Someday in the following couple of months, a spectacle may illuminate the northern sky.There, within the Corona Borealis constellation, at a distance of greater than 2,500 light-years, a celebrity referred to as T Coronae Borealis lurks, construction as much as an explosion that may, briefly, purpose the superstar to change into some of the brightest gadgets within the evening sky.
Astronomers are on tenterhooks looking ahead to this factor to blow, now not simply because it’ll be wonderful, however for the wealth of information we will have the ability to acquire on one of those superstar explosion referred to as a classical nova.
The explanation we all know T Coronae Borealis (T CrB for brief) goes to blow up is as it has carried out so as soon as each and every 80 years, for a minimum of 8 centuries.
Which means that it is very with regards to a once-in-a-lifetime match – and that the generation we need to practice it now massively outstrips what we had all through its ultimate tour, again in February 1946.
“There are a couple of recurrent novae with very brief cycles, however generally, we do not steadily see a repeated outburst in a human lifetime, and seldom one so moderately with regards to our personal machine,” says astronomer Rebekah Hounsell of NASA’s Goddard House Flight Heart.
“It is extremely thrilling to have this front-row seat.”
To not be puzzled with the close to obliteration of stars within the cataclysmic explosions referred to as supernovae, classical novae are smaller explosions that go away the superstar roughly intact. If truth be told, that is a ways from the primary time this actual cosmic object has long past via this enjoy.
The explanation T CrB explodes many times, and on time table, is a quirk of the kind of superstar it’s. It is a binary superstar machine that incorporates the remnant collapsed core of a Solar-like superstar referred to as a white dwarf, and a puffy pink large spouse. frameborder=”0″ permit=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>White dwarfs are very small and really dense, between the dimensions of Earth and the Moon, packing into that measurement as a lot mass as 1.4 Suns. That implies that they’re beautiful gravitationally intense; and if they have got a binary spouse in a detailed sufficient orbit, they have a tendency to siphon off subject matter, predominantly hydrogen.
Through the years, this hydrogen accumulates at the floor of the white dwarf, compressed down because of the gravitational pull. Ultimately, the force and warmth at the backside layer of hydrogen change into so intense that the entire thing ignites in a runaway thermonuclear explosion that violently expels the surplus hydrogen out into house in impressive taste.
That is the nova; and, for T CrB, the duration of time this procedure takes is ready 80 years or so.
Over the past decade, astronomers have noticed the binary machine displaying conduct very similar to the way it behaved main as much as the 1946 explosion; in particular, a dip in brightness that heralds the shut way of the eruption. Their research means that it will happen very quickly – as early as earlier than September 2024.
Which means that astronomers are holding an overly shut eye on somewhat patch of sky clustered with constellations – Lyra, Hercules, Boötes – and somewhat arc of stars sandwiched between them. That is Corona Borealis.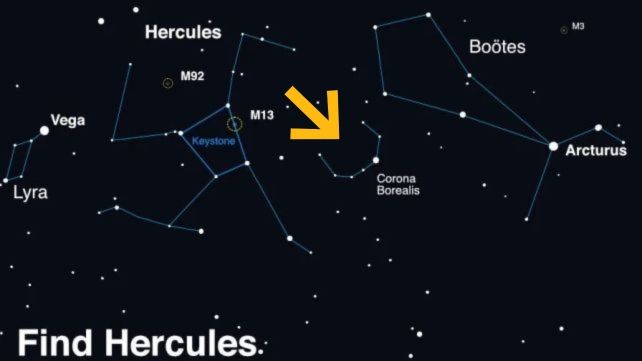 The place you’ll be able to in finding Corona Borealis within the sky. Be careful for a ‘new’ superstar! (NASA)We predict that we will listen concerning the nova just about as quickly because it occurs. It’ll bloom within the sky to change into visual to the bare eye, then step by step fade from visibility over the process every week. So you will have time to get in the market and take a look at it, if that moves your fancy.
The place you’ll be able to in finding Corona Borealis within the sky. Be careful for a ‘new’ superstar! (NASA)We predict that we will listen concerning the nova just about as quickly because it occurs. It’ll bloom within the sky to change into visual to the bare eye, then step by step fade from visibility over the process every week. So you will have time to get in the market and take a look at it, if that moves your fancy.
If truth be told, if you’ll be able to, that may be wonderful. Citizen scientists are being referred to as upon to gather knowledge too. The extra eyes there are on T CrB, the simpler we will have the ability to perceive its flashy outbursts.
And naturally there shall be as many telescopes tuning in as can also be organized, from the longest radio wavelengths, to essentially the most robust X- and gamma radiation.”Recurrent novae are unpredictable and contrarian,” says astrophysicist Koji Mukai of NASA Goddard. “While you suppose there cannot most likely be a reason why they observe a definite set development, they do – and once you begin to depend on them repeating the similar development, they deviate from it totally. We’re going to see how T CrB behaves.”
Uncommon Sky Explosion Coming Quickly: A As soon as-in-a-Lifetime Tournament Visual to The Bare Eye













