Prior to now, map makers frequently positioned monsters on their maps to mark unexplored areas and doubtlessly unhealthy areas. A well-known instance is the ‘Theatrum Orbis Terrarum’ map, created in 1570, which options sea serpents and different sea monsters. Speedy ahead to as of late , and an unexplored Milky Means big name cluster means that astronomers will have to undertake this custom, too. The cluster is referred to as Barbá 2 and is located simply 24,000 light-years or so clear of Earth. An investigation the usage of the star-surveying Gaia house telescope published that the Barbá 2 is full of crimson supergiant stars, stars that may be loads of occasions wider than the solar and as much as one million occasions as luminous because the solar.”There are lots of open clusters within the galaxy. Then again, no longer all open clusters have the similar stage of passion to astronomers,” Ignacio Negueruela, a researcher on the Universidad de Alicante who was once a part of the workforce in the back of the invention of supergiants in Barbá 2, advised House.com. “Clusters wealthy in crimson supergiants are very uncommon and have a tendency to be very a ways away, however they play a an important position in figuring out key facets within the evolution of big stars.”The intimidating measurement and gear of supergiants way those monster stars burn thru their nuclear gas a lot sooner than stars just like the solar. While our big name will exist in its primary collection lifetime for round 10 billion years, supergiants are estimated to closing only some million years.The fast life of supergiants signifies that whilst open clusters like Barbá 2 are not unusual, with over 1,100 already found out within the Milky Means on my own, discovering one full of crimson supergiants is terribly uncommon.Similar: How are excessive “blue supergiant” stars born? Astronomers would possibly in the end know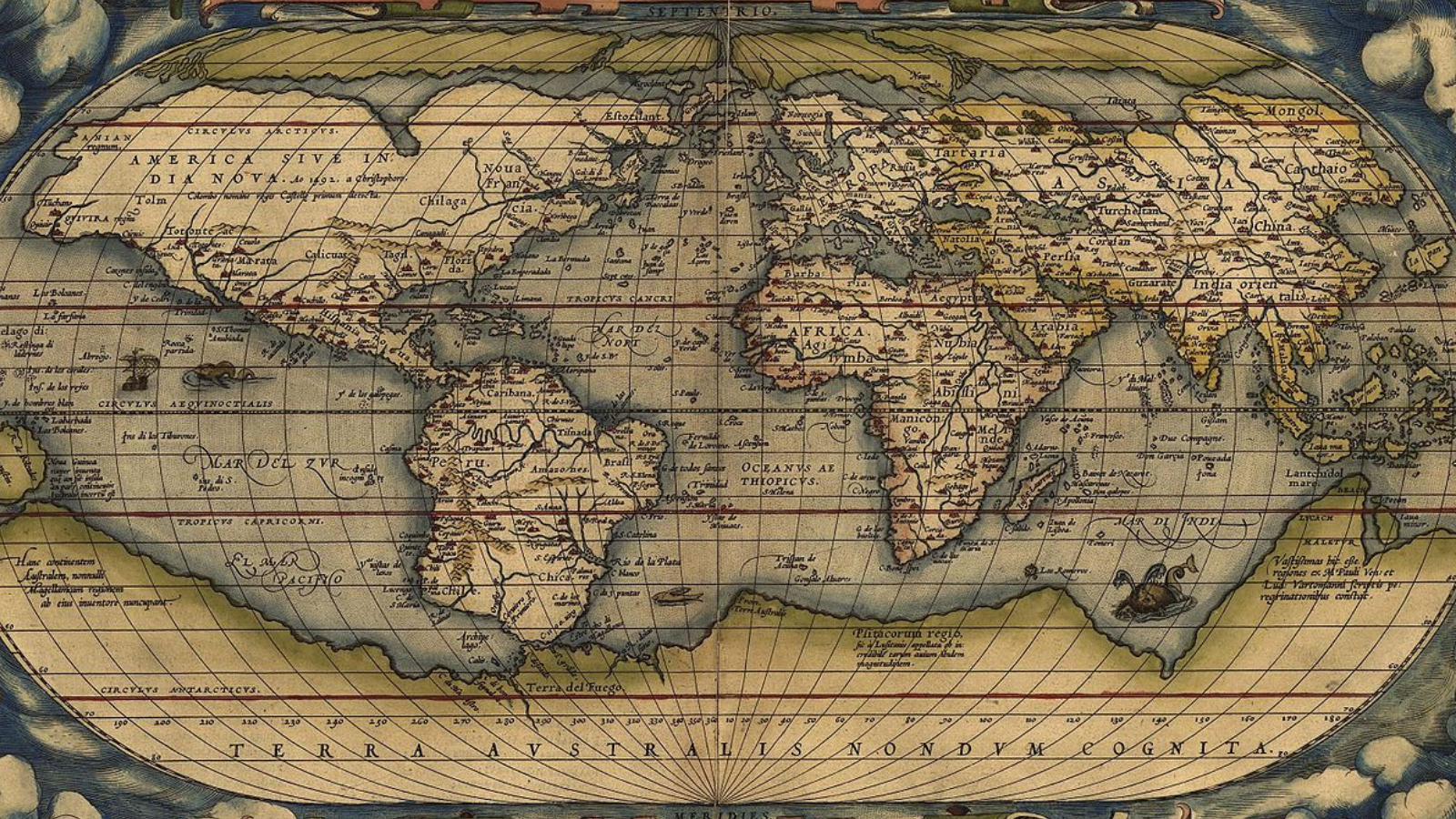 A map of the arena created through Abraham Ortelius in 1570 appearing sea-monsters in unexplored areas of the ocean. (Symbol credit score: Abraham Ortelius – The Library of Congress)Negueruela added that the learn about of open clusters like Barbá 2 which can be wealthy in monster-sized stars might be vital in finding how they turn into crimson supergiants or fail to take action and the way this influences their final destiny.Breaking house information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!”Within the Milky Means, there are just a handful of clusters wealthy in crimson supergiants,” he mentioned. “Discovering a cluster like Barbá 2, which can also be seen with a mid-sized telescope, is a vital and thrilling discovery for astronomers. Being to this point away and suffering from reasonable extinction, the cluster does no longer seem like a lot in optical photographs.”Barbá 2 was once in truth found out round a decade in the past through astronomer Rodolfo Barbá, however after he passed on to the great beyond in 2021, the invention has no longer been printed till now. Therefore, it is just becoming the cluster that now carries his identify.”Rodolfo was once well known amongst his friends for being sluggish to submit. He made many vital discoveries that he shared at conferences or mentioned with colleagues however frequently didn’t get round to publishing,” Negueruela mentioned. “After Rodolfo passed on to the great beyond, his shut collaborator Jesús Maíz took at the activity of making sure that his paintings can be printed.”Not anything lasts eternally, and that’s the reason for sure true even for probably the most monstrous of stars, however simply as is the case with prominent scientists like Barbá, what’s left in the back of is of essential significance. Pink supergiant legacy: Black hollow or neutron big name?Even though stellar our bodies of all sizes have lifetimes that make ours glance in reality insignificant on the subject of period, those stellar lives nonetheless grind to a halt when stars exhaust the gas for nuclear fusion of their cores.The lifetime of any big name is a gentle balancing act between the outward drive of radiation power generated through nuclear fusion in its cores and the inward push of its personal gravity. Whether or not this combat rages for thousands and thousands or billions of years, gravity inevitably wins, however the results of this victory range.For example, stars with sizes very similar to the solar surrender their conflict with gravity once they exhaust the provides of hydrogen of their cores and can not proceed to transform it to helium.The gravitational cave in of those smaller-sized stars creates a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf, which is avoided from additional cave in through a quantum phenomenon known as “electron degeneracy power,” which necessarily stops electrons from all occupying the similar state.
A map of the arena created through Abraham Ortelius in 1570 appearing sea-monsters in unexplored areas of the ocean. (Symbol credit score: Abraham Ortelius – The Library of Congress)Negueruela added that the learn about of open clusters like Barbá 2 which can be wealthy in monster-sized stars might be vital in finding how they turn into crimson supergiants or fail to take action and the way this influences their final destiny.Breaking house information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!”Within the Milky Means, there are just a handful of clusters wealthy in crimson supergiants,” he mentioned. “Discovering a cluster like Barbá 2, which can also be seen with a mid-sized telescope, is a vital and thrilling discovery for astronomers. Being to this point away and suffering from reasonable extinction, the cluster does no longer seem like a lot in optical photographs.”Barbá 2 was once in truth found out round a decade in the past through astronomer Rodolfo Barbá, however after he passed on to the great beyond in 2021, the invention has no longer been printed till now. Therefore, it is just becoming the cluster that now carries his identify.”Rodolfo was once well known amongst his friends for being sluggish to submit. He made many vital discoveries that he shared at conferences or mentioned with colleagues however frequently didn’t get round to publishing,” Negueruela mentioned. “After Rodolfo passed on to the great beyond, his shut collaborator Jesús Maíz took at the activity of making sure that his paintings can be printed.”Not anything lasts eternally, and that’s the reason for sure true even for probably the most monstrous of stars, however simply as is the case with prominent scientists like Barbá, what’s left in the back of is of essential significance. Pink supergiant legacy: Black hollow or neutron big name?Even though stellar our bodies of all sizes have lifetimes that make ours glance in reality insignificant on the subject of period, those stellar lives nonetheless grind to a halt when stars exhaust the gas for nuclear fusion of their cores.The lifetime of any big name is a gentle balancing act between the outward drive of radiation power generated through nuclear fusion in its cores and the inward push of its personal gravity. Whether or not this combat rages for thousands and thousands or billions of years, gravity inevitably wins, however the results of this victory range.For example, stars with sizes very similar to the solar surrender their conflict with gravity once they exhaust the provides of hydrogen of their cores and can not proceed to transform it to helium.The gravitational cave in of those smaller-sized stars creates a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf, which is avoided from additional cave in through a quantum phenomenon known as “electron degeneracy power,” which necessarily stops electrons from all occupying the similar state.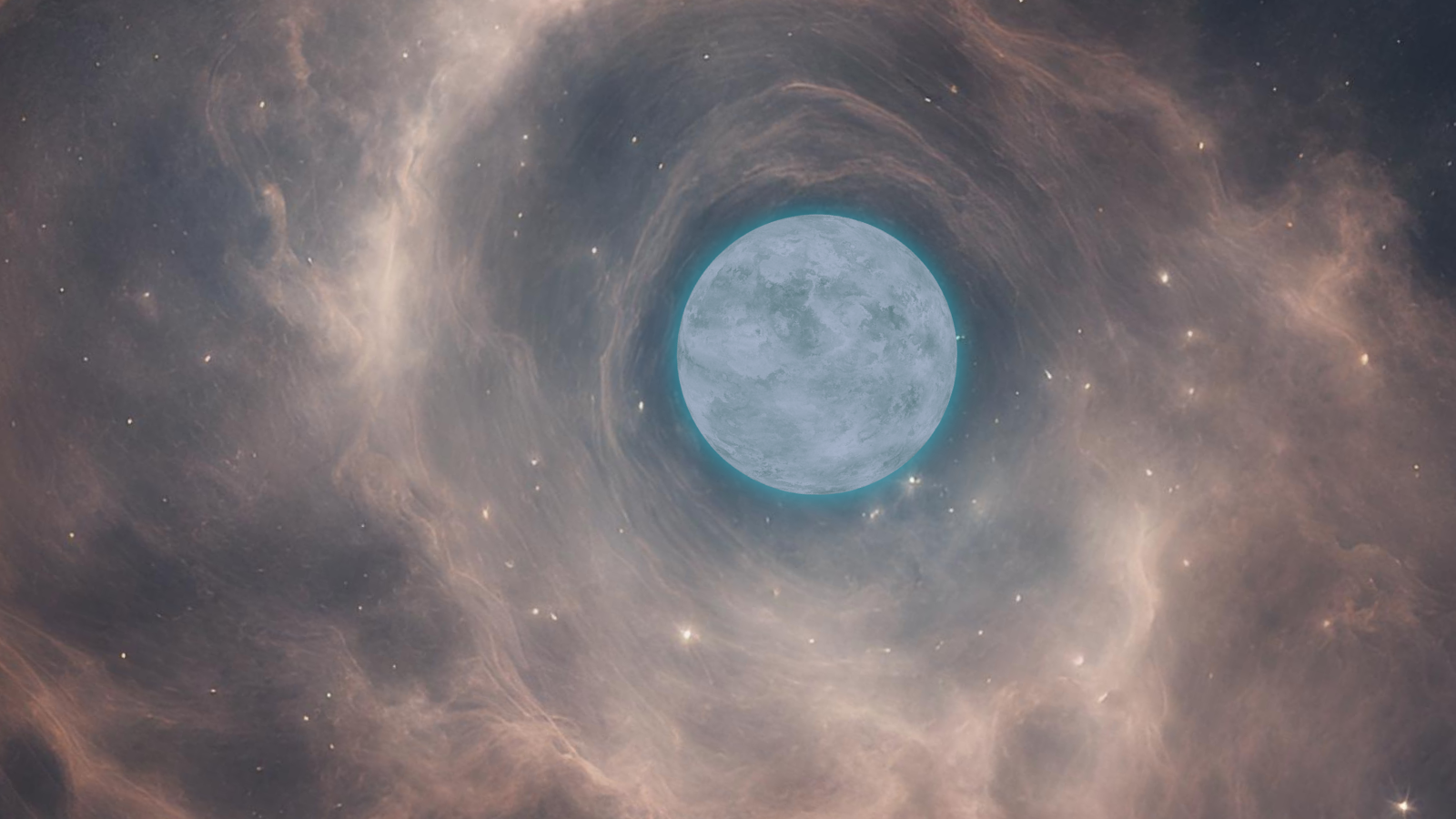 An indication displays the solar as a white dwarf surrounded through fuel and dirt that was once as soon as its outer layers (Symbol credit score: Robert Lea (created with Canva))If a celebrity starts this procedure whilst no less than 8 occasions the mass of the solar and will hold directly to no less than 1.44 occasions of the solar’s mass all over its preliminary cave in (the so-called Chandrasekhar prohibit), when it collapses it will possibly generate sufficient power in its core to fuse helium to heavier components, giving the big name a brand new bout of existence.When helium is exhausted, this procedure repeats; the big name collapses over and over again, fusing heavier and heavier components till the large big name has a core of iron, a component that no big name can fuse to heavier components. The big name undergoes a last cave in, triggering a large supernova explosion that blows away its outer layers. However, there are two conceivable results of this cave in.The crushing down of the large stellar core forces in combination electrons and protons to create a neutron big name, a stellar remnant stuffed with a sea of neutrons, impartial debris that most often exist within the nuclei of atoms with protons. Additional cave in is avoided through “neutron degeneracy power,” the power each and every neutron exerts on surrounding neutrons, however once more this can also be triumph over if a celebrity has sufficient mass.Must whole cave in happen, the big name is remodeled right into a stellar-mass black hollow, a area of house with a mass so dense at its heart that there’s a boundary round it from which no longer even gentle travels speedy sufficient to flee, the so-called “tournament horizon.”
An indication displays the solar as a white dwarf surrounded through fuel and dirt that was once as soon as its outer layers (Symbol credit score: Robert Lea (created with Canva))If a celebrity starts this procedure whilst no less than 8 occasions the mass of the solar and will hold directly to no less than 1.44 occasions of the solar’s mass all over its preliminary cave in (the so-called Chandrasekhar prohibit), when it collapses it will possibly generate sufficient power in its core to fuse helium to heavier components, giving the big name a brand new bout of existence.When helium is exhausted, this procedure repeats; the big name collapses over and over again, fusing heavier and heavier components till the large big name has a core of iron, a component that no big name can fuse to heavier components. The big name undergoes a last cave in, triggering a large supernova explosion that blows away its outer layers. However, there are two conceivable results of this cave in.The crushing down of the large stellar core forces in combination electrons and protons to create a neutron big name, a stellar remnant stuffed with a sea of neutrons, impartial debris that most often exist within the nuclei of atoms with protons. Additional cave in is avoided through “neutron degeneracy power,” the power each and every neutron exerts on surrounding neutrons, however once more this can also be triumph over if a celebrity has sufficient mass.Must whole cave in happen, the big name is remodeled right into a stellar-mass black hollow, a area of house with a mass so dense at its heart that there’s a boundary round it from which no longer even gentle travels speedy sufficient to flee, the so-called “tournament horizon.”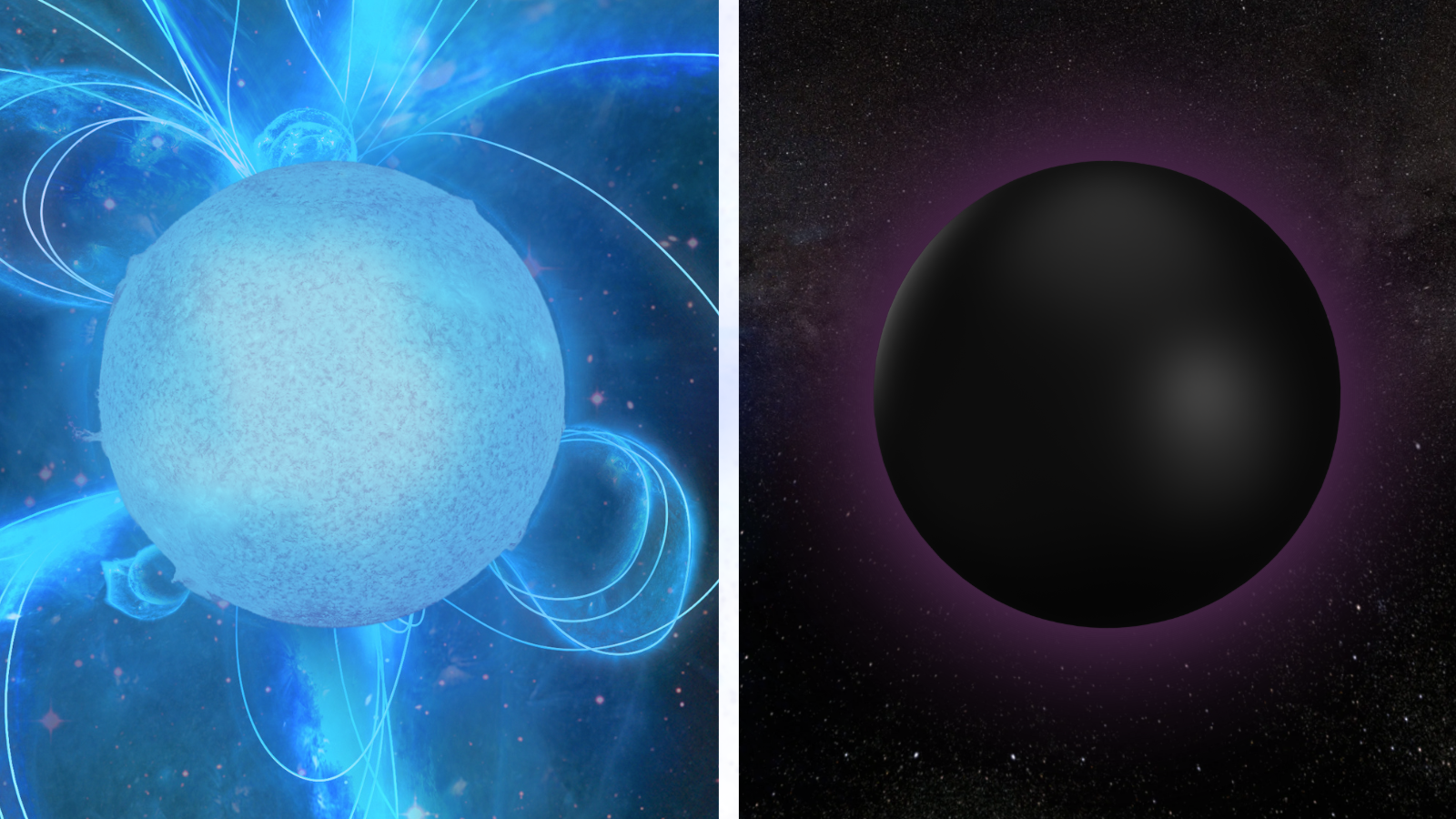 Black hollow or neutron big name: two conceivable fates of supermassive stars (Symbol credit score: Robert Lea (created with Canva))The dividing line to conquer neutron degeneracy power is known as the Tolman–Oppenheimer–Volkoff prohibit, and it’s believed to exist between 2.2 and a couple of.9 occasions the mass of the solar. This implies it’s not as effectively outlined because the Chandrasekhar prohibit, and scientists want to pin this dividing line down with extra simple task.Open clusters full of crimson supergiants that might go through such transformations might be the best lab for exploring the bits and bobs of the advent of neutron stars or black holes and learning why a celebrity takes one trail and no longer the opposite.”Clusters ruled through crimson supergiants are anticipated to be younger open clusters with a hefty choice of stars. They provide us details about the houses of crimson supergiants,” Negueruela defined. “Those clusters are precious to astronomers as a result of they assist us perceive crimson supergiants, that are in a different way difficult to check on their very own.”Supercluster is super-puzzlingNegueruela persisted through explaining that remoted crimson supergiants are tough to represent correctly as a result of their distances from us are frequently unsure, and it is exhausting to decide fundamental houses akin to their mass and age.”It is because crimson supergiants with other intrinsic houses can seem very equivalent at other levels in their lives,” he added.The celebrities in open clusters are all believed to have shaped on the similar time from the similar collapsing cloud of fuel and dirt. This implies astronomers can decide the cluster’s age after which evaluate the houses of the older crimson supergiants within the clusters to these of the more youthful blue stars within the cluster.”The loads of those blue stars are a lot more uncomplicated to determine, which is helping us be told extra concerning the crimson supergiants,” Negueruela mentioned. “Our fashions recommend that the choice of crimson supergiants is at once connected to the cluster’s mass.” That implies astronomers be expecting to peer about 5 supergiants for each 10000 sun plenty. Negueruela identified that there appears to be every other issue at play on this that we don’t but perceive.”We every now and then to find clusters with the similar age and mass, however one cluster is filled with crimson supergiants, whilst every other has just one or two,” he persisted. “There is a component of randomness right here because the crimson supergiant segment in a celebrity’s existence could be very brief, and we’re coping with low numbers, the place small adjustments could have a large have an effect on.” The workforce’s fashions, which are expecting 5 crimson supergiants for a cluster of a undeniable mass, additionally recommend that seeing anyplace from two to 8 supergiants in a cluster is not ordinary. But, the workforce nonetheless suspects one thing else would possibly affect this, with Negueruela suggesting it might be associated with what number of stars within the cluster are a part of binary or multiple-star methods and even the houses of those binaries.
Black hollow or neutron big name: two conceivable fates of supermassive stars (Symbol credit score: Robert Lea (created with Canva))The dividing line to conquer neutron degeneracy power is known as the Tolman–Oppenheimer–Volkoff prohibit, and it’s believed to exist between 2.2 and a couple of.9 occasions the mass of the solar. This implies it’s not as effectively outlined because the Chandrasekhar prohibit, and scientists want to pin this dividing line down with extra simple task.Open clusters full of crimson supergiants that might go through such transformations might be the best lab for exploring the bits and bobs of the advent of neutron stars or black holes and learning why a celebrity takes one trail and no longer the opposite.”Clusters ruled through crimson supergiants are anticipated to be younger open clusters with a hefty choice of stars. They provide us details about the houses of crimson supergiants,” Negueruela defined. “Those clusters are precious to astronomers as a result of they assist us perceive crimson supergiants, that are in a different way difficult to check on their very own.”Supercluster is super-puzzlingNegueruela persisted through explaining that remoted crimson supergiants are tough to represent correctly as a result of their distances from us are frequently unsure, and it is exhausting to decide fundamental houses akin to their mass and age.”It is because crimson supergiants with other intrinsic houses can seem very equivalent at other levels in their lives,” he added.The celebrities in open clusters are all believed to have shaped on the similar time from the similar collapsing cloud of fuel and dirt. This implies astronomers can decide the cluster’s age after which evaluate the houses of the older crimson supergiants within the clusters to these of the more youthful blue stars within the cluster.”The loads of those blue stars are a lot more uncomplicated to determine, which is helping us be told extra concerning the crimson supergiants,” Negueruela mentioned. “Our fashions recommend that the choice of crimson supergiants is at once connected to the cluster’s mass.” That implies astronomers be expecting to peer about 5 supergiants for each 10000 sun plenty. Negueruela identified that there appears to be every other issue at play on this that we don’t but perceive.”We every now and then to find clusters with the similar age and mass, however one cluster is filled with crimson supergiants, whilst every other has just one or two,” he persisted. “There is a component of randomness right here because the crimson supergiant segment in a celebrity’s existence could be very brief, and we’re coping with low numbers, the place small adjustments could have a large have an effect on.” The workforce’s fashions, which are expecting 5 crimson supergiants for a cluster of a undeniable mass, additionally recommend that seeing anyplace from two to 8 supergiants in a cluster is not ordinary. But, the workforce nonetheless suspects one thing else would possibly affect this, with Negueruela suggesting it might be associated with what number of stars within the cluster are a part of binary or multiple-star methods and even the houses of those binaries. An artist’s influence of exoplanets orbiting a crimson supergiant big name (Symbol credit score: Shutterstock)No longer handiest is that this a thriller about supergiant-rich clusters that stay to be investigated, however there are a couple of sudden problems concerning the Barbá 2 cluster. “At the start, all of the identified clusters wealthy in crimson supergiants are situated against the central areas of the Milky Means, except for NGC 7419,” Negueruela added. “This is smart as a result of big name formation is extra intense within the internal galaxy, however it additionally way that every one of them are harder to check on account of heavy extinction [light-blocking] brought about through mud and fuel alongside the road of sight. Barbá 2, to the contrary, is situated in an absolutely other a part of the Milky Means, against the outdoor.”The researcher mentioned that every other attention-grabbing level is the world of the sky this is house to Barbá 2 could be very well-researched as it accommodates many desirable gadgets. Thus, the invention of this supergiant-rich cluster means that in spite of a few years of devoted searches, there are somewhat a couple of hidden treasures available in the market ready to be found out. “I’m slightly stunned that no person else has come throughout Barbá 2,” Negueruela mentioned. “This discovery displays that there’s nonetheless room to enhance our seek strategies.””Discovering this type of clusters is just a first step. To completely exploit their attainable as astrophysical laboratories, we should mix stellar fashions and remark,” Negueruela concluded. “We can attempt to download extra spectra to decide with accuracy the age of the cluster and, therefore, its general mass.”Moreover, we are hoping to be informed from this cluster’s houses to refine our ways for locating equivalent clusters at some point.”The workforce’s paintings is printed at the paper repository website online arXiv.
An artist’s influence of exoplanets orbiting a crimson supergiant big name (Symbol credit score: Shutterstock)No longer handiest is that this a thriller about supergiant-rich clusters that stay to be investigated, however there are a couple of sudden problems concerning the Barbá 2 cluster. “At the start, all of the identified clusters wealthy in crimson supergiants are situated against the central areas of the Milky Means, except for NGC 7419,” Negueruela added. “This is smart as a result of big name formation is extra intense within the internal galaxy, however it additionally way that every one of them are harder to check on account of heavy extinction [light-blocking] brought about through mud and fuel alongside the road of sight. Barbá 2, to the contrary, is situated in an absolutely other a part of the Milky Means, against the outdoor.”The researcher mentioned that every other attention-grabbing level is the world of the sky this is house to Barbá 2 could be very well-researched as it accommodates many desirable gadgets. Thus, the invention of this supergiant-rich cluster means that in spite of a few years of devoted searches, there are somewhat a couple of hidden treasures available in the market ready to be found out. “I’m slightly stunned that no person else has come throughout Barbá 2,” Negueruela mentioned. “This discovery displays that there’s nonetheless room to enhance our seek strategies.””Discovering this type of clusters is just a first step. To completely exploit their attainable as astrophysical laboratories, we should mix stellar fashions and remark,” Negueruela concluded. “We can attempt to download extra spectra to decide with accuracy the age of the cluster and, therefore, its general mass.”Moreover, we are hoping to be informed from this cluster’s houses to refine our ways for locating equivalent clusters at some point.”The workforce’s paintings is printed at the paper repository website online arXiv.
Uncommon Milky Means big name cluster is full of crimson supergiants 1 million occasions brighter than the solar