The universe’s lacking subject could have in spite of everything been discovered.Astronomers suppose common subject — this is, the stuff that’s not darkish subject — makes up about 15% of the universe’s general mass. Alternatively, for years, researchers have run into an issue when seeking to quantify it: They have not been ready to search out about part of that “customary” subject within the stars, galaxies and different house constructions we will be able to see.However now, a big, world group of researchers has discovered that the diffuse hydrogen fuel surrounding maximum galaxies is considerably extra in depth than scientists prior to now idea — so in depth, actually, that it would account for lots of the universe’s lacking subject, the group says.”The measurements are for sure in line with discovering the entire [missing] fuel,” find out about co-author Simone Ferraro, an astronomer on the College of California, Berkeley, mentioned in a commentary. The find out about is recently to be had at the preprint server arXiv and is present process peer evaluation for newsletter within the magazine Bodily Evaluate Letters.The quest for the lacking matterFor their investigation, the researchers used knowledge from the Darkish Power Spectroscopic Tool (DESI) at Kitt Top Nationwide Observatory in Arizona, in addition to from the Atacama Cosmology Telescope in Chile.Comparable: ‘The universe has thrown us a curveball’: Biggest-ever map of house unearths we would possibly have got darkish power completely wrongUsing DESI observations, the group stacked photographs of roughly 7 million galaxies to measure the faint halos of ionized hydrogen fuel on the galaxies’ edges. Those halos are normally too faint to be noticed via customary strategies. So as a substitute, the group measured how a lot the fuel dimmed or brightened radiation from the cosmic microwave background — leftover radiation from the Giant Bang this is prevalent all the way through the universe.Get the arena’s most enticing discoveries delivered directly in your inbox.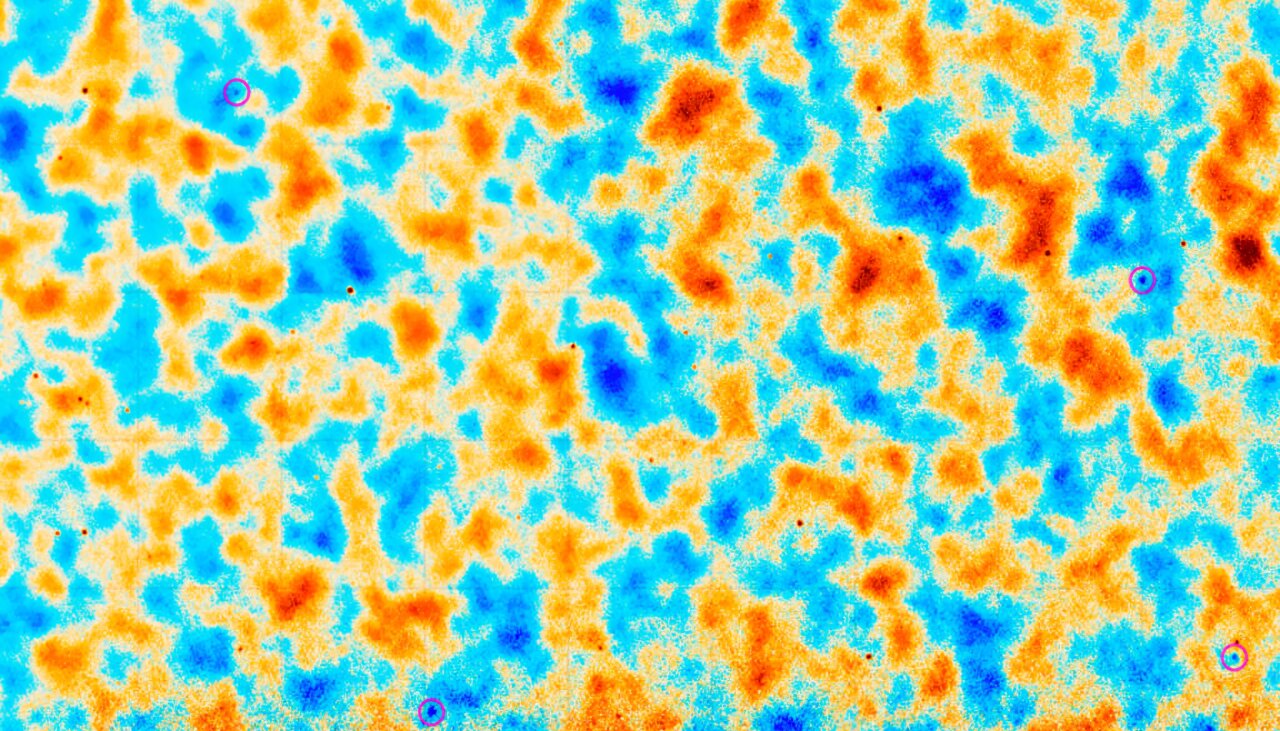 A map of the cosmic microwave background radiation acquired via the Atacama Cosmology Telescope. The circles spotlight spots the place ionized hydrogen fuel has scattered the radiation. (Symbol credit score: ACT; Magazine of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics)The group additionally came upon that the clouds of ionized hydrogen shaped ghostly, just about invisible filaments between galaxies. If it connects lots of the galaxies within the universe, this cosmic internet would simply span some distance sufficient to account for the prior to now undetected subject.Black holes on dutyThe discovery additionally would possibly trade what we find out about black hollow conduct. Scientists to begin with idea the supermassive black holes on the hearts of maximum galaxies best spewed jets of fuel early of their existence cycles. However the presence of such in depth diffuse fuel clouds signifies that those black holes most likely transform lively extra often than prior to now idea.”One of the crucial hypotheses is that [black holes] flip off and on on occasion in what is named an obligation cycle,” first find out about writer Boryana Hadzhiyska, an astronomer on the College of California, Berkeley, mentioned within the commentary.The next move will probably be to include the brand new measurements into present cosmological fashions. “There are an enormous selection of folks fascinated by the usage of our measurements to do an excessively thorough research that incorporates this fuel,” Hadzhiyska mentioned.
A map of the cosmic microwave background radiation acquired via the Atacama Cosmology Telescope. The circles spotlight spots the place ionized hydrogen fuel has scattered the radiation. (Symbol credit score: ACT; Magazine of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics)The group additionally came upon that the clouds of ionized hydrogen shaped ghostly, just about invisible filaments between galaxies. If it connects lots of the galaxies within the universe, this cosmic internet would simply span some distance sufficient to account for the prior to now undetected subject.Black holes on dutyThe discovery additionally would possibly trade what we find out about black hollow conduct. Scientists to begin with idea the supermassive black holes on the hearts of maximum galaxies best spewed jets of fuel early of their existence cycles. However the presence of such in depth diffuse fuel clouds signifies that those black holes most likely transform lively extra often than prior to now idea.”One of the crucial hypotheses is that [black holes] flip off and on on occasion in what is named an obligation cycle,” first find out about writer Boryana Hadzhiyska, an astronomer on the College of California, Berkeley, mentioned within the commentary.The next move will probably be to include the brand new measurements into present cosmological fashions. “There are an enormous selection of folks fascinated by the usage of our measurements to do an excessively thorough research that incorporates this fuel,” Hadzhiyska mentioned.
The universe’s ‘lacking subject’ could have in spite of everything been discovered





![YGOrganization | Develop into A Adorable Lady With “Taotao the Chanter”! [DOOD] YGOrganization | Develop into A Adorable Lady With “Taotao the Chanter”! [DOOD]](https://cdn.ygorganization.com/2025/07/eVPJQm3H-DOOD4.png)