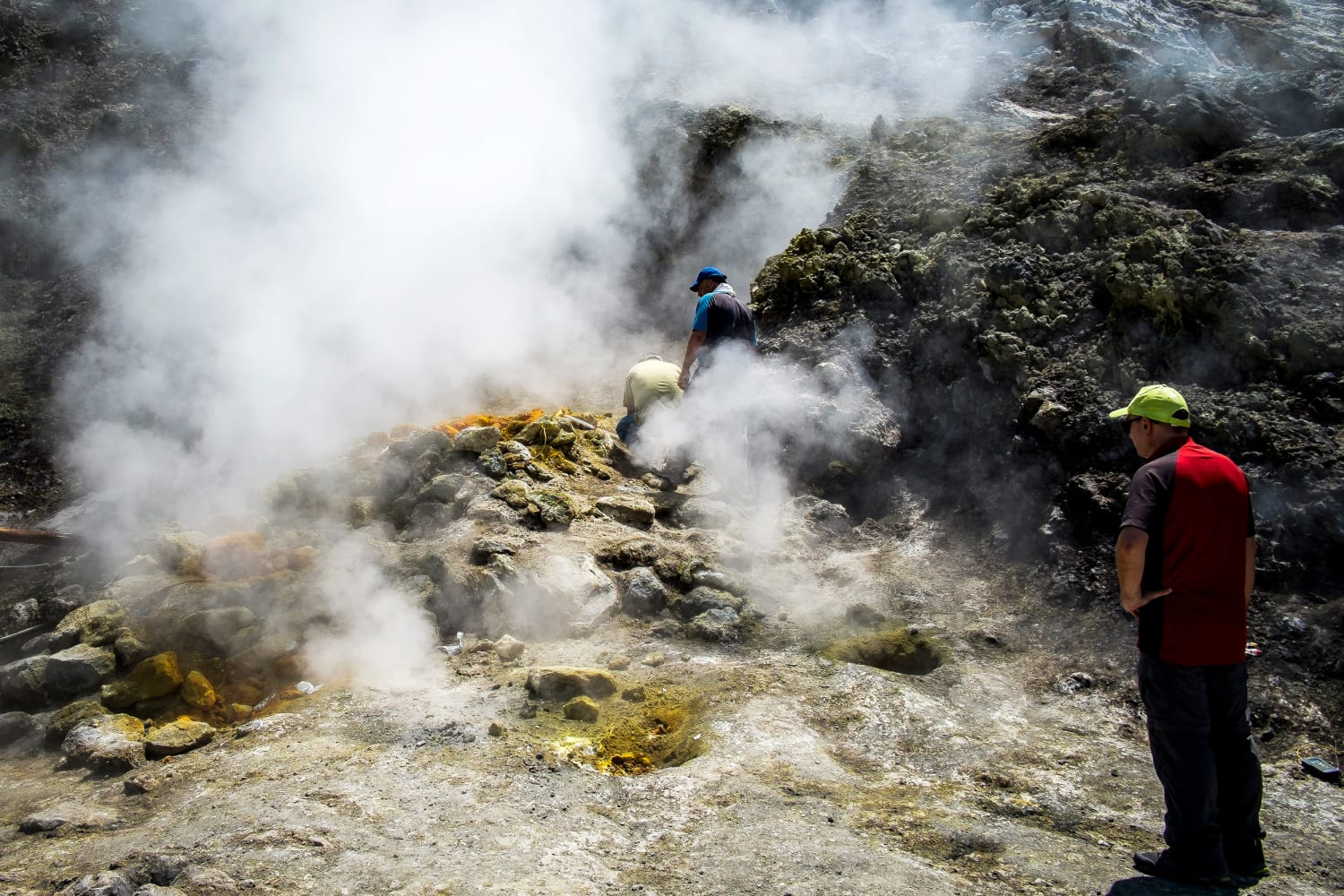
Two long-dormant “supervolcanoes” on two separate continents seem to be stirring to existence. Smartly, possibly.In fresh months, greater than 1000 minor earthquakes have rattled the realm across the Campi Flegrei volcano in southern Italy, stoking fears that it’s going to quickly erupt once more after just about 5 centuries. Some 6,000 miles away, scientists have for many years recorded in a similar fashion small earthquakes and cases of floor deformation on the Lengthy Valley Caldera, a volcano in japanese California that sits adjoining to Mammoth Mountain.However does all this seismic unrest truly portend a volcanic eruption? It kind of relies on whom you ask.Most mavens say there’s no speedy risk of an eruption at both Lengthy Valley or Campi Flegrei. Each volcanoes are calderas — sprawling depressions created way back by means of violent “super-eruptions” that necessarily collapsed in on themselves — which might be regularly tougher to forecast in comparison to the massive mountain-shaped options that folks in most cases consider after they bring to mind volcanoes.Seismic unrest is usually a signal {that a} volcano is waking up, however the complete tale is a lot more complicated.Each Campi Flegrei and the Lengthy Valley Caldera are referred to as supervolcanoes, a time period used to explain a volcano that at one time has erupted greater than 240 cubic miles of subject matter. Michael Poland, a geophysicist on the U.S. Geological Survey and the scientist-in-charge of the Yellowstone Volcano Observatory, stated that whilst Campi Flegrei and Lengthy Valley are able to massive explosions, the supervolcano moniker will also be deceptive.“The very first thing folks suppose is that there’s going to be a civilization-ending eruption,” Poland stated. “You’ll have an impactful explosion at those puts, however the overwhelming majority are smaller eruptions with much less explosive lava flows.”That hasn’t quieted fear within the communities that border the caldera techniques. The Italian town of Naples and its surrounding cities are all in shut proximity to Campi Flegrei, and native executive officers had been making plans tips on how to evacuate tens of 1000’s of folks from the realm, if wanted.The final time Campi Flegrei erupted used to be in 1538, and one of the vital machine’s greatest explosions happened round 39,000 years in the past.In September, the previous head of the Vesuvius observatory at Italy’s Nationwide Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology advised Reuters that the earthquake swarms have been inflicting floor uplift within the space, which might result in structural harm within the port the city of Pozzuoli, situated more or less 20 miles outdoor of Naples.Christopher Kilburn, a professor of volcanology and geophysical hazards at College Faculty London, stated the final length of seismic unrest at Campi Flegrei used to be within the Eighties. Kilburn stated the bottom within the the city of Pozzuoli used to be lifted just about 2 meters, or virtually 6.5 toes, over two years.Nonetheless, there used to be no large eruption. Speedy-forward to nowadays, and Kilburn stated there are some key variations with the seismic unrest that has been seen.“The variation is that nowadays, the uplift has been slightly greater than 1 meter, however over two decades, now not two,” he stated. “And so this entire uplift has lasted 10 instances longer and it’s been about 10 instances slower.”Nonetheless, Kilburn thinks the present job at Campi Flegrei signifies that the construction of the volcano’s crust is converting. In a find out about revealed in June within the magazine Communications Earth & Setting, Kilburn and his colleagues used a type to research the volcano’s conduct and located that the crust of Campi Flegrei is changing into weaker, making it extra liable to rupturing.RecommendedBut even though the crust reaches its snapping point, that would not essentially have catastrophic penalties, Kilburn stated.“If there’s a rupture, there’s no make it possible for magma goes to erupt,” he stated. “And that’s why with the observatory there, the legitimate releases duvet the rest from simply an build up in seismicity thru to a small eruption, as a result of we will be able to’t truly inform the place we’re in that simply but.”Calderas are regularly tough to review as a result of they’re huge depressions over best of large magmatic techniques. Campi Flegrei, as an example, stretches 7 to 9 miles throughout. The Lengthy Valley Caldera in California is set 10 miles vast. And probably the most well-known calderas on the planet, at Yellowstone Nationwide Park, measures 30 miles by means of 45 miles, in line with the U.S. Nationwide Park Carrier.Coincidentally, the Lengthy Valley Caldera additionally noticed an uptick in earthquake job within the Eighties and has been seismically stirring for many years, however scientists had been much less involved general a couple of primary eruption there within the foreseeable long run. That is as a result of there were indicators that the magma underneath it’s been cooling.Ettore Biondi, a analysis scientist within the department of geological and planetary sciences on the California Institute of Generation, has attempted to grasp what has been unfolding in fresh a long time on the Lengthy Valley Caldera. Biondi and his colleagues revealed a find out about final month within the magazine Science Advances detailing a singular approach of collecting acoustic sensing information with fiber-optic cables to seize snapshots of what’s going down underneath the caldera’s floor.An eruption can’t be dominated out utterly, however the researchers discovered {that a} forged rock construction is if truth be told masking the magma chamber on the Lengthy Valley Caldera, which is most likely fighting large eruptions from happening.“That doesn’t suggest that you’ll be able to’t have smaller eruptions, however from a supervolcanic eruption standpoint, I feel as of now we’re at the secure facet,” Biondi stated.He added that this technique of collecting high-resolution underground pictures might be used at different volcano techniques all over the world, and in particular at ones that don’t seem to be neatly understood. The effects may just lend a hand scientists higher look ahead to what is going on at volcanoes after they begin to stir.“For sure volcanoes, we all know rather well what’s happening,” Biondi stated. “For different volcanoes, we don’t have any thought.”The lack to create dependable eruption forecasts owes in large part to the truth that volcano techniques are so various. The way in which one volcano involves existence isn’t essentially how others all over the world sign an eruption is approaching.“We need to spend a large number of time at the volcanic machine, tracking it to grasp what’s customary at that volcano, after which have the ability to acknowledge when one thing turns into ordinary,” stated Poland, of the U.S. Geological Survey.Yellowstone, as an example, is hit by means of a mean of round 2,000 earthquakes yearly, and that seismic job isn’t regarded as out of the abnormal, he stated.At puts like Campi Flegrei and the Lengthy Valley Caldera, scientists had been putting in place the paintings to grasp what the entire rumblings and geological adjustments truly imply.“Volcanoes are kind of like folks — all of them have their very own persona,” Poland stated. “A large a part of volcanology and tracking lively volcanoes is getting to grasp the persona of the precise volcanoes that you just’re occupied with. And a few volcanoes are noisier than others.”Denise Chow is a reporter for NBC Information Science all for common science and local weather exchange.
Two supervolcanoes, a global aside, have the eye of scientists