Existence on Earth is beautiful difficult at the present time, nevertheless it wasn’t at all times so. The fossil file hints at more practical instances, thousands and thousands of years in the past, when every organism consisted of only one cellular.
However round 575 million years in the past – for causes we will be able to handiest bet at – extra complicated lifestyles paperwork with a couple of cells began appearing within the fossil file. We name them the Ediacaran biota.
The strains of this sort of early complicated creatures has simply been unearthed within the South Australian outback, and its intricate design opponents all different fossils sooner than it. Behold, certainly one of Earth’s earliest animals: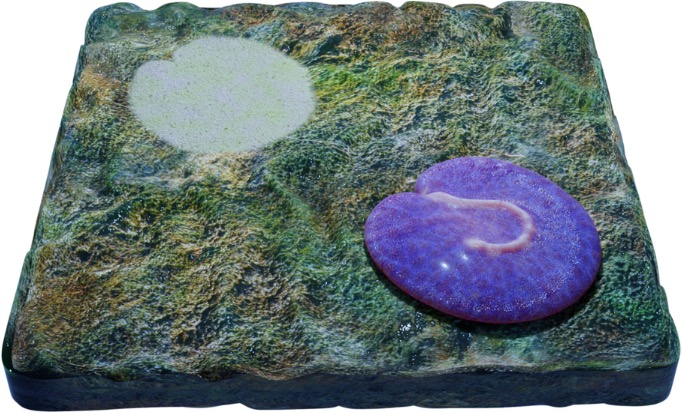 An artist’s impact of Quaestio simpsonorum’s frame in foreground and the impact left within the natural mat in the back of. Be aware the mottled red texture of the organism is a stylistic interpretation, now not according to fossil proof. (Walker Weyland/Evans et al., Evolution & Construction, 2024)Good enough, so it is a flattened, round blob with a mysterious query mark form for a butt crack.
An artist’s impact of Quaestio simpsonorum’s frame in foreground and the impact left within the natural mat in the back of. Be aware the mottled red texture of the organism is a stylistic interpretation, now not according to fossil proof. (Walker Weyland/Evans et al., Evolution & Construction, 2024)Good enough, so it is a flattened, round blob with a mysterious query mark form for a butt crack.
A collaboration between US scientists and paleontologists from the South Australian Museum brings us this exceptional prehistoric lump, Quaestio simpsonorum.
They understand it’s an animal on account of the options it stocks with dwelling individuals of the dominion: a couple of cells, the power to transport, and a frame plan arranged into other halves.
And so they discovered now not one, however greater than a dozen of these items, in conjunction with hint fossils – the imprints in their blobby our bodies preserved ceaselessly within the now-petrified mat of microscopic algae and micro organism that Quaestio as soon as lurked in.
A few of these impressions display moderately offset outlines distinct from the tougher edges of the animal’s imprint, proof that those had been a few of the first animals able to transferring on their very own.
“Probably the most thrilling moments… was once once we flipped over a rock, brushed it off, and noticed what was once clearly a hint fossil in the back of a Quaestio specimen – a transparent signal that the organism was once motile; it would transfer,” Harvard College evolutionary biologist Ian Hughes says.
A little bit smaller than the dimensions of a human palm, the Quaestio’s unique question-mark form – for which it was once named – distinguishes a left and proper aspect, an indication of bilateral symmetry, in conjunction with a a very powerful asymmetrical twist.
“There are not different fossils from this time that experience proven this kind of group so definitively,” Florida State College geologist Scott Evans says.
Asymmetry is an element of modern day animals, together with people, and Quaestio would possibly simply be the primary to adapt this mathematically difficult quirk.
“Finding out the historical past of lifestyles via fossils tells us how animals evolve and what processes motive their extinction, be it local weather trade or low oxygen,” says paleontologist Mary Droser, lead scientist for Nilpena Ediacara Nationwide Park, the place the fossil was once came upon.
Because the web page of Earth’s oldest fossil animals, the Ediacara biota, the nationwide park is being regarded as for UNESCO Global Heritage Web site checklist, to give protection to the precious data of our Earth’s dwelling historical past it comprises.
“We are the one planet that we all know of with lifestyles, in order we glance to search out lifestyles on different planets, we will be able to return in time on Earth to peer how lifestyles developed on the planet,” Droser says.This analysis was once printed in Evolution & Construction.
This Atypical, Fleshy Blob Is One in all Earth’s Earliest Animals