Tiny fragments of microplastics are making their method deep inside of our our bodies in relating to amounts, considerably thru our foods and drinks.Scientists have not too long ago discovered a easy and efficient way of taking away them from water.
A crew from Guangzhou Scientific College and Jinan College in China ran checks on each cushy water and difficult faucet water (which is richer in minerals).
“Faucet water nano/microplastics (NMPs) escaping from centralized water remedy programs are of accelerating world fear, as a result of they pose attainable well being chance to people by the use of water intake,” write the researchers of their paper, printed in February.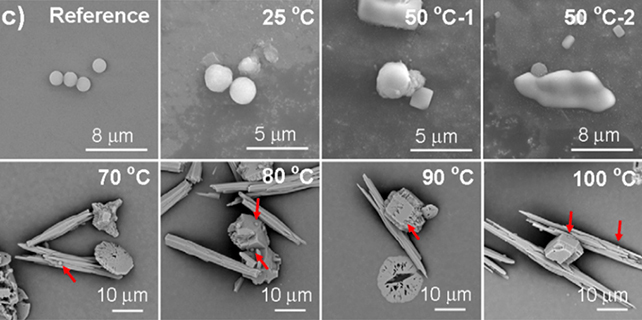 Additional microplastics had been added to decide the effectiveness of the boiling and filtering procedure. (Yu et al., Environmental Science & Generation Letters, 2024)They added in nanoplastics and microplastics prior to boiling the liquid after which filtering out any precipitates.
Additional microplastics had been added to decide the effectiveness of the boiling and filtering procedure. (Yu et al., Environmental Science & Generation Letters, 2024)They added in nanoplastics and microplastics prior to boiling the liquid after which filtering out any precipitates.
In some instances, as much as 90 % of the NMPs had been got rid of through the boiling and filtering procedure, despite the fact that the effectiveness various in keeping with the kind of water.
In fact the massive get advantages is that the general public can do it the usage of what they have already got of their kitchen.
“This easy boiling water technique can ‘decontaminate’ NMPs from family faucet water and has the potential of harmlessly assuaging human consumption of NMPs thru water intake,” the crew writes.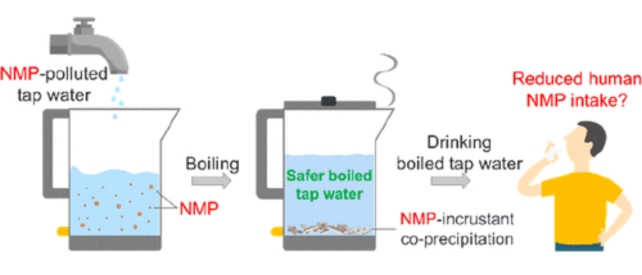 This easy boiling water technique can ‘decontaminate’ NMPs from family faucet water. (Yu et al., Environmental Science & Generation Letters, 2024)A better focus of NMPs was once got rid of from samples of arduous faucet water, which naturally paperwork a build-up of limescale (or calcium carbonate) as it’s heated.
This easy boiling water technique can ‘decontaminate’ NMPs from family faucet water. (Yu et al., Environmental Science & Generation Letters, 2024)A better focus of NMPs was once got rid of from samples of arduous faucet water, which naturally paperwork a build-up of limescale (or calcium carbonate) as it’s heated.
Regularly observed inside of kitchen kettles, the chalky substance paperwork at the plastic’s floor as adjustments in temperature drive the calcium carbonate out of resolution, successfully trapping the plastic fragments in a crust. Tiny fragments of microplastics are making their method deep inside of our our bodies. (pcess609/Canva)Even in cushy water, the place much less calcium carbonate is dissolved, kind of 1 / 4 of the NMPs had been snagged from the water.
Tiny fragments of microplastics are making their method deep inside of our our bodies. (pcess609/Canva)Even in cushy water, the place much less calcium carbonate is dissolved, kind of 1 / 4 of the NMPs had been snagged from the water.
Any bits of lime-encrusted plastic may just then be got rid of thru a easy clear out like the stainless-steel mesh used to pressure tea, the researchers say.
Previous research have measured fragments of polystyrene, polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyethylene terephthalate in potable faucet water, which we are eating day-to-day in various amounts.
To place the way to without equal take a look at, the researchers added much more nanoplastic debris, which have been successfully decreased in quantity. Consuming boiled water (as soon as it is cooled, in fact) may change into a extra in style follow. (Mikkaphoto/Canva)”Consuming boiled water it appears is a viable long-term technique for lowering world publicity to NMPs,” write the researchers.
Consuming boiled water (as soon as it is cooled, in fact) may change into a extra in style follow. (Mikkaphoto/Canva)”Consuming boiled water it appears is a viable long-term technique for lowering world publicity to NMPs,” write the researchers.
“Consuming boiled water, on the other hand, is ceaselessly thought to be a neighborhood custom and prevails most effective in a couple of areas.”
The analysis crew hopes that ingesting boiled water may change into a extra in style follow as plastics proceed to take over the sector.
Whilst it is nonetheless now not sure precisely how destructive this plastic is to our our bodies, it is obviously now not the healthiest of snacks. Representation of the intestine microbiome in a human digestive gadget. (nopparit/Canva Professional)Plastics have already been connected to adjustments within the intestine microbiome and the frame’s antibiotic resistance.
Representation of the intestine microbiome in a human digestive gadget. (nopparit/Canva Professional)Plastics have already been connected to adjustments within the intestine microbiome and the frame’s antibiotic resistance.
The crew at the back of this newest find out about needs to look extra analysis into how boiled water may just stay synthetic fabrics out of our our bodies – and in all probability counter probably the most alarming results of microplastics which are rising. Plastics proceed to take over the sector. (mbala mbala merlin/Canva)”Our effects have ratified a extremely possible way to cut back human NMP publicity and established the root for additional investigations with a miles greater choice of samples,” write the authors.
Plastics proceed to take over the sector. (mbala mbala merlin/Canva)”Our effects have ratified a extremely possible way to cut back human NMP publicity and established the root for additional investigations with a miles greater choice of samples,” write the authors.
The analysis has been printed in Environmental Science & Generation Letters.An previous model of this text was once printed in March 2024.
There is a Unusually Simple Method to Take away Microplastics From Consuming Water













