Abstract: Introducing fish to tots’ diets may scale back their possibility of neurodevelopmental delays.The learn about, involving 142 kids, discovered that consuming fish once or more per week was once related to lowered neurodevelopmental prolong dangers, and this affiliation was once additional influenced via the kid’s microbiome. The analysis took under consideration quite a lot of social and environmental components, emphasizing the function of vitamin, in particular fish intake, in neurodevelopment. This learn about provides new insights into nutritional affects on early formative years construction and the significance of microbial range in nutrient usage.Key Details:Common fish intake in tots is related to decreased neurodevelopmental delays, as noticed in a learn about of 142 kids.The protecting impact of fish intake on neurodevelopment is enhanced via the variety of the kid’s microbiome.The learn about managed for quite a lot of social and environmental components, highlighting the unbiased affect of vitamin on neurodevelopment.Supply: Penn StateAdding fish to a baby’s repertoire of finger meals might assist give protection to them from neurodevelopmental delays, in step with researchers on the Penn State Faculty of Drugs. The crew studied 142 kids from delivery to age 18 months and located that eating fish once or more per week was once related to a discounted possibility of neurodevelopmental delays. Intriguingly, the certain affect of fish intake on neurodevelopment was once amplified via a kid’s microbiome.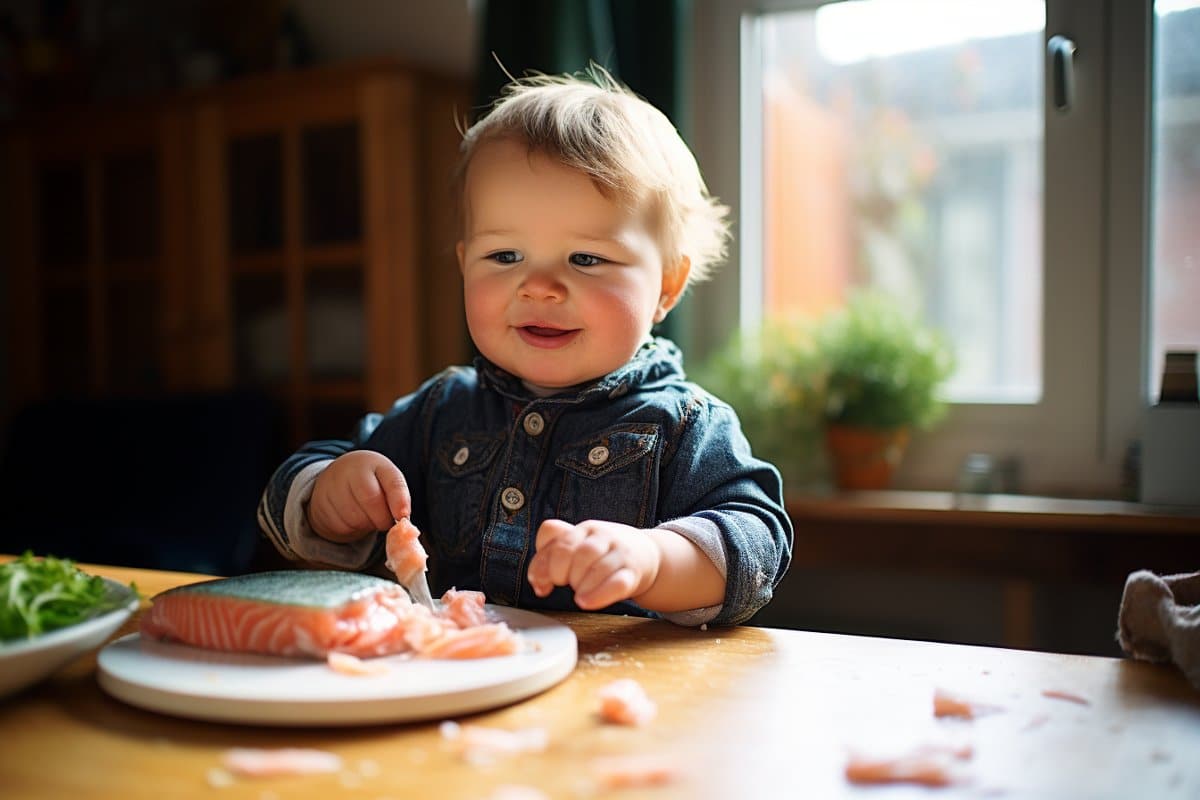  Certainly, the researchers discovered that past those social and environmental components, kids who ate fish once or more a week have been much less more likely to show neurodevelopmental delays at 18 months previous, and this protecting impact was once enhanced via microbial range. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsThe analysis, which indicated the affiliation persists throughout social and environmental issues, was once revealed within the magazine Microorganisms.“Whilst some neurodevelopmental stipulations are related to genetics, rising proof means that environmental components and social determinants of well being might engage with genes to persuade neurodevelopment,” stated first creator Terrah Keck-Kester, assistant professor of pediatrics at Penn State.“Our findings recommend that vitamin, in particular fish intake, is also one issue that would have an effect on neurodevelopmental results.”The crew assessed the diet of 142 babies at 6 and 365 days of age the use of the Toddler Feeding Practices II Survey, a standardized questionnaire advanced via the Meals and Drug Management and the Facilities for Illness Keep an eye on and Prevention. The researchers additionally accumulated saliva samples from the babies at 6 months and measured the task ranges of various micro organism inside the samples.“We selected saliva on account of its ease of get entry to at well-child visits, its proximity to the creating mind, and as the mouth represents one of the vital first websites of microbial touch for babies exploring their bodily international,” stated corresponding creator Steven Hicks, affiliate professor of pediatrics at Penn State.In spite of everything, the use of parental responses to a Survey of Wellbeing in Younger Youngsters, a screening software this is identified via the American Academy of Pediatrics, the crew decided the presence or absence of neurodevelopmental delays—outlined as delays in talents construction reminiscent of operating, talking, and social interplay—within the kids at age 18 months.The crew discovered that neurodevelopmental delays have been related with out a toddler fish intake at 365 days. Neurodevelopmental delays have been additionally related to greater task of 2 salivary microbes—Candidatus gracilibacteria and Chlorobi.“There’s at all times the query, “Are the findings extra associated with variables as opposed to those being studied?’” Keck-Kester stated. “For instance, imagine components that resolve whether or not an individual is in a position to consume extra fish of their vitamin. With our statistical research, we have been in a position to keep watch over for plenty of of those components.”Keck-Kester defined that the crew additionally studied social determinants of well being—reminiscent of maternal pressure, circle of relatives source of revenue, and get entry to to well being care, in addition to demographic contributions, reminiscent of race and ethnicity and age in their house—that would affect neurodevelopmental results. The researchers discovered that Hispanic kids have been much more likely to stand neurodevelopmental demanding situations.Certainly, the researchers discovered that past those social and environmental components, kids who ate fish once or more a week have been much less more likely to show neurodevelopmental delays at 18 months previous, and this protecting impact was once enhanced via microbial range.“Our effects recommend that microbial range is also necessary for the metabolism and usage of crucial vitamins, reminiscent of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are related to fish intake,” Hicks stated.About this vitamin and neurodevelopment analysis newsAuthor: Terrah Keck-Kester
Certainly, the researchers discovered that past those social and environmental components, kids who ate fish once or more a week have been much less more likely to show neurodevelopmental delays at 18 months previous, and this protecting impact was once enhanced via microbial range. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsThe analysis, which indicated the affiliation persists throughout social and environmental issues, was once revealed within the magazine Microorganisms.“Whilst some neurodevelopmental stipulations are related to genetics, rising proof means that environmental components and social determinants of well being might engage with genes to persuade neurodevelopment,” stated first creator Terrah Keck-Kester, assistant professor of pediatrics at Penn State.“Our findings recommend that vitamin, in particular fish intake, is also one issue that would have an effect on neurodevelopmental results.”The crew assessed the diet of 142 babies at 6 and 365 days of age the use of the Toddler Feeding Practices II Survey, a standardized questionnaire advanced via the Meals and Drug Management and the Facilities for Illness Keep an eye on and Prevention. The researchers additionally accumulated saliva samples from the babies at 6 months and measured the task ranges of various micro organism inside the samples.“We selected saliva on account of its ease of get entry to at well-child visits, its proximity to the creating mind, and as the mouth represents one of the vital first websites of microbial touch for babies exploring their bodily international,” stated corresponding creator Steven Hicks, affiliate professor of pediatrics at Penn State.In spite of everything, the use of parental responses to a Survey of Wellbeing in Younger Youngsters, a screening software this is identified via the American Academy of Pediatrics, the crew decided the presence or absence of neurodevelopmental delays—outlined as delays in talents construction reminiscent of operating, talking, and social interplay—within the kids at age 18 months.The crew discovered that neurodevelopmental delays have been related with out a toddler fish intake at 365 days. Neurodevelopmental delays have been additionally related to greater task of 2 salivary microbes—Candidatus gracilibacteria and Chlorobi.“There’s at all times the query, “Are the findings extra associated with variables as opposed to those being studied?’” Keck-Kester stated. “For instance, imagine components that resolve whether or not an individual is in a position to consume extra fish of their vitamin. With our statistical research, we have been in a position to keep watch over for plenty of of those components.”Keck-Kester defined that the crew additionally studied social determinants of well being—reminiscent of maternal pressure, circle of relatives source of revenue, and get entry to to well being care, in addition to demographic contributions, reminiscent of race and ethnicity and age in their house—that would affect neurodevelopmental results. The researchers discovered that Hispanic kids have been much more likely to stand neurodevelopmental demanding situations.Certainly, the researchers discovered that past those social and environmental components, kids who ate fish once or more a week have been much less more likely to show neurodevelopmental delays at 18 months previous, and this protecting impact was once enhanced via microbial range.“Our effects recommend that microbial range is also necessary for the metabolism and usage of crucial vitamins, reminiscent of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are related to fish intake,” Hicks stated.About this vitamin and neurodevelopment analysis newsAuthor: Terrah Keck-Kester
Supply: Penn State
Touch: Terrah Keck-Kester – Penn State
Symbol: The picture is credited to Neuroscience NewsOriginal Analysis: Open get entry to.
“Toddler Saliva Microbiome Process Modulates Dietary Affects on Neurodevelopment” via Terrah Keck-Kester et al. MicroorganismsAbstractInfant Saliva Microbiome Process Modulates Dietary Affects on NeurodevelopmentNeurodevelopment is influenced via advanced interactions between environmental components, together with social determinants of well being (SDOH), diet, or even the microbiome. This longitudinal cohort learn about of 142 babies examined the speculation that microbial task modulates the results of diet on neurodevelopment.Salivary microbiome task was once measured at 6 months the use of RNA sequencing. Toddler diet was once assessed longitudinally with the Toddler Feeding Practices survey.The main end result was once presence/absence of neurodevelopmental prolong (NDD) at 18 months at the Survey of Wellbeing in Younger Youngsters. A logistic regression type using two microbial components, one dietary issue, and two SDOH accounted for 33.3% of the variance between neurodevelopmental teams (p < 0.001, AIC = 77.7). NDD was once related to Hispanic ethnicity (OR 18.1, 2.36–139.3; p = 0.003), no fish intake (OR 10.6, 2.0–54.1; p = 0.003), and greater Candidatus Gracilibacteria task (OR 1.43, 1.00–2.07; p = 0.007). House constructed after 1977 (OR 0.02, 0.001–0.53; p = 0.004) and Chlorobi task (OR 0.76, 0.62–0.93, p = 0.001) have been related to decreased possibility of NDD. Microbial alpha range modulated the impact of fish intake on NDD (X2 = 5.7, p = 0.017).Those knowledge recommend some great benefits of fish intake for neurodevelopment is also mediated via microbial range. Affirmation in a bigger, randomized trial is needed.
Tots Who Devour Fish Have Decrease Developmental Prolong Dangers – Neuroscience Information