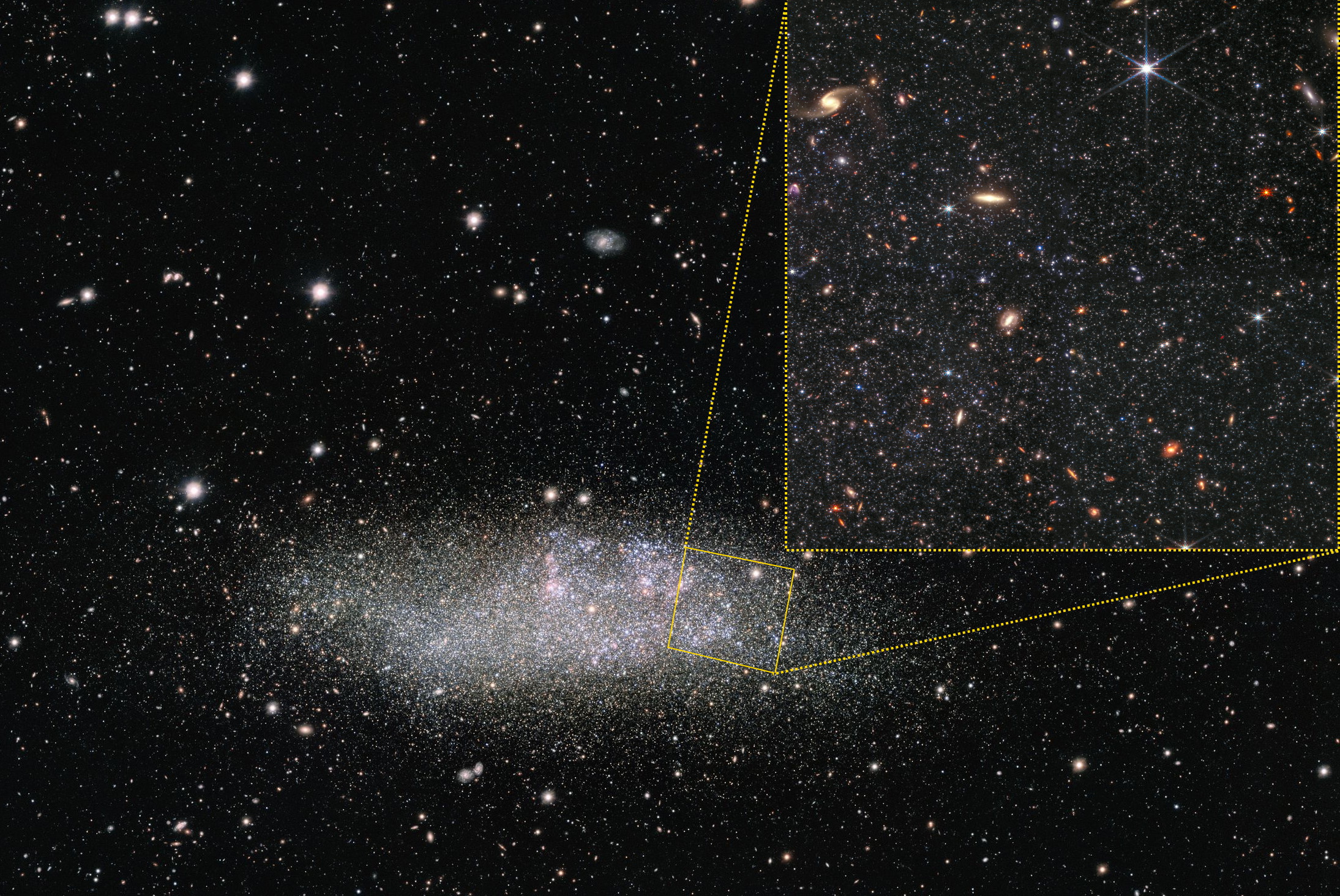 A large-field view of dwarf galaxy Wolf-Lundmark-Melotte (WLM), along with the area that JWST imaged the use of its NIRCam device (inset). The ability of JWST to expose particular person stars, even the faint, low-luminosity ones, in galaxies like this one situated ~3 million light-years away is poised to set us on a greater trail towards working out the star-formation historical past in our Universe throughout cosmic time.
A large-field view of dwarf galaxy Wolf-Lundmark-Melotte (WLM), along with the area that JWST imaged the use of its NIRCam device (inset). The ability of JWST to expose particular person stars, even the faint, low-luminosity ones, in galaxies like this one situated ~3 million light-years away is poised to set us on a greater trail towards working out the star-formation historical past in our Universe throughout cosmic time.
Credit: ESO; Acknowledgement: VST/OmegaCAM Native Crew Survey; NASA, ESA, CSA, Okay. McQuinn (RU); Processing: Z. Levay (STScI); Edits: E. Siegel
So how are we able to give an explanation for this?Possibly the main thought is to bear in mind how construction formation works within the Universe. To start with, it’s the areas of biggest overdensity — the place the true density exceeds the cosmic moderate density by way of the best quantity — that gravitationally cave in first. This is applicable to galaxies of all sizes and lots more and plenty: giant ones, intermediate sized ones, small ones, and the tiniest ones of all.However right here’s the place the adaptation is available in.In case your tiny galaxy is within the neighborhood of alternative galaxies, together with high-mass galaxies, they’re going to draw one every other to provide upward push to a galaxy crew. Inside that crew, probably the most huge galaxies are going to come back to dominate: they’ll sink to the middle, they’ll draw in and accrue the smaller mass galaxies, and when subject from the intergalactic medium falls into that galaxy crew, it’ll be probably the most huge galaxies that take in most-to-all of it. In different phrases, if a tiny galaxy is located with different, greater galaxies close by, it’s the most important galaxies which might be going to dominate. Just like a kitten positioned in a delight of lions, the smallest galaxies fail to see a cosmic banquet, even if there’s an abundance of subject. For the primary 550 million years of the Universe, impartial, light-blocking atoms persist within the house between galaxies, proceeding what’s referred to as the cosmic darkish ages. Whilst that subject material persists, starlight is in large part absorbed, and can not penetrate via this “fog.” As soon as the closing of that impartial subject turns into reionized, starlight can propagate freely in the course of the Universe, marking the tip of the reionization epoch.
For the primary 550 million years of the Universe, impartial, light-blocking atoms persist within the house between galaxies, proceeding what’s referred to as the cosmic darkish ages. Whilst that subject material persists, starlight is in large part absorbed, and can not penetrate via this “fog.” As soon as the closing of that impartial subject turns into reionized, starlight can propagate freely in the course of the Universe, marking the tip of the reionization epoch.
Credit score: M. Alvarez, R. Kaehler, and T. Abel / chart by way of Giant Suppose
Then again, in case your tiny galaxy is remoted, there are not any different competition for that infalling intergalactic subject. There is not any ram force stripping; there are not any tidal interactions; there is not any “scorching halo” of fuel that stops gravitational infall or cave in onto a smaller, lower-mass object. As a substitute, Leo P, as a result of its cosmic isolation, had that preliminary segment of star-formation that kicked out the remainder fuel inside of it, resulting in an early inhabitants of stars: the similar form of inhabitants that most probably existed in those tiny, dwarf galaxies that reionized the Universe again all over the primary half-a-billion years of cosmic historical past.However then, as a result of its isolation, intergalactic subject step by step started to accrue onto this galaxy: rebuilding its shops of fuel through the years. Sooner or later, after billions of years of expansion, sufficient subject collected {that a} molecular cloud of fuel collapsed, triggering a brand new burst of star-formation: a bigger one than the preliminary one. The cycle repeated itself, and after every other few billion years of quiet, star-formation ignited for a 3rd time, after which persisted quietly and frequently: a procedure that’s nonetheless ongoing lately.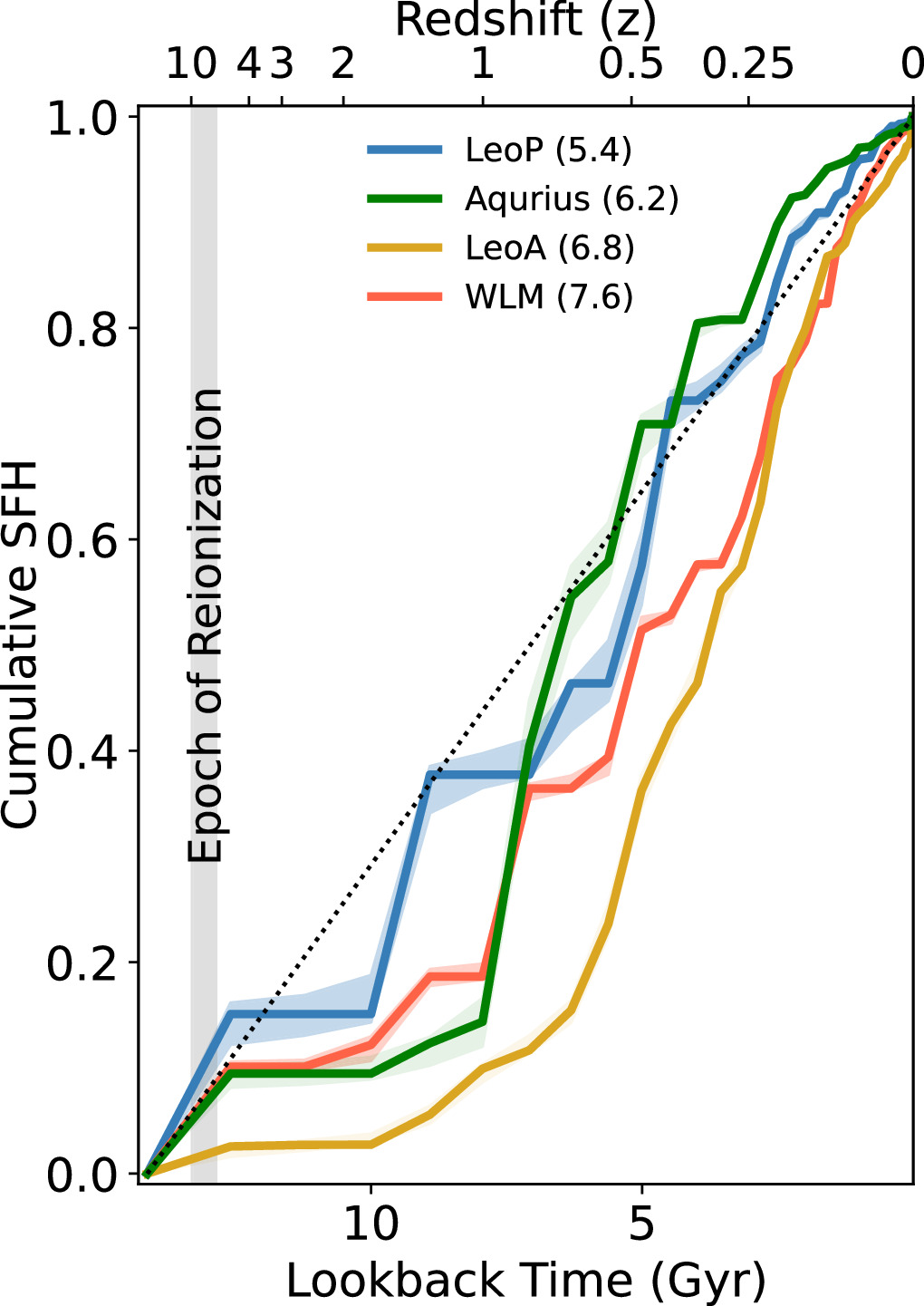 Leo P isn’t the primary quite remoted dwarf galaxy to have its star-formation historical past studied with trendy house telescopes, however it’s the lowest-mass, maximum remoted dwarf galaxy to show off this actual form of star-formation historical past. With an preliminary starburst that peaks all over the epoch of reionization, adopted by way of an extended quiet length, it’s going to but function the template for the way tiny, remoted galaxies develop up within the Universe.
Leo P isn’t the primary quite remoted dwarf galaxy to have its star-formation historical past studied with trendy house telescopes, however it’s the lowest-mass, maximum remoted dwarf galaxy to show off this actual form of star-formation historical past. With an preliminary starburst that peaks all over the epoch of reionization, adopted by way of an extended quiet length, it’s going to but function the template for the way tiny, remoted galaxies develop up within the Universe.
Credit score: Okay.B.W. McQuinn et al., Astrophysical Magazine, 2024
After we put all of those items in combination — what took place inside of this galaxy blended with what took place in different ultra-faint dwarf galaxies, plus what we already know in regards to the epoch of reionization — we begin to arrive at a unified image for the way the tiniest galaxies within the Universe develop up. To start with, there are few sufficient galaxies within the Universe, and little sufficient time for them to merge, that those ultra-faint dwarf galaxies are the commonest sort: with a mass of no various hundred thousand sun lots. They gravitate, cave in, shape stars, and it’s the sunshine from the ones stars that reionize the Universe. Usually, that burst of star-formation supplies sufficient comments to forestall long run star-formation from happening, in ultra-faint dwarfs like this and most likely in much more huge galaxies.However then, the evolution of anyone specific ultra-faint dwarf is dependent mightily on its atmosphere. If it will get drawn right into a galaxy crew or cluster, it most probably received’t be capable to accrue to any extent further star-forming subject material, and will probably be “frozen in” as a relic from the previous. Its greater, extra huge neighbors will act like territorial bullies, gobbling up any infalling subject and leaving almost none for the smaller satellites. In isolation, alternatively, it may well keep growing and flourish, the place new reservoirs of fuel will result in star-formation billions of years at some point, in each bursts and in a steady stable circulation, relying at the details of its historical past. In a wealthy crew, star-formation ceases for the tiniest galaxies. However in isolation, ongoing star-formation is all however assured.
Join the Begins With a Bang publication
Trip the universe with Dr. Ethan Siegel as he solutions the most important questions of all