Astronomers have found out one thing unexpected in regards to the universe’s smallest and faintest magnificence of galaxies: Extremely-Diffuse Galaxies (UDGs).A analysis group learning those galaxies discovered that round part of those they investigated confirmed indicators of movement that defy earlier theories in regards to the formation and evolution of such nation-states. Specifically, the group discovered an surprising rotational movement of stars inside many of those dwarf galaxies.The scientists reached those findings whilst learning stellar movement in 30 UDGs within the Hydra galaxy cluster positioned over 160 million light-years clear of us. The findings may exchange our working out of ways UDGs shape and evolve.”The consequences we received have been doubly enjoyable,” Chiara Buttitta, a researcher on the Nationwide Institute for Astrophysics and co-author of a paper on those effects, mentioned in a remark. “No longer simplest have been we in a position to infer the stellar motions in those extraordinarily faint galaxies, however we discovered one thing we did not be expecting to look at.”The group applied the “Having a look into the faintest With MUSE,” or LEWIS, staring at program, carried out by way of the MUSE integral box spectrograph that is put in at the Very Huge Telescope (VLT). The VLT is the arena’s maximum complex visible-light astronomical observatory, and is positioned in Chile.The foundation of faint galaxiesUDGs have been first found out in 2015; the formation and evolution of those ultrafaint, surprisingly elongated galaxies in an instant introduced a puzzle for astronomers.The LEWIS findings allowed the brand new find out about’s group to decide that UDGs live in environments that very much range with regards to their bodily homes, the volume of darkish subject they comprise and the motions and compositions in their stars.Particularly, the scientists have been in a position to habits an in depth investigation of the UDG designated “UDG32.” This dwarf galaxy is positioned on the tail finish of a filament of gasoline connected to the spiral galaxy dubbed “NGC 3314A.”Breaking house information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!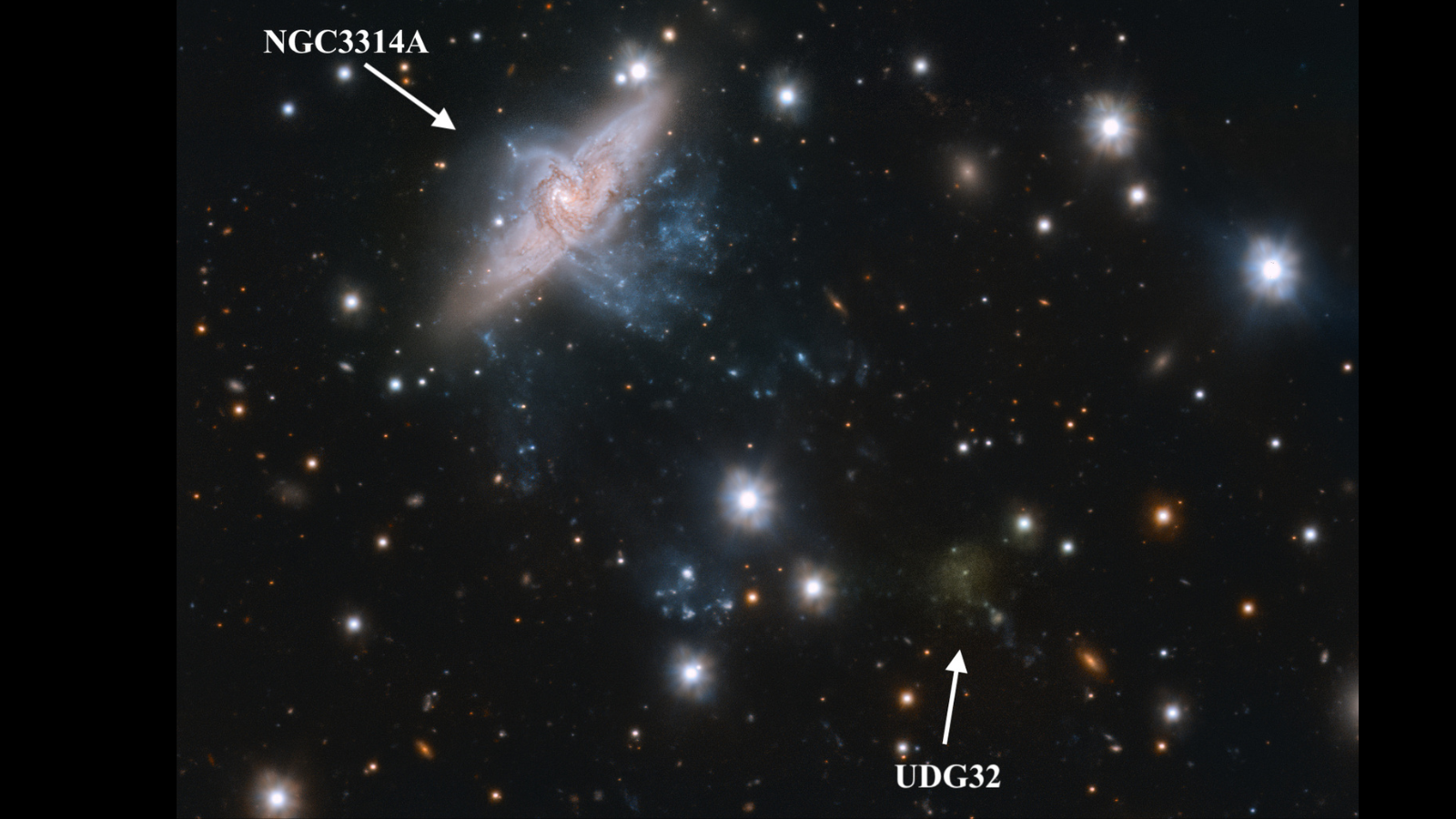 Symbol of the galaxies NGC3314 and UDG32 obtained with the OmegaCAM put in at the VST telescope (Symbol credit score: ESO/INAF- E. Iodice)One conceivable idea in regards to the formation of UDGs suggests they shape when filaments of gasoline are dragged from better galaxies by way of gravitational interactions.If gasoline clouds stay in those filaments, those clouds can develop into overly dense and cave in, forming stars that develop into the root of a UDG.The knowledge from LEWIS showed that UDG32’s affiliation with the filament tail of NGC3314A is not the results of a coincidental alignment. There is something extra that makes UDG32 seem to be positioned on the tip of NGC3314A’s tidal tail.
Symbol of the galaxies NGC3314 and UDG32 obtained with the OmegaCAM put in at the VST telescope (Symbol credit score: ESO/INAF- E. Iodice)One conceivable idea in regards to the formation of UDGs suggests they shape when filaments of gasoline are dragged from better galaxies by way of gravitational interactions.If gasoline clouds stay in those filaments, those clouds can develop into overly dense and cave in, forming stars that develop into the root of a UDG.The knowledge from LEWIS showed that UDG32’s affiliation with the filament tail of NGC3314A is not the results of a coincidental alignment. There is something extra that makes UDG32 seem to be positioned on the tip of NGC3314A’s tidal tail.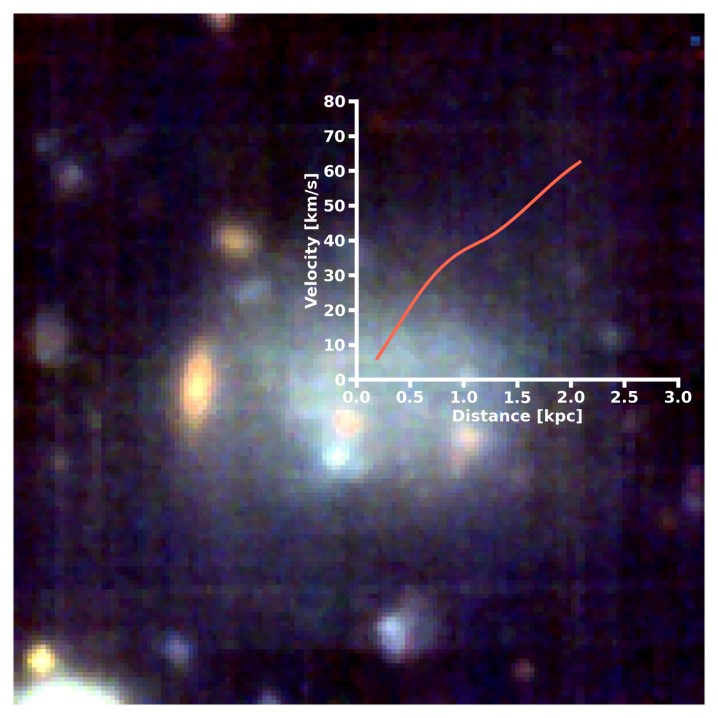 A UDG with a graph appearing the speed of the celebrities inside it. (Symbol credit score: C. Butitta/INAF)Moreover, UDG32 is extra enriched in parts heavier than hydrogen and helium, which astronomers jointly name “metals,” than different UDGs within the Hydra cluster.Metals are cast by way of the nuclear processes going on on the hearts of stars and are dispersed when those stars explode on the ends in their lives to develop into the development blocks of the following technology of stars.That is fascinating as a result of, in spite of the celebrities in UDG32 being more youthful than the celebrities in different Hydra cluster UDGs, they’re richer in metals. This implies they shaped within the pre-metal-enriched gasoline and mud shed by way of a bigger and extra historic galaxy, supporting the concept that this UDG was once dragged from its spiral galaxy neighbor.The group’s effects are essential validation for the LEWIS mission, which has so far doubled the collection of UDGs which were analyzed spectroscopically. Moreover, LEWIS has supplied the primary “world” view of those faint galaxies inside a galaxy cluster this is nonetheless forming.”The LEWIS mission was once a problem. When this program was once accredited by way of ESO we discovered that it was once a goldmine of knowledge to be explored. And that’s what it grew to become out to be,” Enrichetta Iodice, the LEWIS clinical director, mentioned within the remark.”The ‘power’ of LEWIS, because of the integral spectroscopy of the device used, lies in having the ability to find out about concurrently, for each and every particular person galaxy, now not simplest the motions of the celebrities, but in addition the common stellar inhabitants,” Iodice added, “and, subsequently, have indications at the formation age and the homes of globular clusters, basic tracers additionally for the darkish subject content material.”By means of striking in combination the person effects, like in a puzzle, we reconstruct the formation historical past of those programs.”The group’s analysis was once detailed throughout two papers revealed within the magazine Astronomy & Astrophysics.
A UDG with a graph appearing the speed of the celebrities inside it. (Symbol credit score: C. Butitta/INAF)Moreover, UDG32 is extra enriched in parts heavier than hydrogen and helium, which astronomers jointly name “metals,” than different UDGs within the Hydra cluster.Metals are cast by way of the nuclear processes going on on the hearts of stars and are dispersed when those stars explode on the ends in their lives to develop into the development blocks of the following technology of stars.That is fascinating as a result of, in spite of the celebrities in UDG32 being more youthful than the celebrities in different Hydra cluster UDGs, they’re richer in metals. This implies they shaped within the pre-metal-enriched gasoline and mud shed by way of a bigger and extra historic galaxy, supporting the concept that this UDG was once dragged from its spiral galaxy neighbor.The group’s effects are essential validation for the LEWIS mission, which has so far doubled the collection of UDGs which were analyzed spectroscopically. Moreover, LEWIS has supplied the primary “world” view of those faint galaxies inside a galaxy cluster this is nonetheless forming.”The LEWIS mission was once a problem. When this program was once accredited by way of ESO we discovered that it was once a goldmine of knowledge to be explored. And that’s what it grew to become out to be,” Enrichetta Iodice, the LEWIS clinical director, mentioned within the remark.”The ‘power’ of LEWIS, because of the integral spectroscopy of the device used, lies in having the ability to find out about concurrently, for each and every particular person galaxy, now not simplest the motions of the celebrities, but in addition the common stellar inhabitants,” Iodice added, “and, subsequently, have indications at the formation age and the homes of globular clusters, basic tracers additionally for the darkish subject content material.”By means of striking in combination the person effects, like in a puzzle, we reconstruct the formation historical past of those programs.”The group’s analysis was once detailed throughout two papers revealed within the magazine Astronomy & Astrophysics.
Those dwarf galaxies within the Hydra cluster are baffling scientists: ‘We discovered one thing we did not be expecting’