Right now of 12 months, because the solar rises over Antarctica, a “hollow” opens up in Earth’s ozone layer.The ozone layer is an important planetary boundary that protects all existence on Earth from the solar’s harmful ultraviolet radiation. However as our analysis displays, a sequence of bizarre occasions in recent times led to ozone holes that lasted longer.
The Montreal Protocol, which got here into drive simply 4 years after the ozone hollow was once came upon in 1985, has been vastly a hit in combating many ozone-depleting gases from getting into the ambience.
However the hollow will proceed to open every 12 months for a minimum of any other 4 a long time on account of the lengthy lifetimes of gases emitted final century.
Ozone depletion could also be connected with local weather exchange, and there are different rising problems which might have an effect on ozone restoration. Those come with extra widespread mega-wildfires because of local weather exchange, emissions from rocket launches and extra satellite tv for pc particles burning up within the higher surroundings.
All this means ozone depletion is a long way from a solved downside.
Why ozone mattersMost atmospheric ozone is living within the stratosphere, at round 10-50km above Earth’s floor, the place it absorbs the solar’s ultraviolet-B rays.
In New Zealand and Australia, summertime top UV ranges are upper – occasionally by way of up to 30 % – than at related latitudes within the Northern Hemisphere.
That is because of decrease ranges of air air pollution, moderately decrease ozone quantities traditionally and proximity to the solar, which is nearer all over Southern Hemisphere summers.
New Zealand and Australia even have the easiest melanoma charges on the planet. That is partially on account of the upper UV ranges, however there are different contributing elements, together with stepped forward prognosis because of higher consciousness.
If the Montreal Protocol had no longer been carried out, melanoma charges could be considerably upper these days.
How the ozone hollow contributes to local weather changeEven despite the fact that maximum ozone-depleting gases are actually banned, it’s going to take a long time earlier than they’re long gone from the stratosphere.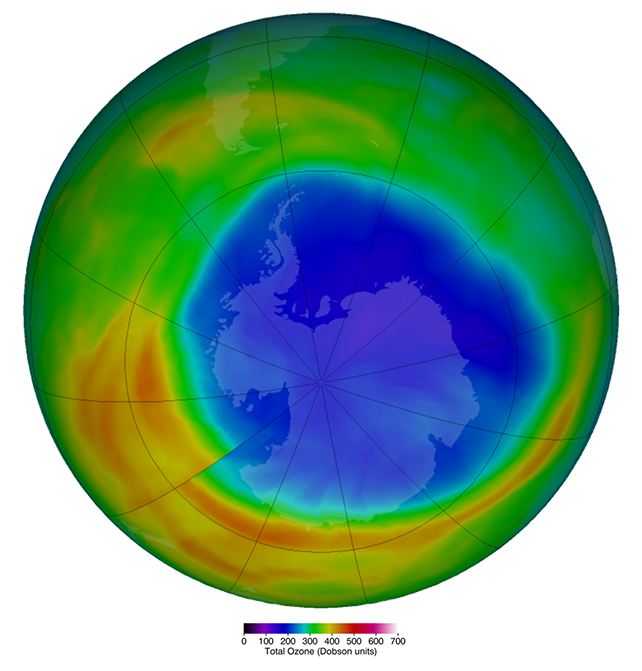 n fresh years, the ozone hollow above Antarctica has lasted longer. (Ozone Watch/NASA)Within the intervening time, the ozone hollow continues to shape above Antarctica every spring, inflicting cascading adjustments in temperature, winds and rainfall patterns around the Southern Hemisphere.
n fresh years, the ozone hollow above Antarctica has lasted longer. (Ozone Watch/NASA)Within the intervening time, the ozone hollow continues to shape above Antarctica every spring, inflicting cascading adjustments in temperature, winds and rainfall patterns around the Southern Hemisphere.
Ozone depletion reasons the present westerly winds at southern mid-latitudes (the “Roaring Nineteen Forties”) to beef up and shift towards Antarctica all over summertime. This has higher floor melting on Antarctic ice cabinets and is converting summertime rainfall and temperature patterns in New Zealand and Australia.
Whilst the ozone hollow drives local weather exchange, coverage and restoration of the ozone layer has further advantages for the local weather.
Many ozone-depleting gases, similar to chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) also are potent greenhouse gases. By means of phasing out those gases, the Montreal Protocol has helped the arena keep away from a catastrophic cave in of the worldwide ozone layer, and in addition restricted world warming.
One learn about estimated the Montreal Protocol behind schedule the primary ice-free summer time within the Arctic by way of as much as 15 years.
Ozone depletion and local weather exchange are interlinked problems. Whilst ozone depletion impacts Southern Hemisphere local weather, world ozone restoration is in flip suffering from emissions of dominant greenhouse gases similar to carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide and methane.
Technological inventions convey new threatsThe discovery of the ozone hollow in 1985 was once a big wonder. Whilst the alarm bells were sounded within the 1970’s that CFCs smash stratospheric ozone, scientists did not expect the lifestyles of the huge hollow above Antarctica.
It was once some years after the ozone hollow was once came upon that scientists started to know simply how ozone depletion works within the chilly Antarctic stratosphere.
The Montreal Protocol is arguably essentially the most a hit environmental treaty, however the ozone tale brings power surprises. The timing of ozone restoration relies partly on long term emissions however there are different contributing elements.
Contemporary analysis displays mega-wildfires such because the Australian bushfires of 2019 can give a contribution to ozone depletion. An building up in civilian rocket launches is anticipated to place extra ozone-depleting gases and aerosols into the stratosphere.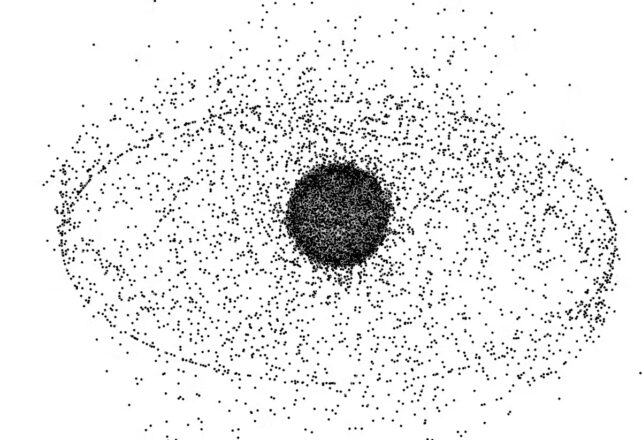 House particles re-entering Earth’s surroundings may give a contribution to ozone depletion. (NASA, CC BY-SA)Upper quantities of particles from satellite tv for pc re-entry might give a contribution to ozone loss by way of introducing aerosols into the higher surroundings.
House particles re-entering Earth’s surroundings may give a contribution to ozone depletion. (NASA, CC BY-SA)Upper quantities of particles from satellite tv for pc re-entry might give a contribution to ozone loss by way of introducing aerosols into the higher surroundings.
On most sensible of those problems come debatable “geoengineering” proposals, wherein aerosols are intentionally injected into the stratosphere to scale back the speed of worldwide warming.
This might most probably expend ozone additional and the sort of initiatives will have to be given cautious idea – at the side of myriad different issues earlier than such proposals are carried out.Historical past tells us technological innovation can convey answers (such because the alternative of CFCs by way of non-ozone depleting gases) but additionally unanticipated penalties. A long way from being a “solved” Twentieth-century downside, ozone stays crucial factor, albeit in new and prior to now unimagined techniques.![]()
Laura Revell, Affiliate Professor in Environmental Physics, College of Canterbury; Dan Smale, Primary Technician, Nationwide Institute of Water and Atmospheric Analysis, and Richard McKenzie, Emeritus, Nationwide Institute of Water and Atmospheric ResearchThis article is republished from The Dialog beneath a Ingenious Commons license. Learn the unique article.
There is a Explanation why Why The Ozone Hollow Will Stay Opening Up For A long time






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1231124954-fac4ab8390b34b8690301febddb0a92b.jpg)







