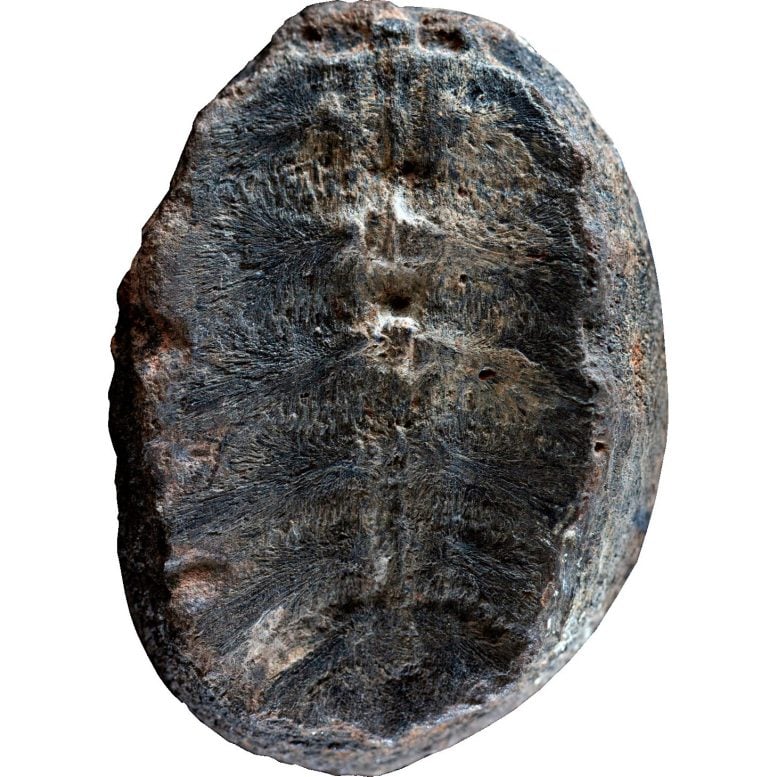
 The fossil that used to be firstly interpreted to be a plant, however researchers have now found out is the interior of the shell of a child turtle. Credit score: Fabiany Herrera and Héctor Palma-Castro
The fossil that used to be firstly interpreted to be a plant, however researchers have now found out is the interior of the shell of a child turtle. Credit score: Fabiany Herrera and Héctor Palma-Castro
Researchers nicknamed the fossil “Turtwig” after a Pokemon that’s half-turtle, half-plant.
From the Nineteen Fifties to the Nineteen Seventies, a Colombian priest named Padre Gustavo Huertas accumulated rocks and fossils close to a the town known as Villa de Levya. Two of the specimens he discovered had been small, spherical rocks patterned with traces that gave the impression of leaves; he labeled them as a kind of fossil plant. However in a brand new learn, revealed within the magazine Palaeontologia Electronica, researchers re-examined those “plant” fossils and located that they weren’t vegetation in any respect: they had been the fossilized stays of child turtles.
“It used to be actually unexpected to seek out those fossils,” says Héctor Palma-Castro, a paleobotany pupil on the Universidad Nacional de Colombia.
The vegetation in query were described by way of Huertas in 2003 as Sphenophyllum colombianum. The fossils come from Early Cretaceous rocks, between 132 and 113 million years in the past, throughout the dinosaurs’ generation. Fossils of Sphenophyllum colombianum had been unexpected right now and position — the opposite recognized contributors of the genus Sphenophyllum died out greater than 100 million years prior. The vegetation’ age and locality piqued the passion of Fabiany Herrera, the Negaunee assistant curator of fossil vegetation on the Box Museum in Chicago, and his pupil, Palma-Castro.
Wrong Id
“We went to the fossil assortment on the Universidad Nacional de Colombia in Bogotá and began having a look on the vegetation, and once we photographed them, we idea, ‘that is bizarre,’” says Herrera, who has been accumulating Early Cretaceous vegetation from northwestern South The united states, a space of the sector with little paleobotanical paintings.
To start with look, the fossils, about 2 inches in diameter, gave the impression of rounded nodules containing the preserved leaves of the plant Sphenophyllum. However Herrera and Palma-Castro spotted key options that weren’t rather proper.
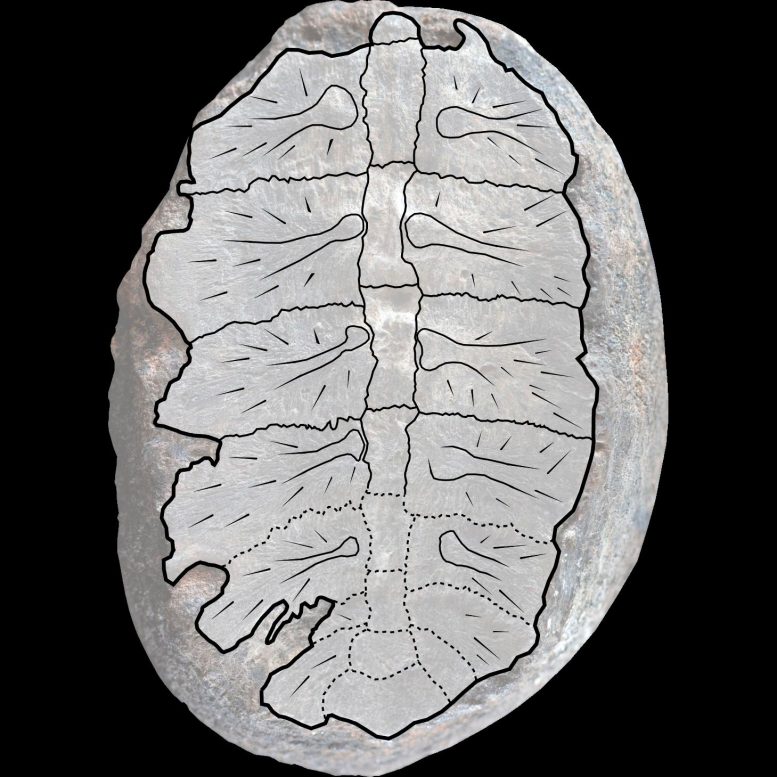 Drawing highlighting the rib and again bones, superimposed onto the fossil. Credit score: Photograph by way of Fabiany Herrera and Héctor Palma-Castro; drawing by way of Edwin-Alberto Cadena and Diego Cómbita-Romero.
Drawing highlighting the rib and again bones, superimposed onto the fossil. Credit score: Photograph by way of Fabiany Herrera and Héctor Palma-Castro; drawing by way of Edwin-Alberto Cadena and Diego Cómbita-Romero.
“We spent days looking out thru wood cupboards for fossil vegetation. After we after all discovered this fossil, interpreting the form and margin of the leaf proved difficult,” says Palma-Castro.
“Whilst you have a look at it intimately, the traces observed at the fossils don’t seem like the veins of a plant— I used to be sure that it used to be perhaps bone,” says Herrera. So he reached out to an previous colleague of his, Edwin-Alberto Cadena.
“They despatched me the footage, and I stated, “This for sure looks as if a carapace’— the bony higher shell of a turtle,” says Cadena, a paleontologist who specializes in turtles and different vertebrates on the Universidad del Rosario in Bogotá. When he noticed the dimensions of the footage, Cadena recollects, “I stated, ‘Smartly, that is exceptional, as a result of this isn’t just a turtle, nevertheless it’s additionally a hatchling specimen, it’s very, very small.”
Cadena and his pupil, Diego Cómbita-Romero of the Universidad Nacional de Colombia, additional tested the specimens, evaluating them with the shells of each fossil and fashionable turtles. “After we noticed the specimen for the primary time I used to be astonished, for the reason that fossil used to be lacking the everyday marks at the out of doors of a turtle’s shell,” says Cómbita-Romero. It used to be just a little bit concave, like a bowl. At that second we discovered that the visual a part of the fossil used to be the opposite facet of the carapace, we had been having a look on the a part of the shell this is within the turtle.”
Main points within the turtle’s bones helped the researchers estimate how previous it used to be at dying. “Turtle enlargement charges and sizes range,” says Cómbita-Romero, so the workforce checked out options just like the thickness of its carapace and the spots the place its ribs had been knitting in combination into forged bone. “It is a function unusual in hatchlings however seen in juveniles. All this data means that the turtle most likely died with a fairly advanced carapace, between 0 to at least one years previous, in a post-hatchling level,” he says.
The Importance of the Discovery
“That is if truth be told actually uncommon to seek out hatchlings of fossil turtles basically,” says Cadena. “When the turtles are very younger, the bones of their shells are very skinny, so they may be able to be simply destroyed.”
The researchers say that the rarity of fossilized child turtles makes their discovery a very powerful one. “Those turtles had been most likely family members of different Cretaceous species that had been as much as fifteen toes lengthy, however we don’t know a lot about how they if truth be told grew to such large sizes,” says Cadena.
The researchers don’t fault Padre Huertas for his mistake— the preserved shells actually do resemble many fossil vegetation. However the options that Huertas idea had been leaves and stems are if truth be told the changed rib bones and vertebrae that make up a turtle’s shell. Cómbita-Romero and Palma-Castro nicknamed the specimens as “Turtwig,” after a Pokémon that’s half-turtle, half-plant.
“Within the Pokémon universe, you come across the concept that of mixing two or extra components, comparable to animals, machines, vegetation, and so on. So, if in case you have a fossil to start with labeled as a plant that seems to be a child turtle, a couple of Pokémon instantly spring to mind. On this case, Turtwig, a child turtle with a leaf connected to its head,” says Palma-Castro.” In paleontology, your creativeness and capability to be amazed are at all times put to the take a look at. Discoveries like those are actually particular as a result of they no longer most effective make bigger our wisdom concerning the previous but in addition open a window to the varied probabilities of what we will be able to discover.”
Re-Comparing Historic Collections
The scientists additionally word the significance of those fossils within the higher scheme of Colombian paleontology. “We resolved a small paleobotanical thriller, however extra importantly, this learn presentations the wish to re-study historic collections in Colombia. The Early Cretaceous is a important time in land plant evolution, in particular for flowering vegetation and gymnosperms. Our long term activity is to find the forests that grew on this a part of the sector,” says Herrera.
Reference: “An Early Cretaceous Sphenophyllum or a hatchling turtle?” by way of Héctor D. Palma-Castro, Diego A. Cómbita-Romero, Edwin-Alberto Cadena, Mónica R. Carvalho and Fabiany Herrera, December 2023, Palaeontologia Electronica.
DOI: 10.26879/1306
This challenge used to be supported by way of the Nationwide Geographic Society, grant (EC-96755R-22) Finding Early Cretaceous Floras from Northern South The united states & the Negaunee Integrative Analysis Middle, Box Museum.













