Abstract: A brand new find out about delves into little one mind construction and its affect on social interactions and rigidity restoration all over the primary 12 months of existence. Thru practical MRI scans and interactive duties with moms, researchers follow early neural patterns. One find out about unearths that higher mind community connectivity at 3 months correlates with advanced infant-mother dyadic flexibility at 6 months.Every other find out about explores connections between mind networks and babies’ rigidity restoration, dropping mild on possible signs of later emotion dysregulation and psychological well being problems.Key Details:Toddler Construction Venture at UIUC makes use of practical MRI scans and interactive duties to grasp the early neural foundation of social interactions and rigidity restoration.Better connectivity inside particular mind networks at 3 months pertains to advanced infant-mother dyadic flexibility at 6 months.Connections between mind networks play a a very powerful position in babies’ talent to recuperate from rigidity, doubtlessly impacting their long-term emotional law and psychological well being.Supply: Beckman InstituteCaregivers have a good time many milestones between a toddler’s delivery and their first birthday. Right through those twelve months, many babies move from being not able to reinforce their head to crawling and status, and from staring at their oldsters to smiling, babbling, and waving at them. Some small children even say their first phrases or take their first steps.Toddler mind functioning within the first few months might set the foundation for this crucial enlargement, and researchers within the Interdisciplinary Lab for Social Construction on the College of Illinois Urbana-Champaign labored with households to discover this a very powerful developmental length. Thru an initiative referred to as the Toddler Construction Venture, the ILSD not too long ago printed two research exploring how early mind process pertains to the versatility of babies’ social interactions and their talent to recuperate from rigidity.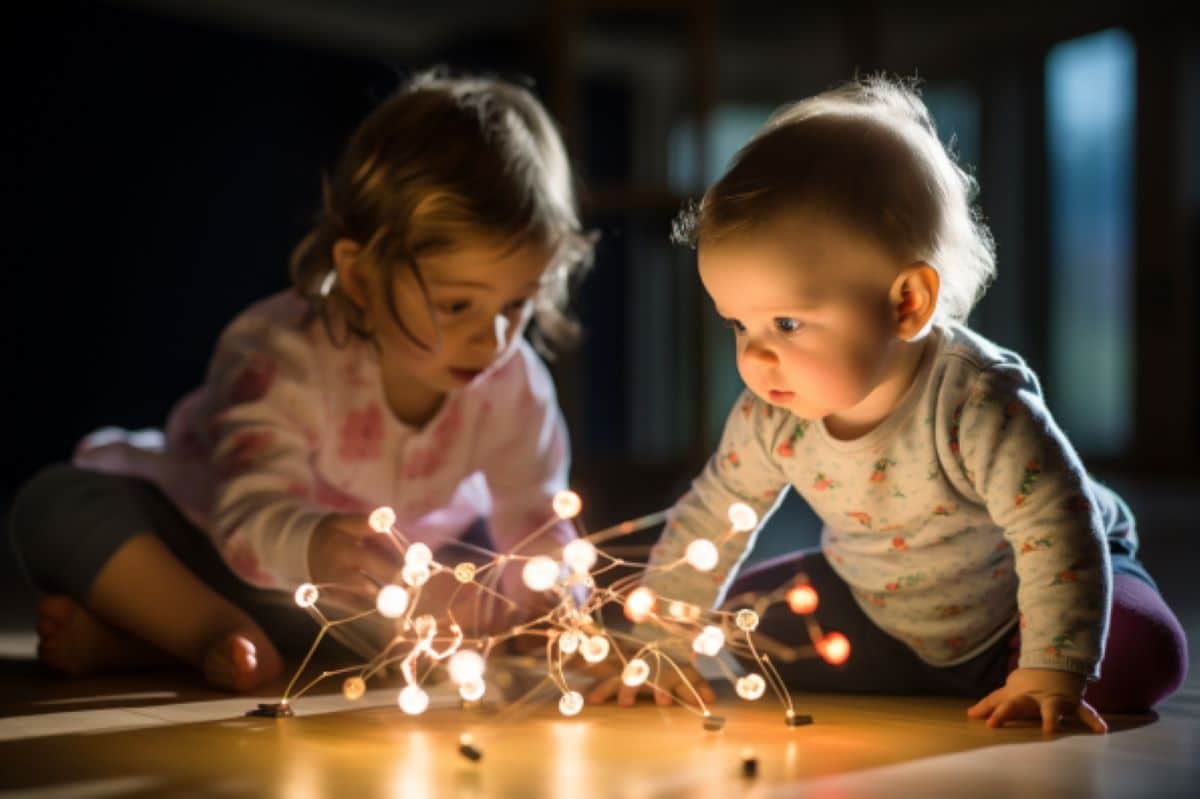  Higher sure connectivity between the amygdala and salience networks at 3 months used to be connected to a reduced talent to recuperate from rigidity at 6 months. Credit score: Neuroscience Information“The principle impetus for the challenge used to be to raised perceive the interaction between babies’ neural functioning and environmental helps—in particular interactions with caregivers—in shaping babies’ capability to control rigidity and focal point their consideration,” mentioned Nancy McElwain, a researcher on the Beckman Institute of Complicated Science and Era and a analysis professor of human construction and circle of relatives research at UIUC. McElwain leads the ILSD, which specializes in early social and emotional construction within the context of caregiving relationships.At 3 months of age, 35 babies participated in a practical MRI consultation on the Beckman Institute to evaluate their mind construction—no simple feat, taking into consideration those scans needed to be performed whilst the babies had been naturally asleep. Babies had been positioned in a distinct cradle to reinforce them inside the MRI system and had been equipped with a number of ranges of ear coverage.At 3, 6, and 9 months, the similar babies finished more than a few interactive duties with their moms, together with an workout referred to as a still-face consultation. The consultation starts with the pair taking part in head to head for two mins. That is adopted by way of a social stressor for the baby, all over which the mum holds a impartial expression and does no longer reply to them. After 2 mins, or faster if the baby turns into very dissatisfied, the mum resumes commonplace interplay with the baby for any other 2 mins.Many little one neuroscience research depend on caregiver questionnaires and reviews to evaluate babies’ behaviors, however this challenge concerned direct statement of moms and their babies. Movies of the babies and their moms had been analyzed body by way of body, with main points in their expressions, vocalizations, and gaze instructions famous in milliseconds. This allowed the researchers to seize very temporary however doubtlessly necessary adjustments in conduct.Within the first find out about, printed in Cerebral Cortex, ILSD researchers investigated whether or not an little one’s mind process correlates with dyadic flexibility—the level to which the baby and their mom promptly and simply regulate their very own feelings, vocalizations, and a spotlight in reaction to one another’s behaviors.The level of this adaptability used to be seen all over the primary section, or play episode, of the still-face consultation. Even youngsters lower than a 12 months previous show this adaptability when interacting with their caregivers, which is able to point out each the functioning of a parent-child courting and the way nimbly the pair can adapt to converting calls for within the setting or inside states of the baby.The researchers had been particularly keen on two key networks within the social mind: the default-mode community, which is concerned with introspection and an little one’s belief in their emotions all over social interactions; and the salience community, which is connected with figuring out significant main points within the setting (for instance, dialog cues like a caregiver’s smile).Each networks expand abruptly all over the primary 12 months of existence and play necessary roles in adults’ social interactions, however restricted analysis exists on their relevance for babies.Researchers discovered that higher simultaneous process—referred to as practical connectivity—of elements inside the default-mode and salience networks at 3 months previous correlated with higher infant-mother dyadic flexibility at 6 months of age. This find out about additionally discovered that higher anticorrelation between the 2 networks at 3 months—one community expanding in process whilst the opposite decreases—correlated with higher dyadic flexibility at 6 months.“Via the 3rd month of existence, we’re witnessing preliminary patterns of synchronization inside those social mind networks, in addition to anticorrelations between them. The early functioning of those neural networks might underlie how smartly the child is in a position to have interaction with the caregiver in a versatile means, possibly by way of supporting the advance of an little one’s talent to procedure inside and social data,” mentioned Xiaomei Li, lead creator of this find out about and a present postdoctoral fellow at Queen’s College. She used to be a Ph.D. pupil within the ILSD when the paper used to be printed.Li hopes that those findings will assist oldsters see small children as energetic members to their courting, with their interactions formed by way of babies’ particular person variations.“Variations could also be mirrored in babies’ social interactions as how smartly they’re ready to sign up their oldsters’ cues, or how smartly they’re ready to understand their very own wishes and keep up a correspondence them to others,” she mentioned.“In those tactics, babies co-construct their interactions with their oldsters. Spotting that babies are energetic members can permit oldsters to raised construction their interactions with their small children.”In a 2nd find out about printed in Developmental Science, the ILSD researchers investigated how the energy of connections between mind networks correlated with babies’ skills to recuperate from rigidity. They targeted at the amygdala community, an emotional processing area, and its connections with the default mode and salience networks.The stressor for this find out about used to be the second one episode of the still-face consultation, wherein the mum stops responding to the baby. An little one’s talent to recuperate from this rigidity used to be seen as the level to which they socially engaged when moms resumed commonplace responses.“We wish to know the neural mechanisms underlying early construction of rigidity law as a result of rigidity law is essential each early on and for emotional law and psychological well being whilst youngsters develop up,” mentioned Yannan Hu, the lead creator of this find out about and a present postdoctoral analysis affiliate on the Beckman Institute. She used to be a Ph.D. pupil within the ILSD on the time of its e-newsletter.Higher sure connectivity between the amygdala and salience networks at 3 months used to be connected to a reduced talent to recuperate from rigidity at 6 months. To recuperate from a hectic state of affairs, it’s useful for babies to acknowledge sure cues and understand the surroundings as secure.Even supposing robust connections between the amygdala and salience networks might assist babies acknowledge stressors or possible threats within the setting, over the top focal point on figuring out such unfavourable cues could have the drawback of decreasing the baby’s talent to wait to sure cues.“Effects that hyperlink neurological observations with an little one’s talent to regulate rigidity have the possible to tell early psychological well being screening and intervention paintings,” Hu mentioned. “Via pinpointing possible signs of later emotion dysregulation or psychological well being problems, youngsters susceptible to creating those problems will also be recognized and supported.”Because of the complexity of kid construction, perception from more than one fields is effective. This challenge concerned researchers from human construction and circle of relatives research, bioengineering, and neuroscience.The processing and research of fMRI information required experience from collaborators together with Brad Sutton, a professor of bioengineering and the technical director of the Biomedical Imaging Heart on the Beckman Institute; Ryan Larsen, a physicist and researcher on the Beckman Institute; Wei Gao, a professor of biomedical sciences at Cedars Sinai Clinical Heart; and Haitao Chen, a Ph.D. pupil on the College of California Los Angeles.About this neurodevelopment analysis newsAuthor: Lauren Otolski
Higher sure connectivity between the amygdala and salience networks at 3 months used to be connected to a reduced talent to recuperate from rigidity at 6 months. Credit score: Neuroscience Information“The principle impetus for the challenge used to be to raised perceive the interaction between babies’ neural functioning and environmental helps—in particular interactions with caregivers—in shaping babies’ capability to control rigidity and focal point their consideration,” mentioned Nancy McElwain, a researcher on the Beckman Institute of Complicated Science and Era and a analysis professor of human construction and circle of relatives research at UIUC. McElwain leads the ILSD, which specializes in early social and emotional construction within the context of caregiving relationships.At 3 months of age, 35 babies participated in a practical MRI consultation on the Beckman Institute to evaluate their mind construction—no simple feat, taking into consideration those scans needed to be performed whilst the babies had been naturally asleep. Babies had been positioned in a distinct cradle to reinforce them inside the MRI system and had been equipped with a number of ranges of ear coverage.At 3, 6, and 9 months, the similar babies finished more than a few interactive duties with their moms, together with an workout referred to as a still-face consultation. The consultation starts with the pair taking part in head to head for two mins. That is adopted by way of a social stressor for the baby, all over which the mum holds a impartial expression and does no longer reply to them. After 2 mins, or faster if the baby turns into very dissatisfied, the mum resumes commonplace interplay with the baby for any other 2 mins.Many little one neuroscience research depend on caregiver questionnaires and reviews to evaluate babies’ behaviors, however this challenge concerned direct statement of moms and their babies. Movies of the babies and their moms had been analyzed body by way of body, with main points in their expressions, vocalizations, and gaze instructions famous in milliseconds. This allowed the researchers to seize very temporary however doubtlessly necessary adjustments in conduct.Within the first find out about, printed in Cerebral Cortex, ILSD researchers investigated whether or not an little one’s mind process correlates with dyadic flexibility—the level to which the baby and their mom promptly and simply regulate their very own feelings, vocalizations, and a spotlight in reaction to one another’s behaviors.The level of this adaptability used to be seen all over the primary section, or play episode, of the still-face consultation. Even youngsters lower than a 12 months previous show this adaptability when interacting with their caregivers, which is able to point out each the functioning of a parent-child courting and the way nimbly the pair can adapt to converting calls for within the setting or inside states of the baby.The researchers had been particularly keen on two key networks within the social mind: the default-mode community, which is concerned with introspection and an little one’s belief in their emotions all over social interactions; and the salience community, which is connected with figuring out significant main points within the setting (for instance, dialog cues like a caregiver’s smile).Each networks expand abruptly all over the primary 12 months of existence and play necessary roles in adults’ social interactions, however restricted analysis exists on their relevance for babies.Researchers discovered that higher simultaneous process—referred to as practical connectivity—of elements inside the default-mode and salience networks at 3 months previous correlated with higher infant-mother dyadic flexibility at 6 months of age. This find out about additionally discovered that higher anticorrelation between the 2 networks at 3 months—one community expanding in process whilst the opposite decreases—correlated with higher dyadic flexibility at 6 months.“Via the 3rd month of existence, we’re witnessing preliminary patterns of synchronization inside those social mind networks, in addition to anticorrelations between them. The early functioning of those neural networks might underlie how smartly the child is in a position to have interaction with the caregiver in a versatile means, possibly by way of supporting the advance of an little one’s talent to procedure inside and social data,” mentioned Xiaomei Li, lead creator of this find out about and a present postdoctoral fellow at Queen’s College. She used to be a Ph.D. pupil within the ILSD when the paper used to be printed.Li hopes that those findings will assist oldsters see small children as energetic members to their courting, with their interactions formed by way of babies’ particular person variations.“Variations could also be mirrored in babies’ social interactions as how smartly they’re ready to sign up their oldsters’ cues, or how smartly they’re ready to understand their very own wishes and keep up a correspondence them to others,” she mentioned.“In those tactics, babies co-construct their interactions with their oldsters. Spotting that babies are energetic members can permit oldsters to raised construction their interactions with their small children.”In a 2nd find out about printed in Developmental Science, the ILSD researchers investigated how the energy of connections between mind networks correlated with babies’ skills to recuperate from rigidity. They targeted at the amygdala community, an emotional processing area, and its connections with the default mode and salience networks.The stressor for this find out about used to be the second one episode of the still-face consultation, wherein the mum stops responding to the baby. An little one’s talent to recuperate from this rigidity used to be seen as the level to which they socially engaged when moms resumed commonplace responses.“We wish to know the neural mechanisms underlying early construction of rigidity law as a result of rigidity law is essential each early on and for emotional law and psychological well being whilst youngsters develop up,” mentioned Yannan Hu, the lead creator of this find out about and a present postdoctoral analysis affiliate on the Beckman Institute. She used to be a Ph.D. pupil within the ILSD on the time of its e-newsletter.Higher sure connectivity between the amygdala and salience networks at 3 months used to be connected to a reduced talent to recuperate from rigidity at 6 months. To recuperate from a hectic state of affairs, it’s useful for babies to acknowledge sure cues and understand the surroundings as secure.Even supposing robust connections between the amygdala and salience networks might assist babies acknowledge stressors or possible threats within the setting, over the top focal point on figuring out such unfavourable cues could have the drawback of decreasing the baby’s talent to wait to sure cues.“Effects that hyperlink neurological observations with an little one’s talent to regulate rigidity have the possible to tell early psychological well being screening and intervention paintings,” Hu mentioned. “Via pinpointing possible signs of later emotion dysregulation or psychological well being problems, youngsters susceptible to creating those problems will also be recognized and supported.”Because of the complexity of kid construction, perception from more than one fields is effective. This challenge concerned researchers from human construction and circle of relatives research, bioengineering, and neuroscience.The processing and research of fMRI information required experience from collaborators together with Brad Sutton, a professor of bioengineering and the technical director of the Biomedical Imaging Heart on the Beckman Institute; Ryan Larsen, a physicist and researcher on the Beckman Institute; Wei Gao, a professor of biomedical sciences at Cedars Sinai Clinical Heart; and Haitao Chen, a Ph.D. pupil on the College of California Los Angeles.About this neurodevelopment analysis newsAuthor: Lauren Otolski
Supply: Beckman Institute
Touch: Lauren Otolski – Beckman Institute
Symbol: The picture is credited to Neuroscience NewsOriginal Analysis: Closed get entry to.
“Purposeful neural community connectivity at 3 months predicts infant-mother dyadic flexibility all over play at 6 months” by way of Xiaomei Li et al. Cerebral CortexOpen get entry to.
“Associations between little one amygdala practical connectivity and social engagement following a stressor: A initial investigation” by way of Yannan Hu et al. Developmental ScienceAbstractFunctional neural community connectivity at 3 months predicts infant-mother dyadic flexibility all over play at 6 monthsEarly functioning of neural networks most probably underlies the versatile switching between inside and exterior orientation and could also be key to the baby’s talent to successfully interact in social interactions. To check this speculation, we tested the affiliation between babies’ neural networks at 3 months and infant-mother dyadic flexibility (denoting the structural variability in their interplay dynamics) at 3, 6, and 9 months. Contributors incorporated thirty-five babies (37% ladies) and their moms (87% White). At 3 months, babies participated in a resting-state practical magnetic resonance imaging consultation, and practical connectivity (FC) inside the default mode (DMN) and salience (SN) networks, in addition to DMN-SN internetwork FC, had been derived the usage of a seed-based manner.When babies had been 3, 6, and 9 months, infant-mother dyads finished the Nonetheless-Face Paradigm the place their particular person engagement behaviors had been seen and used to quantify dyadic flexibility the usage of state area research.Effects published that higher within-DMN FC, within-SN FC, and DMN-SN anticorrelation at 3 months predicted higher dyadic flexibility at 6 months, however no longer at 3 and 9 months.Findings recommend that early synchronization and interplay between neural networks underlying introspection and salience detection might reinforce babies’ versatile social interactions as they transform increasingly more energetic and engaged social companions.AbstractAssociations between little one amygdala practical connectivity and social engagement following a stressor: A initial investigationFunctional structure of the baby mind, particularly practical connectivity (FC) inside the amygdala community and between the amygdala and different networks (i.e., default-mode [DMN] and salience [SAL] networks), supplies a neural foundation for little one socioemotional functioning. But, little is understood in regards to the extent to which early within- and between-network amygdala FC are associated with little one rigidity restoration around the first 12 months of existence. On this find out about, we tested associations between amygdala FC (i.e., within-network amygdala connectivity, and between-network amygdala connectivity with the DMN and SAL) at 3 months and little one restoration from a light social stressor at 3, 6 and 9 months. At 3 months, thirty-five babies (13 ladies) underwent resting-state practical magnetic resonance imaging all over herbal sleep. Babies and their moms finished the still-face paradigm at 3, 6, and 9 months, and little one rigidity restoration used to be assessed at each and every time level as the share of little one social engagement all over the reunion episode. Bivariate correlations indicated that higher sure within-network amygdala FC and bigger sure amygdala-SAL FC, however no longer amygdala-DMN FC, at 3 months predicted decrease ranges of rigidity restoration at 3 and six months, however had been nonsignificant at 9 months.Those findings supply initial proof that early practical synchronization inside the amygdala community, in addition to segregation between the amygdala and the SAL, might give a contribution to little one rigidity restoration within the context of little one–mom interplay.
Toddler Mind Construction and Social Interactions – Neuroscience Information