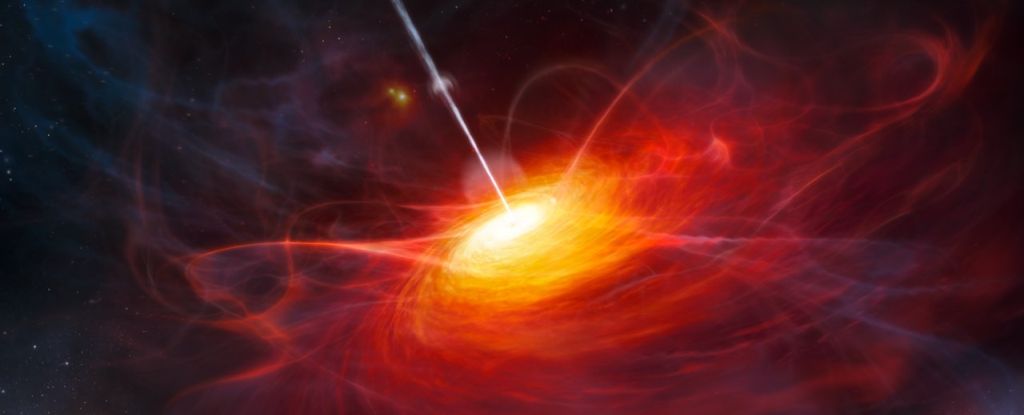
A black hollow found out lurking within the Cosmic Daybreak is simply means too large to simply give an explanation for. Sitting on the middle of a galaxy known as J1120+0641, it pointers the scales at smartly over one thousand million Suns’ price of mass.
Larger black holes exist throughout us nowadays. The issue is the when of J1120+0641’s lifestyles. At not up to 770 million years after the Large Bang, it is laborious to determine how the black hollow had the time to achieve that a lot mass.
We’ve got identified concerning the galaxy and its overstuffed black hollow for greater than a decade, and scientists had concepts about the way it got here to be. Now, observations the usage of the JWST have nixed a type of notions. Through all measures taken, J1120+0641 seems “shockingly standard”, leaving open extra unique explanations for the black hollow’s weight-gain.
The invention of J1120+0641 used to be introduced again in 2011, and for a couple of years it remained essentially the most far-off quasar galaxy identified. It used to be a just right few years, in fact. So far as we knew, J1120+0641 used to be an outlier, with one conceivable reason for its measurement nonetheless at the desk.
Quasar galaxies are galaxies that experience a central supermassive black hollow feeding at an amazing fee. They are surrounded by means of an infinite cloud of gasoline and dirt, which they slurp down as rapid as they may be able to. The friction and gravity across the black hollow warmth the fabric, inflicting it to polish brightly.
However the pace at which a black hollow can feed isn’t countless. The utmost solid fee is decided by means of its Eddington restrict, past which the heated subject material shines so brightly that radiation power would exceed gravitational pull, pushing the fabric away and leaving not anything for the black hollow to feed upon.
Now, black holes can in brief input super-Eddington accretion, the place they push via this restrict and guzzle as a lot subject material as they may be able to sooner than the radiation power kicks in. This is likely one of the conceivable explanations for the black hollow on the middle of J1120+0641 and, as we discover them in higher numbers, different massive black holes lurking initially of the Universe.
To search for the indicators of super-Eddington accretion, astronomers wanted information of a enough answer to accomplish an in depth research of the galaxy’s gentle, in search of signatures related to excessive processes. And for this, we wanted JWST, essentially the most robust house telescope ever constructed, optimized for peering into the ones far-off reaches of house and time.
JWST seen the galaxy in early 2023, and a crew led by means of astronomer Sarah Bosman of the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Germany teased aside the sunshine it accrued to catalog the homes of the fabric across the black hollow: an enormous torus of mud at the outskirts, and a sparkling disk swirling round and feeding into the black hollow.
This research unearths that the black hollow is in fact feeding lovely generally – there is not anything about its accretion that looks considerably other from different, more moderen quasar galaxies.
One conceivable reason for those large black holes is that further mud used to be main astronomers to overestimate their plenty. And but there is not any signal of extra mud, both.
That signifies that J1120+0641 is what apparently to be: a gorgeous standard quasar galaxy, with a black hollow that isn’t guzzling down subject material at a super-high fee. The black hollow, and how it feeds, had been already fairly mature by the point we seen it, inside a couple of hundred million years of the Large Bang
“General, the brand new observations best upload to the thriller: Early quasars had been shockingly standard,” Bosman says. “Regardless of through which wavelengths we practice them, quasars are just about equivalent in any respect epochs of the Universe.”
Which means that super-Eddington accretion is not the strategy to the expansion of puzzlingly huge black holes on the daybreak of time.
The opposite main clarification is that the black holes shaped from lovely massive ‘seeds’ first of all. Slightly than a gradual, sluggish procedure from one thing the dimensions of a celeb, this idea proposes that the black holes shaped from the cave in of clumps of topic and even extraordinarily massive stars as much as loads of 1000’s of occasions the mass of the Solar, giving their expansion a head get started.
As we discover increasingly of those behemoths lurking within the fog initially of the Universe, this perception turns out much less ordinary, and extra like the most efficient conceivable clarification we now have for this mysterious epoch in our Universe’s historical past.The analysis has been revealed in Nature Astronomy.
This Mysterious Black Hollow at The Daybreak of Time Weighs a Billion Suns