When asteroid 2024 YR4 first published itself to people on 27 December 2024, it perceived to have simply proven up out of nowhere.A complete asteroid does not simply materialize out of not anything, although, and now astronomers have decided what 2024 YR4 is manufactured from, what it looks as if, and the surprising position within the Sun Device that it got here from.
2024 YR4 hails from the center of the principle asteroid belt that hangs out between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter – and it used to be driven against Earth by means of a gravitational interplay with Jupiter, which normally protects the internal Sun Device from flying rocks.
“We’re slightly stunned about its beginning within the central primary asteroid belt, which is a location within the asteroid belt that we didn’t suppose many Earth-crossing asteroids may just originate from,” says astronomer Bryce Bolin of Eureka Medical in the USA.
2024 YR4 first captured the sector’s consideration by means of elevating the alarm of attainable have an effect on. Even though it posed no risk all through the Earth flyby on which it used to be found out, preliminary observations steered that it used to be on a trajectory that would deliver it inside placing vary of Earth on its subsequent go-around in 2032.
The chance has since been downgraded to almost not anything (even if the Moon would possibly nonetheless be within the firing line, with a couple of p.c probability of have an effect on). 2024 YR4 is referred to as a ‘town killer’ asteroid, no longer as a result of it is going to hit Earth, however as a result of if it did, the devastation it will wreak can be lovely large.
When doubtlessly hazardous asteroids display up, it will be significant for planetary protection to check them. How giant they’re, how they transfer thru house, and what they are manufactured from can all play a task in have an effect on, and the place they arrive from tells us if we must watch that nook of the Sun Device for different risks.
So the invention of 2024 YR4, and the preliminary alarms it raised, set scientists to paintings. Bolin and his colleagues used the W.M. Keck and Gemini South telescopes to procure detailed observations of the gap rock, to position in combination probably the most correct description of its traits.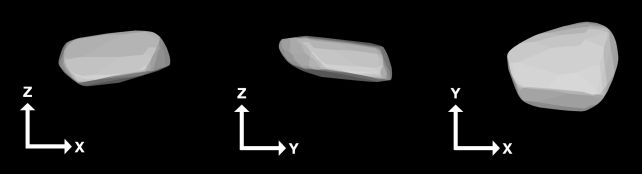 Form type of 2024 YR4 compiled from photometry of the asteroid from the Minor Planet Heart archive, the VLT archive, and the Gemini South telescope. (Bolin et al., arXiv, 2024)”YR4 spins as soon as each and every 20 mins, rotates in a retrograde route, has a flattened, abnormal form, and is the density of cast rock,” Bolin says.
Form type of 2024 YR4 compiled from photometry of the asteroid from the Minor Planet Heart archive, the VLT archive, and the Gemini South telescope. (Bolin et al., arXiv, 2024)”YR4 spins as soon as each and every 20 mins, rotates in a retrograde route, has a flattened, abnormal form, and is the density of cast rock,” Bolin says.
“The form of the asteroid supplies us with clues as to the way it shaped, and what its structural integrity is. Realizing those homes is the most important for figuring out how a lot effort or what sort of method must be used to deflect the asteroid whether it is deemed a risk.”
Asteroids come in numerous other flavors. The commonest are the carbonaceous asteroids, that are made up of a mixture of other minerals, and will (however do not at all times) have a sexy loosey-goosey ‘rubble pile’ composition, like Bennu, Ryugu, and Dimorphos, famously the topic of an asteroid redirection check project.
S-type asteroids are a lot denser, normally a unmarried chew of siliceous rock. The researchers imagine that that is the composition of 2024 YR4, data that might tell methods for have an effect on mitigation.
It additionally measures between 30 and 65 meters (98–213 toes) throughout, and has a flattened form rather like a hockey puck. Since maximum asteroids are concept to have shapes like potatoes or spinning tops, this can be a bit unexpected, and would possibly assist astronomers find out how 2024 YR4 shaped.
This data, the staff says, will assist scientists assess the homes of alternative doubtlessly hazardous asteroids. It’s going to additionally assist refine rapid-response commentary tactics for asteroids that, like 2024 YR4, simply seem as although out of nowhere.
And the researchers are very excited to peer what the rock will do sooner or later.
“It is one of the vital biggest items in fresh historical past that would hit the Moon,” Bolin says. “If it does, it will give scientists an extraordinary probability to check how the scale of an asteroid pertains to the scale of the crater it creates – one thing we’ve not been ready to measure at once ahead of.”The analysis will seem in The Astrophysical Magazine Letters, and is to be had on arXiv.
‘Town Killer’ Asteroid’s Starting place Traced to an Surprising A part of The Sun Device