Astronomers have noticed the eroding stays of 100 dwarf galaxies which have been violently stripped in their outer layer of stars by means of better galaxies. Those disrupted galaxies constitute the “lacking hyperlink” within the evolution of a puzzling form of galaxy known as ultra-compact dwarf galaxies (UCDs).The invention displays that UCDs — that are a number of the densest collections of stars within the universe — are the fossilized stays of ordinary dwarf galaxies which have been destroyed in violent gravitational encounters with different galaxies.Astronomers first came upon UCDs greater than twenty years in the past. The ultra-dense galaxies posed a thriller for astronomers as a result of they’re smaller and extra compact than bizarre dwarf galaxies however better than the celebrity clusters they maximum intently resemble. Scientists theorized that UCDs had been the stays of destroyed dwarf galaxies, however they lacked an intermediate galaxy to lend a hand ascertain the transition. So astronomers on the Gemini North telescope atop Mauna Kea in Hawai’i started on the lookout for those cosmic lacking hyperlinks across the Virgo Cluster — a gaggle of round 2,000 galaxies positioned round 65 million light-years from Earth. The telescope noticed dozens of dwarf galaxies that appear to be present process this change.”Our effects give you the maximum entire image of the foundation of this mysterious magnificence of galaxy that used to be came upon just about 25 years in the past,” Eric Peng, a NOIRLab astronomer on the Kavli Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics at Peking College, stated in a commentary. “Right here we display that 106 small galaxies within the Virgo cluster have sizes between commonplace dwarf galaxies and UCDs, revealing a continuum that fills the ‘measurement hole’ between celebrity clusters and galaxies.”Comparable: Astronomers simply stuck the tiniest cannibal galaxy within the universePeng is a co-author of a paper detailing the invention of those lacking hyperlink galaxies printed Wednesday, Nov. 8, within the magazine Nature.The just lately recognized galaxies appear to be within the early levels of UCD formation. All are positioned on the subject of huge galaxies. This means that the gravitational affect of the within reach huge galaxies has stripped those smaller cosmic items in their stars and fuel.The astronomers additionally noticed items inside the Virgo Cluster with stretched and diffuse envelopes of fuel and stars, as though they’re these days being dragged away. Different items appear to turn other stages of this UCDtransition.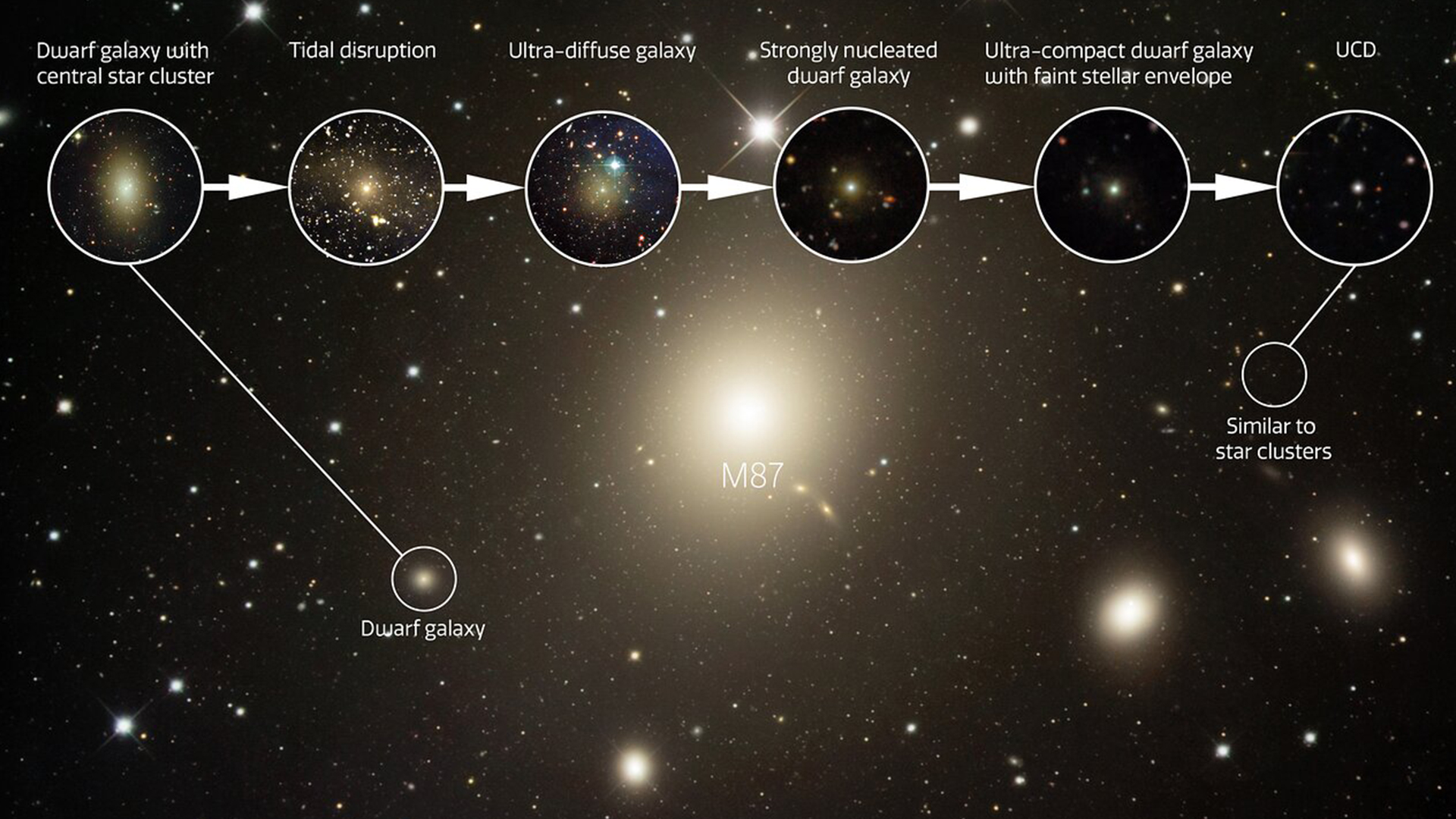 A picture of NGC 3628 or the “Hamburger Galaxy” captured by means of Víctor M. Blanco 4-meter Telescope with its tidal tail of stars containing the ultra-compact dwarf galaxy NGC 3628-UCD1. (Symbol credit score: CTIO/NOIRLab/DOE/NSF/AURA)”After we analyzed the Gemini observations and eradicated all of the background contamination, lets see that those transition galaxies existed nearly solely close to the most important galaxies,” lead writer Laixiang Wang, a scientist at Peking College, stated within the commentary. “We in an instant knew that environmental transformation needed to be vital.”When organized right into a time series, the workforce were given an image of what seems to be the tale of those star-robbed galaxies. “It is thrilling that we will in spite of everything see this change in motion,” Peng concluded.”It tells us that many of those UCDs are visual fossil remnants of historic dwarf galaxies in galaxy clusters, and our effects counsel that there are probably many extra low-mass remnants to be discovered.”
A picture of NGC 3628 or the “Hamburger Galaxy” captured by means of Víctor M. Blanco 4-meter Telescope with its tidal tail of stars containing the ultra-compact dwarf galaxy NGC 3628-UCD1. (Symbol credit score: CTIO/NOIRLab/DOE/NSF/AURA)”After we analyzed the Gemini observations and eradicated all of the background contamination, lets see that those transition galaxies existed nearly solely close to the most important galaxies,” lead writer Laixiang Wang, a scientist at Peking College, stated within the commentary. “We in an instant knew that environmental transformation needed to be vital.”When organized right into a time series, the workforce were given an image of what seems to be the tale of those star-robbed galaxies. “It is thrilling that we will in spite of everything see this change in motion,” Peng concluded.”It tells us that many of those UCDs are visual fossil remnants of historic dwarf galaxies in galaxy clusters, and our effects counsel that there are probably many extra low-mass remnants to be discovered.”














